Last Updated on April 18, 2025 by Owen McGab Enaohwo
![What Is a RACI Chart? [How to Create One With Examples]](https://www.sweetprocess.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/raci-chart.png)
Are you tired of project chaos and confusion? Do you struggle with unclear roles and responsibilities, leading to delays and stress?
A RACI chart is a game-changer for project managers. It ensures everyone is on the same page and working toward a common goal.
Each letter in this acronym takes away your worries over your project. With “R” representing responsible, “A” representing accountable, “C” for consulted, and “I” meaning informed, your project/tasks are off to a great start and a satisfying finish.
In this guide, we’ll explore a RACI chart and how to create one easily. We will also provide practical RACI chart examples to get you started. In addition, you’ll see how SweetProcess, a project management tool, is designed to make running your project easier with RACI. Say goodbye to project headaches and hello to smooth sailing with a clear and effective RACI chart!
Sign up for a free trial of SweetProcess right here. You can take a quick tour or read on until the end.
Table of Contents
What the RACI Acronym Stands For [+ Roles and Responsibilities]
How to Create a RACI Chart in 7 Simple Steps
How to Manage Your Projects Efficiently Using SweetProcess
Why Is a RACI Chart Important in Project Management?
Pros and Cons of Using a RACI Chart
RACI Chart Examples: Practical Applications in the Real World
When to Use RACI Charts in Project Management
Common RACI Chart Challenges and How to Avoid Them
The 7 Best RACI Alternatives to Manage Your Project
Keep Your Team Synchronized and Accountable Using SweetProcess
What Is a RACI Chart?

A RACI chart is an acronym that stands for responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed. It’s a systematic way to define roles within a project team. Specifically, it identifies the person(s) responsible for a project task, those accountable for overseeing it and granting final approval, those consulted for specialized advice, and those informed of progress updates.
A RACI chart can ensure your project starts and ends on the right note by eliminating confusion around RACI roles and expectations. This tool fosters clear communication, ensuring every project participant understands their role and responsibilities, minimizing confusion at every stage.
What the RACI Acronym Stands For [+ Roles and Responsibilities]
![What the RACI Acronym Stands For [+ Roles and Responsibilities]](https://www.sweetprocess.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/raci-chart-3.jpg)
The RACI acronym is fundamental in project management, ensuring clear roles and responsibilities. Let’s explain what each letter means and how it impacts your team’s workflow.
Responsible
People listed as responsible are the ones who directly perform a specific task. They’re expected to complete tasks and deliver outputs. They take ownership of their work and report progress to the accountable role.
Examples of People You Can Assign to the Responsible Role
Team members: Those who will execute specific tasks, such as developers, writers, or designers.
Task leaders: Individuals leading specific tasks like project team leads or subproject managers.
Subject matter experts: Specialists in specific areas, like IT, marketing, or finance.
Accountable
This set of individuals will be held accountable for the success or failure of each phase of a task as they oversee the overall project or task. They ensure the completion of tasks and projects, make decisions, and allocate resources. They set goals and objectives, monitor progress and performance, and hold the responsible roles accountable for their work. Usually, one person is required for this role.
The key difference between responsible and accountable roles lies in their scope:
- You are responsible for a task if it is your job to complete it; it is your duty to get it done.
- You are accountable for a task if it’s your job to ensure it’s completed, even if you don’t do it yourself; you oversee its completion and are answerable for the outcome.
In summary, responsible roles execute tasks, while accountable roles oversee and guarantee their successful completion.
Examples of People You Can Assign to the Accountable Role
Project managers: Overall project leaders are responsible for its success.
Team leads: Leaders of specific teams or departments accountable for their team’s tasks.
Department heads: Heads of various departments are accountable for their department’s tasks and projects.
Consulted
These are the knowledge houses for our task, which must be consulted before making decisions. They provide expertise and guidance, offer input and advice, share knowledge and best practices, collaborate with responsible teams, and help shape decisions and solutions.
Examples of People You Can Assign to the Consulted Role
Subject matter experts: Experts in specific areas are consulted for their knowledge and input.
Stakeholders: Individuals or groups interested in the project or task, like investors or customers.
Advisors: External experts or consultants providing guidance and advice.
Informed
The informed group consists of individuals who must be kept informed throughout the task. They receive regular updates and progress reports, stay informed about project developments and changes, provide feedback, and may offer input.
This group relies on transparent communication to stay informed and up-to-date, ensuring they know project milestones and outcomes.
Examples of People You Can Assign to the Informed Role
External stakeholders: Parties outside the organization, like investors, partners, or suppliers.
Clients: Customers or clients receiving the project’s output or service.
Executive team: Senior management, such as CEOs, CTOs, or COOs, needs to be informed of project progress.
Business owners: Entrepreneurs or organization owners who need to be updated on project phase status.
How to Create a RACI Chart in 7 Simple Steps
Creating a RACI chart can seem like a challenge. Follow these seven simple steps to create a clear and effective RACI chart for your team. Watch this short video for more clarity.
Step 1: List all tasks or deliverables
First, you’ll want to list all the activities associated with your project. Lay it all out. Brainstorm and write down all your project’s activities, tasks, and deliverables. Be comprehensive and include every detail, no matter how small. Make sure to write down each task clearly and concisely.
Step 2: Identify the project roles
List all the individuals involved in the project, including team members, stakeholders, and external partners. Attach the RACI codes (R, A, C, or I) to each task, indicating the level of involvement for each person.
Step 3: Create a chart with a column for each role and a row for each task
When you’re done creating the tasks and listing the roles, set up a table, spreadsheet, or Google sheet and carefully organize them into rows and columns, with the roles (RACI) being on the columns and the tasks going under the row. Ensure the chart is clear, organized, and easy to read.
