Last Updated on February 27, 2025 by Owen McGab Enaohwo

Would you rather be sanctioned for not complying with regulatory standards or lose your customers due to their dissatisfaction with your products or services? Either alternative is just as bad as the other. Imagine suffering both problems at once.
That’s the fate of businesses that don’t implement a quality management system. They set themselves up for failure without realizing it. Don’t let your business fall into that category, especially when you can prevent it.
SweetProcess is a choice quality management system for building a compliance culture that resonates with your customers. Sign up for a 14-day free trial without a credit card.

Quality Management System Full Guide – Table of Contents
What Is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
Benefits of Quality Management System in an Organization
Types of Quality Management Systems (QMS)
9 Core Elements of a Quality Management System (QMS)
How to Set up and Implement a Quality Management System for Your Company
How to Create a Quality Management System Using SweetProcess
Principles of Quality Management System You Must Imbue in Your Organization
Skyrocket Your Business Operations With Quality Management Systems
What Is a Quality Management System (QMS)?

Quality Management System (QMS) is an instrument for documenting business policies, processes, procedures, and other requirements an organization needs to comply with established regulatory standards and satisfy its customers. It’s a system that helps businesses uphold the best practices outlined by governing bodies and authorities in society’s interest.
Consumer safety would be in jeopardy if there were no gatekeepers in the global market. Manufacturers would sell all kinds of products and services with little or no caution to enrich themselves. Fortunately, that isn’t the case with authorities establishing regulations to protect consumers. Organizations must comply with regulatory requirements to operate in the market, and a quality management system (QMS) positions them well for that.
High value is the core of a QMS. The end game of every commercial product or service is to satisfy a need, especially for a customer. It takes more than the barest minimum effort to achieve customer satisfaction. The offering must be of high standards regarding production material, mode of operations, and delivery.
Consumers may not have the means to make manufacturers comply with regulatory standards, but they can exercise a fundamental right to boycott substandard products or services. Businesses that fail to prioritize quality in their operations are at risk of folding due to a lack of patronage.
In their defense, the many moving pieces in business environments can be distracting, impacting the quality of an organization’s product or service delivery. Adopting a quality management system helps to uphold the best operational practices in meeting customer expectations and complying with regulatory standards. This entails a series of functions, such as creating business policies, documenting processes, and training employees.
Benefits of Quality Management System in an Organization
A quality management system benefits businesses in their engagements with regulatory bodies, customers, and employees. Its benefits include the following:
Consistency in Operations
Being consistent in operations requires a deliberate effort to standardize business processes. If two employees were assigned a task without standard instructions, they would produce different results. The discrepancies in their performances aren’t good for business reputation and sustainability, not to mention regulatory compliance risks.
A QMS helps identify and implement the most efficient processes for standardization. They guarantee the same high-quality results even when different people execute tasks. This is because the outcomes of tasks don’t depend on the skills of executors but on established guidelines.
Developing a blueprint for consistent operations with a QMS is vital in scaling a business. New and established workers in different areas can use the documented process to execute tasks and achieve established quality performance.
Ensures Customer Satisfaction

The high business competition in today’s market gives customers many options to choose from. Understandably, they gravitate toward the best alternatives. Organizations using a QMS implement the most efficient processes to enhance their operations, which has a ripple effect on customer satisfaction.
A QMS propels businesses to deliver the safest products and services. Following outlined guidelines solidifies their delivery to customers. Take complaint handling, for instance: how an organization manages customer complaints speaks volumes. There’s a tendency for employees to engage customers disapprovingly in the absence of a quality process for resolving complaints. A QMS mandates customer-facing staff to follow documented procedures that prioritize customer interest, regardless of the staff’s opinion. Such a consumer-centric approach increases customer retention.
In the early 2000s, Xerox, a digital solutions company, was fined millions of dollars by the Securities and Exchange Commission for allegedly inflating the performance of its operations. The scandal and its ripple effects led Xerox into a $16-billion debt. The company bounced back from such a major crisis and rebuilt its reputation by making customer satisfaction the main focus of its operations.
Saves cost