Step 4: Assign the RACI to each role and task
Define each role and its responsibilities. Remember the roles: responsible (R), accountable (A), consulted (C), informed (I). Look out for any ambiguities and clarify them to ensure everyone understands their roles. When distributing a RACI chart, include definitions for responsible, accountable, informed, and consulted roles so stakeholders know exactly what to expect.
Step 5. Review with your team and all involved project stakeholders.
Share the RACI chart with the team and stakeholders. Explain the roles and responsibilities and encourage feedback and questions.
Step 6: Review the RACI chart
Verify the chart’s accuracy and completeness, ensuring each task has a clear owner and accountability and all roles are properly assigned.
Step 7: Revisit the RACI chart regularly
Schedule regular reviews and updates to reflect changes in the project or team.
Update the chart as tasks are completed, new tasks are added, or team members change roles. Maintain the chart as a living document to ensure it remains a true representation of responsibilities within the team.
How to Manage Your Projects Efficiently Using SweetProcess
While on your RACI journey, you’ll see multiple software to help you organize your charts. Most will be frustrating, and only some will meet your needs, like SweetProcess. SweetProcess is a project management software designed to help you manage your projects efficiently and effectively while considering the principles of RACI. Here’s what it can do for you and your organization.
Document Procedures, Processes, and Tasks in One Place
SweetProcess allows you to document all your processes and procedures in one place – effectively, too. It offers a place to list all your tasks and assign roles to your team members. This software can turn your organization into what you’ve always dreamed of.
This was true for Kevin Trapp, the director of operations at Forensic Consulting Services. He was responsible for ensuring efficiency and consistency in the organization. Still, as the company expanded, he saw that achieving the same excellent consistency quickly became challenging because the workflow was not streamlined. There wasn’t adequate documentation to show everyone what was expected of them. He was constantly bombarded with questions as teammates struggled to understand their parts until he found SweetProcess, which helped the company experience employee efficiency and growth alongside consistent output.
How to Create Procedures and Processes on SweetProcess
Here’s how to create procedures and processes on SweetProcess.
Click on “Procedures” and then click on “Create Procedure.”
Give your procedure a title and click on “Continue.”
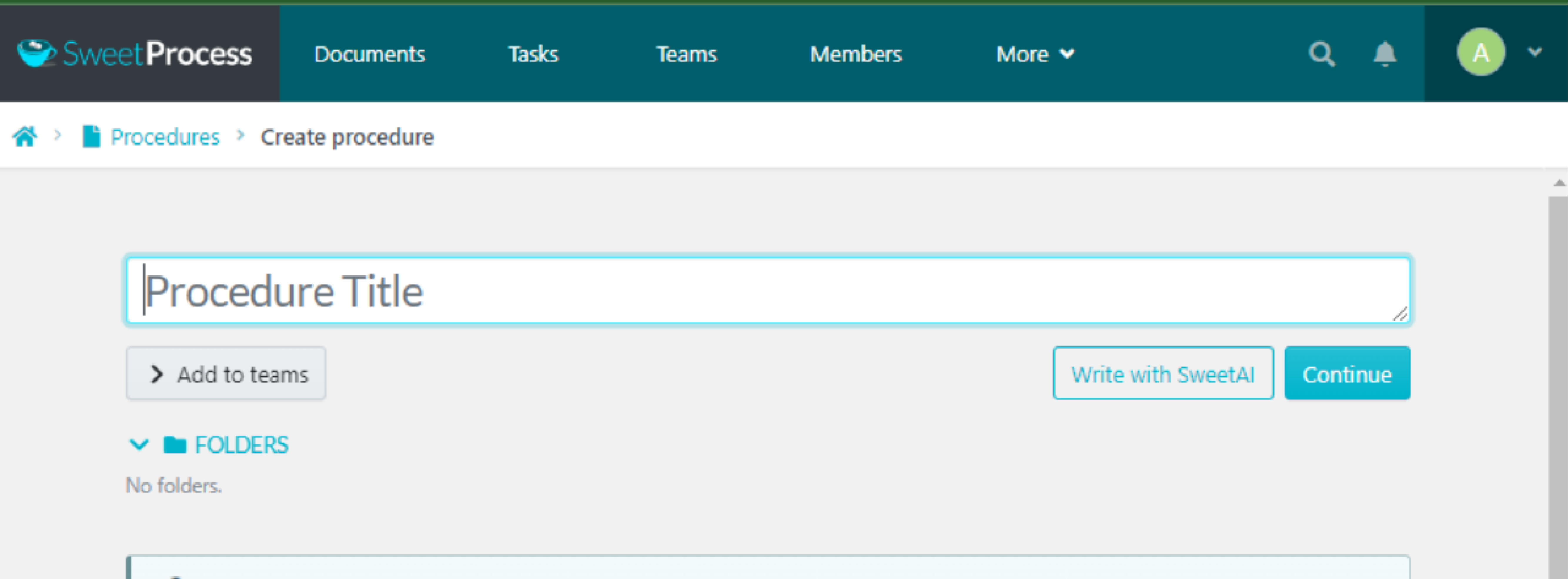
Click on the pencil symbol beside the title.
Fill out your procedure details and click “Finished Editing.”
How to Create a Policy in SweetProcess Manually
Click on “More.”
Select “Policies.”
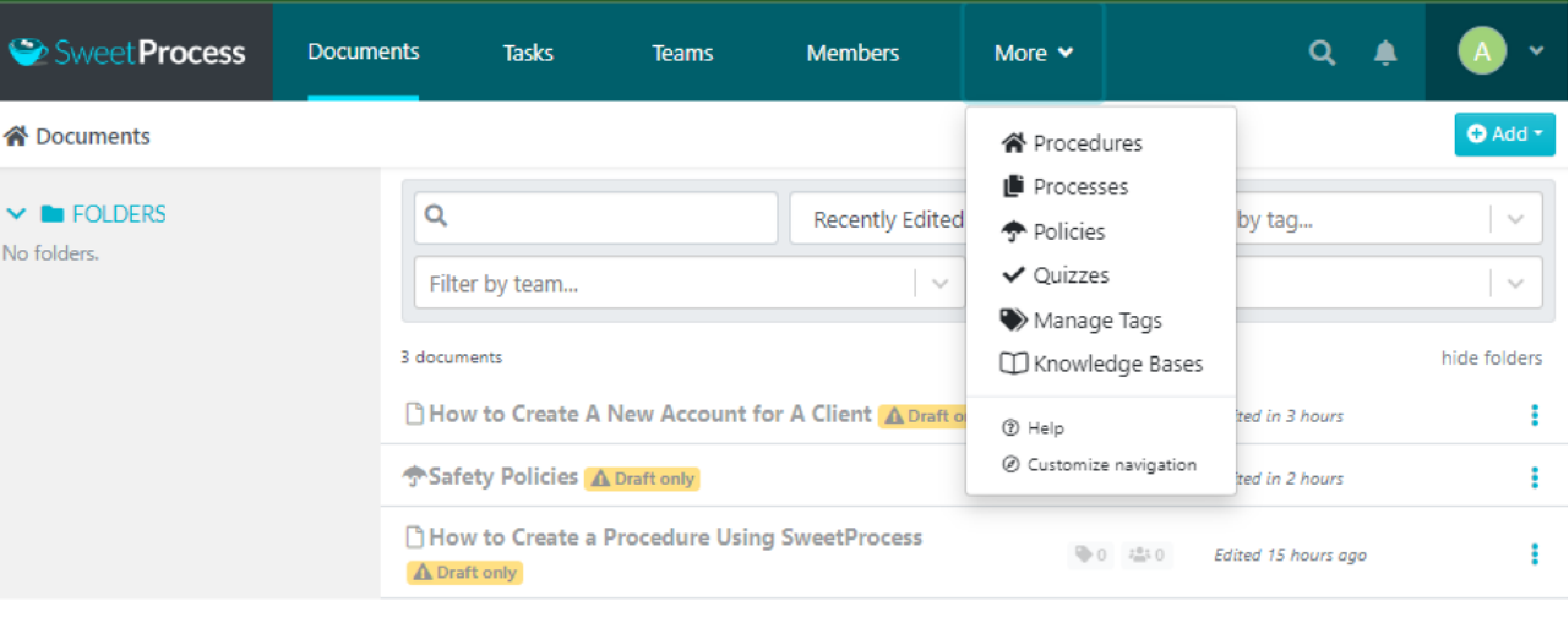
Click on “Create Policy.”
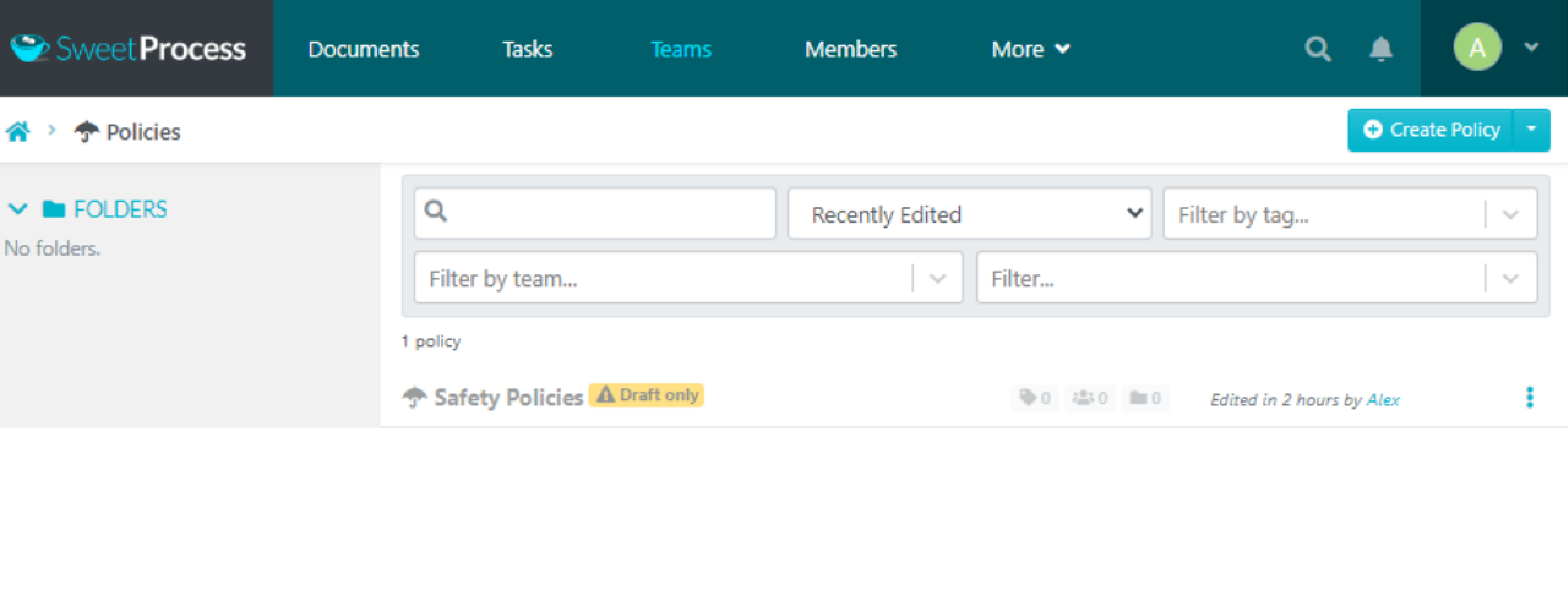
Give your policy a title and click on “Continue.”
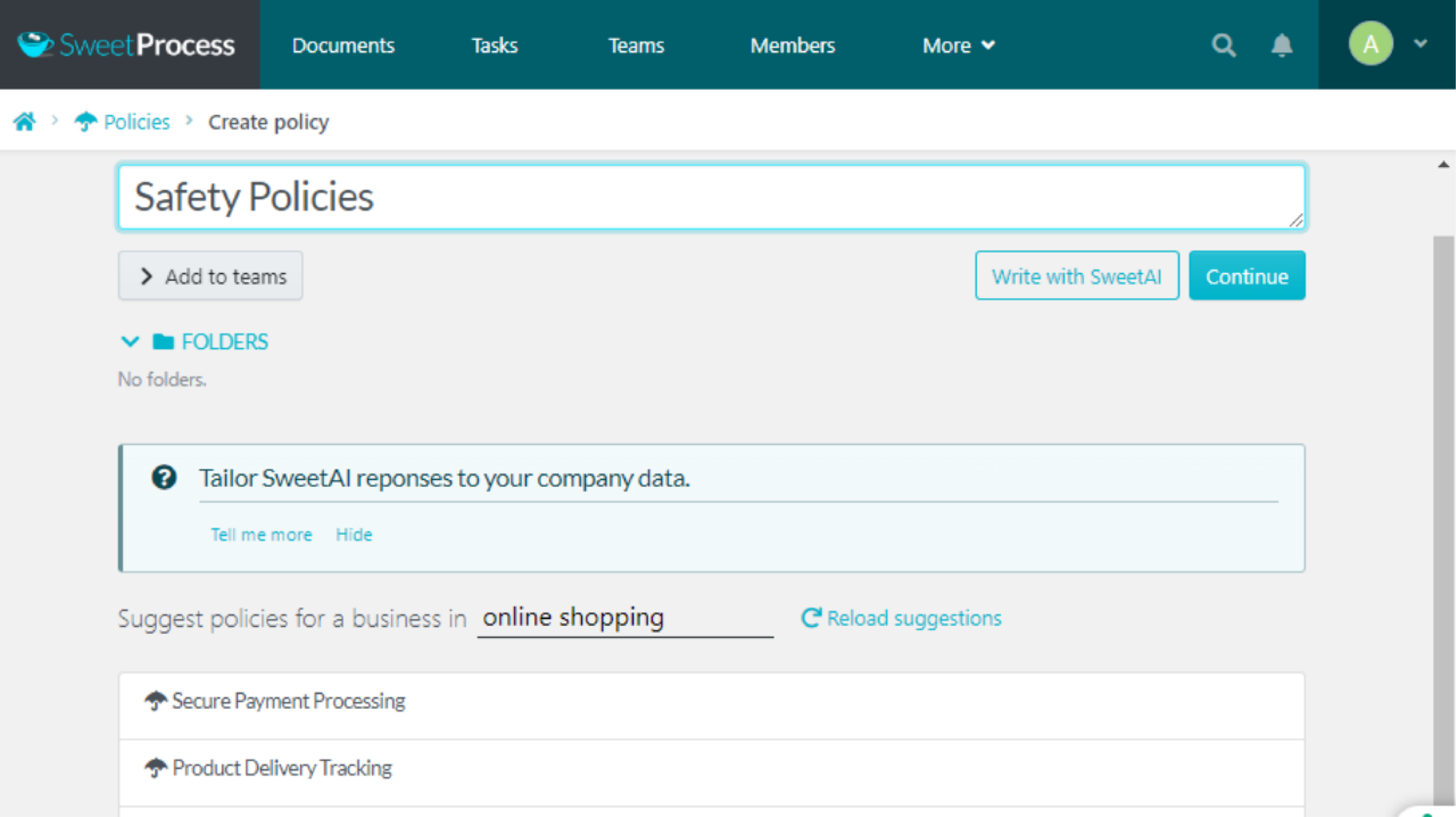
Click on the pencil icon to build your policy.
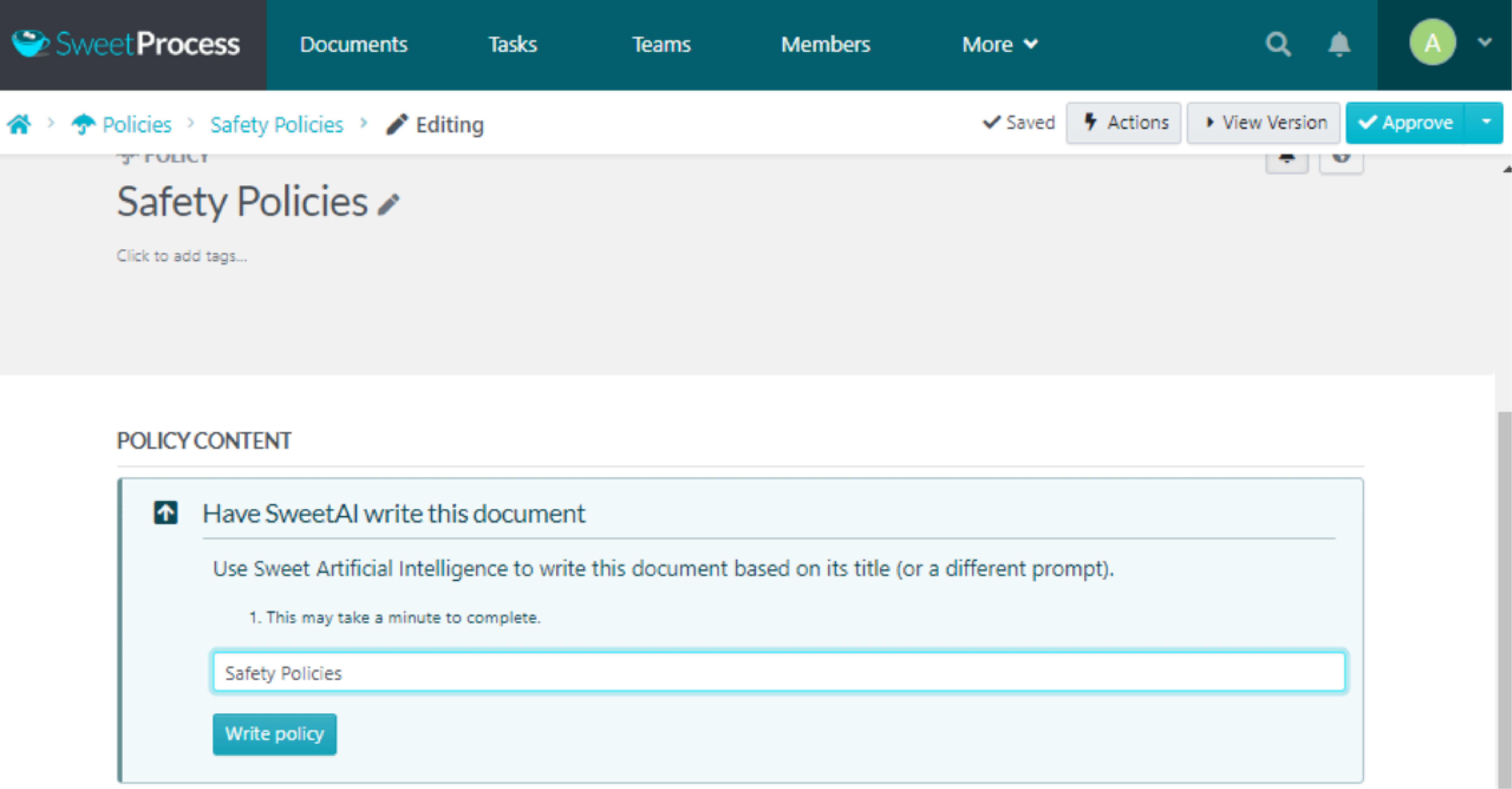
Fill in the necessary details of your policy and click “Save changes.”
How to Create a Procedure in SweetProcess Using AI
Click on “Procedures” and then click on “Create Procedure.”
Enter the procedure title and click “Write with SweetAI.”
Click on the pencil icon to edit the content to suit your style.
Click on “Approve” to publish the document.
How to Create a Policy in SweetProcess Using AI
Click on “More.”
Select “Policies” and click on “Create Policy.”
Enter the policy title and click “Write with SweetAI.”
Click on ‘’Approve’’ to publish the document.
Turn Procedures and Processes Into Actionable Tasks
SweetProcess streamlines your operations by centralizing repetitive tasks, ensuring seamless efficiency across your team. With our tool, you can effortlessly transform your procedures into actionable tasks, providing clarity and direction for your staff. By eliminating guesswork and missteps, SweetProcess propels your business growth, unlocking new heights of productivity and success. It certainly did for Don Houk at Next7 IT.
Sarah Genay, the portfolio analytics manager at Ginkgo Residential (a real estate company), struggled with employees having little knowledge of their responsibilities. Unclear expectations hindered the team’s performance negatively. While Sarah was placed in charge of documenting the company’s procedures, she saw that knowledge wasn’t distributed evenly in the company and that something had to be done quickly. With SweetProcess, the RACI framework was visually displayed on the dashboard, empowering each team member to understand their roles and tasks, fostering accountability, and driving performance management and improvement.
Follow these steps to create a RACI chart on SweetProcess.
Step 1: Log in and click the “Create Procedure” button.
Step 2: Enter the title of the procedure.
Step 3: Add the teams or individuals to the task, i.e., the individual(s) who will be responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed.
Step 4: Click on the procedure title to add the description of the task and each role.
Step 5: Enter the RACI acronym and meaning so each person’s role can be quickly identified.
Step 6: Click on the “Add a Step” button.
Step 7: Give the step your title and description of the task.
Step 8: Click on “Finish editing” to save the draft of the step.
Step 9: Finish editing the draft of the procedure. Click the “Approve” button to make the live version of your RACI chart available.
Step 10: The online version of your RACI chart is now live, and all parties involved know their roles.
Collaborate With Team Members in Real Time
SweetProcess enables real-time collaboration and continuous improvement for your team. You can organize teams to mirror your company’s work breakdown structure and control access to procedures, processes, and policies. With email reminders, notifications, and chat features, your team is empowered to suggest improvements and give approval as required. Foster a culture of active decision-making and continuous quality improvement.
Manage Tasks and Track the Latest Activity by Team Members
With SweetProcess, you can always be aware of your team’s progress by tracking the latest activity or looking back in the history of any task or procedure. You can monitor assigned tasks closely and track them as every step is checked off until completion.
With these powerful features and the ease of use of SweetProcess, you can take your business to the next level without much hassle. Sign up for a free trial right here to begin a worthwhile experience.
Why Is a RACI Chart Important in Project Management?

A RACI chart is more than just a diagram. It is an important tool for project success. Here’s why a RACI chart is essential in the project management process.
Clear Role Definition
Working with multiple people becomes less hassle with a RACI chart. The saying, “There is a place for everything and everything in its place,” fits into your tasks. RACI charts give clear guidelines for what everyone ought to do.
It’s easy for tasks to become entirely different at the finish stage because ideas could have been communicated better. Who takes the blame when the project falls apart because of assumptions and miscommunication? You won’t need to ask this when using a RACI chart.
When who’s responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for each task has been clearly defined, no one is at a loss for what is expected of them.
Streamlined Communication
A RACI chart ensures that all stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the project. This encourages a healthy collaborative environment where everyone is on the same page. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, teams can avoid communication breakdowns, unnecessary delays, and workflow bottlenecks, which produces a more efficient and productive project workflow.
Clearer Expectations
When you use a RACI chart in your organization, team members clearly understand their tasks, responsibilities, and deadlines. Everyone knows what’s expected of them, eliminating confusion and uncertainty.
This clarity prevents duplication of effort, missed deadlines, and wasting time. Rather, your team members can work efficiently and confidently, knowing that they’re focusing on the right tasks at the right time.
Conflict Prevention
A RACI chart helps teams address conflicts that could happen before they arise, thereby reducing the risk of misunderstandings, miscommunication, and delays. By assigning clear ownership and accountability, your team members can identify and resolve issues early on or even avoid them completely. They’ll save time, reduce stress, and have a relaxed team environment where everyone works seamlessly.
Efficient Project Execution
A RACI diagram ensures that projects are executed efficiently, with clear roles and responsibilities enabling teams to stay focused and on track. By avoiding confusion and miscommunication, your team can complete tasks quickly and effectively. This will allow them to meet deadlines, achieve their projects’ goals, and deliver high-quality results.
Pros and Cons of Using a RACI Chart

Like most project management tools, RACI charts have their advantages and disadvantages. Let’s begin with the pros.
Pros of a RACI Chart
Clearer Expectations
RACI charts set expectations for who is managing or responsible for work. This helps eliminate confusion and clarifies accountability. It also ensures team members understand their roles and responsibilities, reducing errors and promoting accountability.
Optimized Resources and Workflow
Clearly defined roles enable team members to focus on their specific responsibilities, minimizing unnecessary meetings and miscommunication and saving time and resources. This ensures a more efficient use of human resources, resulting in a streamlined workflow, reduced waste, and improved productivity.
Simplified Decision-Making
The RACI matrix template serves as a reference point for resolving disputes, addressing challenges, and guiding decision making. Throughout the project lifecycle, the RACI chart is a valuable reference point, enabling you to involve the right people in the right decisions, avoid unnecessary bottlenecks, and ensure clear ownership and accountability. With this, you can be sure that decisions are made efficiently and effectively, removing unnecessary delays or confusion and with clear accountability.
Streamlined Communication
The RACI matrix helps involve the right people at the right time, speeding up decision-making and reducing feedback delays. It ensures that relevant information is shared with stakeholders, prevents miscommunication, and promotes transparency.
Reduced People Overload
Employing the RACI chart in your organization reduces the bombardment of suggestions from team members. The distinction between consulted and informed helps separate feedback providers from the general team. This way, no overwhelming opinions will take time to review and implement. The RACI chart also ensures that team members are adequately supported with necessary tasks, reducing stress and burnout.
Improved Accountability
A RACI chart improves accountability because its matrix defines an accountable person for each task. It ensures that someone is ultimately responsible for a project’s success and can be held responsible for the outcome. This also encourages team members to take ownership of their work, keeping your team at its best and free from finger-pointing.
Enhanced Collaboration
By clarifying roles and responsibilities, RACI charts foster collaboration and reduce confusion among team members, promoting a more cohesive and effective team dynamic, encouraging teamwork and collaboration, and breaking down silos.
Increased Efficiency
By streamlining communication and decision-making, RACI charts enhance efficiency across teams. They clarify roles and responsibilities, reducing confusion and ensuring tasks are completed promptly. This structure minimizes delays, enhances collaboration, and supports Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) by optimizing workflow management. The result? Faster project completion, improved outcomes, and reduced operational costs.
Reduced Micromanaging
RACI charts reduce micromanagement thanks to their clearly defined roles and responsibilities for everyone. Since everyone’s role is listed, everyone knows what they’re to do. This promotes trust among team members and allows them to work more independently, reducing the risk of overcontrol.
Cons of a RACI Chart
The cons of a RACI chart include the following:
Role Ambiguity
The RACI model doesn’t provide enough detail about each role’s specific responsibilities. This may cause confusion and potential overlap, making team members unsure of their tasks. All of these can ultimately lead to delays and inefficiencies.
Tasks May Be Unclear
A RACI matrix only shows who is responsible for each task without explaining what needs to be done. This lack of clarity can lead to misunderstandings and errors, as team members may not fully understand what is expected of them.
Limited Applicability
RACI charts may not be suitable for all types of projects, including simple projects and those with rapidly changing requirements. The RACI framework best suits projects with well-defined requirements and clear roles. The RACI chart may quickly become outdated or irrelevant in projects with evolving requirements.
Actionable Steps May Be Unclear
RACI charts don’t specify the actions team members need to take, which can cause confusion and delays. As a result, team members may need additional guidance to understand the steps they need to take to complete their tasks. Without clear work instructions, team members may struggle to complete tasks efficiently.
Unnecessary Complexity
RACI charts can be quite complicated and add unnecessary complexity to projects. This is especially true for those with simple workflows. Not every project needs a RACI chart. (More on this soon.) The added complexity can lead to confusion, frustration, and decreased productivity.
Difficulty in Role Definition
It can be challenging to fit project roles into only the four RACI categories, especially in projects with unique or specialized roles. This can lead to confusion and potential errors in assigning the various responsibilities, and team members may struggle to understand their roles and responsibilities.
Confusing Terminology
If not clearly defined, RACI terms can be confusing. This can be worse for small teams where individuals may hold multiple roles. This can lead to misunderstandings and errors in assigning responsibilities. Without clear definitions, team members may misinterpret their roles.
Inflexibility
RACI charts are best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and may be ineffective for projects with changing requirements or decisions. The RACI framework can be inflexible and may need to adapt better to changing project needs.
It is now clear what the upsides and downsides of a RACI chart are. How can one use this tool practically?
RACI Chart Examples: Practical Applications in the Real World

In this section, you’ll see how RACI charts are applied in real-world scenarios.
Developing a New Software Product
First, we’ll draw our chart with columns and rows for tasks and roles. The roles will include product manager, development team, quality assurance team, stakeholders, and marketing team. Tasks will include product definition, design, development, user testing, software promotion, etc. Next, assign R-A-C-I accordingly. The roles and functions should follow this pattern.
Product Manager (R): Defines product requirements and ensures they meet customer needs
Project Manager (A): Oversees the project timeline, budget, and resources
Development Team (R/C): Designs, develops, and tests the software
QA Team (R/C): Conducts quality assurance and testing
Stakeholders (I): Includes customers, investors, and executives who need project updates
Marketing Team (I): Responsible for promoting the software post-launch
Developing a New Real Estate Property
Draw your RACI chart and input the necessary fields. The following roles and tasks will fall under the appropriate fields:
Project manager, development manager, architect, contractors, investors, sales manager, potential buyers, site coordination, selection, design, sales, building, funding, marketing, etc. The R-A-C-I should be assigned as follows:
Project Manager (R): Coordinates site selection, design, construction, and sales
Development Manager (A): Oversees the project’s overall strategy and success
Architect (R/C): Designs the property and ensures architectural integrity
Contractors (R/C): Builds the property according to the design project plan
Investors (I): Provides funding for the project and needs updates
Sales Manager (A): Leads sales and marketing efforts
Potential Buyers (I): Interested in purchasing the property
Producing a New Marketing Campaign
Like with the first two, draw out your chart and fill in the roles and tasks headings. Creative team, campaign strategy, product manager, content team, media buyer, sales team, video/image creation, advertising, budget, etc. After assigning R-A-C-I, you should have a clear representation of what you aim to achieve, like this:
Creative Team (R): Develops the campaign concept and creative assets
Campaign Manager (A): Oversees campaign strategy, budget, and timeline
Product Manager (C): Provides product insights and ensures alignment
Content Team (R/C): Creates campaign content (e.g., copy, images, videos)
Media Buyer (R/C): Purchases advertising space and manages media planning
Target audience (I): The intended audience for the marketing campaign
Sales Team (I): Benefits from the campaign’s lead generation and sales
With this illustration, you have some ideas for setting yours up for future projects. As you’ll see in the next section, a RACI chart is designed to address particular problems.
When to Use RACI Charts in Project Management

RACI charts are a powerful resource, best leveraged when clear roles and responsibilities are crucial.
Complex Projects
A RACI chart is a good bet when embarking on a complex project. In complex projects with multiple stakeholders, it ensures everyone understands their roles and responsibilities, making sure everything runs smoothly. It can also help you avoid investing time in unnecessary communication or providing updates to non-stakeholders.
The Decision-Making or Approval Process Could Hold up the Project
A RACI chart prevents unnecessary project delays in decision-making by ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
Cross-Functional Teams
If you have cross-functional teams, a RACI chart is good for clarifying task ownership and decision-making responsibilities. Its objective approach to project management will prevent conflicts and ensure effective collaboration.
There’s Conflict About Task Ownership and Decision-Making
If your organization usually has conflicts because of task ownership, a RACI chart can help resolve disputes by clearly defining task ownership and decision-making responsibilities. This way, everyone understands their roles and responsibilities and can collaborate effectively. It also helps when you’re not sure about responsibilities. By creating a RACI chart, you can make educated guesses about assignments.
The Project’s Workload Is Not Evenly Distributed
Consider using a RACI chart if your workload is not evenly distributed. A RACI chart helps you identify overloads and distribute the workload more evenly. When used in advance, you can spot overloads and distribute them fairly. It’ll prevent your team members from having burnout from too many responsibilities and see that everyone’s workload is balanced.
When Miscommunication Occurs
If your organization frequently struggles with communication, a RACI chart can solve this problem. A RACI chart prevents miscommunication by clarifying roles and responsibilities, ensuring everyone is on the same page, and reducing errors.
Need to Onboard Someone to a New Role Quickly
A RACI chart enables quick employee onboarding by clearly understanding roles and responsibilities. It enables new team members to contribute effectively, ensures project continuity, and reduces the impact of turnover on the project.
Next, let’s tackle the common pitfalls to avoid when using RACI charts, ensuring you get the most out of this powerful tool.
Common RACI Chart Challenges and How to Avoid Them

Creating a RACI chart can come with challenges. The following are some common obstacles and how to overcome them:
Lack of Buy-in From Your Team and Stakeholders
The RACI matrix requires active participation and commitment from all team members and stakeholders. Without their buy-in, the matrix becomes an ordinary formality instead of a helpful tool, which can cause your projects to be unsuccessful. To avoid this, it’s necessary to involve all stakeholders in creating and updating the RACI matrix and address any concerns or questions they may have.
Overemphasis on Hierarchy
The RACI matrix can sometimes dwell too much on existing hierarchical structures, leading to a top-down approach that negatively impacts and stifles collaboration and innovation. This can result in a lack of creativity, poor decision-making, and a lack of ownership among team members. To avoid this, strike a balance between hierarchy and collaboration, ensuring that all team members feel valued and empowered to contribute.
Overcomplicating Stakeholders Communication
Sometimes, the RACI chart can overcomplicate communication with stakeholders, leading to confusion, miscommunication, and tension. You can prevent this by ensuring that communication is clear and concise and meets each stakeholder’s needs. You can create a communication plan showing the frequency, format, and content of communication with each stakeholder.
Setting It and Forgetting It
A common pitfall in using the RACI chart is to set it up and forget it exists. Setting it is one thing, and using it is another. It is the same as forgetting to monitor, evaluate, or improve its effectiveness. It can lead to poor performance, missed opportunities, or wasted resources. To avoid this, you should treat the RACI matrix as a dynamic and flexible tool, not a static and fixed document.
Lack of Real-time Updates
You may feel the job is done when you’ve successfully created your organization’s RACI chart. Not exactly. A RACI matrix is not a static document. This means it needs to be updated regularly to reflect changes in the project. If you don’t do this, your chart will quickly turn into an outdated and static information tool. To tackle this, schedule regular reviews and updates of the RACI matrix, ensuring that all team members are aware of the changes and their impact on the project.
Ambiguity in Role Definitions
The RACI relies on a clear definition of roles, and terms like “responsible” and “accountable” can be confusing as they are used interchangeably. Confusing these roles can lead to miscommunication and a lack of clarity in the project. Integrating an Organizational Chart alongside the RACI matrix can help visualize reporting lines and clarify who holds each role. To avoid this, it’s important to define roles clearly and ensure that all team members understand their responsibilities and accountabilities.
Complexity in Large Projects
The RACI matrix can become quite challenging to manage in large, complex projects. This can lead to inconsistencies and inaccuracies, which can have damaging consequences for the project. To avoid this, it’s essential to ensure that the matrix is regularly reviewed and updated. You also want to include a clear process for addressing and resolving inconsistencies and inaccuracies as they arise.
These challenges may arise in your organization when you introduce the RACI chart system. Let’s have a quick look at other alternatives you can consider.
The 7 Best RACI Alternatives to Manage Your Project
Let’s look at seven alternative methods to manage your project and team besides the RACI chart.
PACSI
PACSI is a tool for responsibility planning that defines stakeholder roles as perform (the one who carries out the activity), accountable (the one answerable for the completion of the task), control (this person[s] reviews the activity’s result), suggest (gives expert advice), and informed (receives information about the activity’s result). In this method, various stakeholders can review and reject the actions of a single individual who’s ultimately responsible for a task. PACSI strives to create a clear distinction between the roles of perform and accountable so that every member understands each other’s responsibilities by distinguishing between the person accountable for delivering the task and the one who reviews the quality of the results.
CARS
CARS is a method that emphasizes the importance of support from team members for those responsible for tasks. It stands for communicate (and it includes both consulted and informed parties), approve (the person who makes decisions), responsible (the individual who performs the work), and support (those who help the responsible individuals).
RASCI
RASCI is a responsibility assignment matrix that is built on the RACI method. It adds “support” as it recognizes the value of supporters who assist without leading tasks or acquiring ultimate responsibility. This method is helpful for teams that want to acknowledge the contributions of supporters without burdening them with responsibility. It sees supporters as valuable resources that help to get things done. Note that RASCI bears almost the same disadvantage as the RACI method.
DACI
DACI is a decision-driven approach designed for executive teams to streamline strategic decisions. It stands for driver (the leader of the decision-making process), approver (the one with the authority to make the final decision), contributors (provide expertise or information to inform the decision), and informed (these get notified about the decision outcomes). DACI is useful for teams that must make strategic decisions quickly and efficiently. DACI isn’t focused on a task-driven role but only tackles directive decisions.
RAPID
RAPID is a decision-making framework designed to promote collaboration and personal choice. This framework outlines specific roles and responsibilities for team members involved in the decision-making process. The RAPID acronym stands for:
Recommend: Team members analyze information and provide recommendations for action.
Agree: Stakeholders review and agree on the recommended course of action before moving forward.
Perform: Team members implement the decision.
Input: Subject matter experts provide data and insights to inform the decision-making process.
Decide: Here, the designated decision-maker makes the final call.
By using the RAPID framework, teams can ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page and accountable for decision outcomes. This makes it an ideal approach for teams that require collaborative decision-making.
CLAM
CLAM is a method that provides a unique perspective on task-related roles. It ensures that each team member understands his or her responsibilities.
CLAM stands for:
Contribute: These are individuals who are both consulted and actively involved in the work. They bring their expertise and insights to the table, making significant contributions to the project.
Lead: The lead role is responsible for delegating and managing project tasks. They oversee the project’s progress, ensure that tasks are completed on time, and adjust as needed.
Approve: The approver makes informed decisions about the project’s direction and scope. They review recommendations, provide feedback, and give the final approval for task completion.
Monitor: The monitor role involves tracking progress, identifying potential roadblocks, and receiving regular updates. This ensures the project stays on track and any issues are promptly addressed.
RAS
RAS is a simplified version of the CARS model but without the communication aspect; it is dealt with separately. It provides an efficient approach to assigning responsibilities. It stands for responsible (performs the work), approves (makes decisions), and supports (assists). RAS is useful for teams that want a simple way to assign responsibilities without unnecessary complexity.
Keep Your Team Synchronized and Accountable Using SweetProcess

RACI charts offer you a reliable way to manage your projects successfully by eliminating confusion and promoting clarity. Follow the steps in this ultimate guide and remember the pitfalls to avoid when using a RACI chart, and you’re all set. Combine this with the SweetProcess project management software, and you get a sweet recipe for happy teams, continuous growth, and consistency. Sign up to begin your free trial of SweetProcess. No credit card is required.