Redundancies go unchecked when there’s a focus on performing actions and not the outcomes of those actions. To increase customer satisfaction, a business might have duplicated processes that take up resources. The motive is commendable, but they waste resources, especially when they could achieve the same results without the duplicates.
Documenting SOPs reveals redundancies that would ordinarily go unnoticed. This is because steps in the process can be visualized to see their connection and relevance. Visualizing processes also identifies bottlenecks that consume resources and elongate tasks.
Prevents Legal Risk
Business laws are in place to protect the interests of society. Organizations risk facing legal actions when they breach existing laws. Consumers may be the end users of products and services but aren’t powerless. They have a right to sue businesses that jeopardize their well-being. Neglecting regulatory requirements is the fastest way to get into legal trouble. Social media powerhouse Meta, owners of Facebook, were fined $1.3 billion in 2023 for violating EU data privacy regulations.
Businesses leverage all legal means to beat the competition. This includes taking legal action against competitors that flout regulations so they will dominate the market. Implementing a QMS guides organizations along the right path in their operations and facilitates better risk management. Having envisaged risky behaviors and situations, they develop policies and processes to avert them.
Evidence-Based Decision-Making

Decision-making ranks high among sensitive business activities as it can lead to positive or negative actions. Business leaders are naturally inclined to make decisions by impulse without considering all related factors. A QMS guides them in adopting an evidence-based decision-making process that evaluates the situation’s internal and external factors before choosing an alternative to minimize negative outcomes.
Documenting processes and other business instructions in a QMS guides employees in making the right decisions on their jobs daily. They have a go-to system to seek clarity whenever in doubt. An effective quality management application collects performance data from tracking engagement activities. Leaders can measure the effectiveness of processes and predict their outcomes by analyzing data accurately.
Enhanced Employee Efficiency
Employee efficiency is an outcome of their knowledge and skill level. Established workers are generally more efficient than their new colleagues because they have had more time to acquire knowledge and skill sets. A QMS enables businesses to close this knowledge gap by conducting structured training. It facilitates quick and convenient learning with training materials in different formats like text, video, audio, etc.
Trainers can measure trainees’ performances and offer more assistance in deficient areas. A quality management system can also be used to streamline training and onboarding processes by automating repetitive tasks.
Enterprises can leverage a QMS to promote continuous improvement by regularly training all staff. This is essential to introduce better practices and adapt to rising requirements in their industries.
Competitive Advantage

One way businesses can attain high-level and sustainable success is to build a competitive advantage on the strength of their operations. This is achievable by streamlining workflow and normalizing efficiency. When they empower employees with the information to perform their jobs well, they achieve higher customer satisfaction—a key factor in building competitive advantage.
Using a QMS streamlines the workflow and makes information accessible to employees. It promotes collaboration and communication, allowing employees to share feedback on their processes and identify improvement opportunities.
Types of Quality Management Systems (QMS)
Different quality management systems exist to accommodate the unique needs of businesses in various industries. A hospitality business has different needs than a manufacturing business because they serve different purposes. Even if both companies implement quality management, they may need to work with different quality management systems.
Let’s look at the most common types of quality management systems.
Standardized Systems
Standardized systems are a series of frameworks for maintaining high quality in specific industries. The quality requirements are developed by industry experts who understand the risks associated with businesses in those industries and outline measures to prevent them.
A common standard for quality management is the ISO 9001 standard. A brainchild of the International Organization for Standardization, it contains inputs from professionals in different regions and is valid in most countries. Acquiring the ISO 9001 certification proves that a business meets the regulatory requirements in providing quality products and services.
Honeywell International, a publicly traded multinational company, has maintained consistency in its operations for more than a century by deploying quality management systems such as ISO 9001. It operates by established processes that guarantee high performance and results.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a systematic process for detecting errors in ongoing processes for continuous improvement. Mostly used in the manufacturing industry, it identifies bottlenecks in the supply chain and facilitates regular employee training, empowering them to deliver better products and services to customers.
TQM thrives on improving business processes while adhering to regulatory standards. An example is kanban, a visual inventory control system used especially in manufacturing. It runs on the just-in-time (JIT) inventory model, which streamlines ordering raw materials directly from suppliers as they run out.
Marriott is famous for adopting TQM as part of its quality management efforts. It uses a lateral leadership model that empowers its managers with all the information they need to make decisions for customer satisfaction. This ensures a swift resolution of customers’ complaints, which makes them happier.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
Continuous quality improvement (CQI) holds that no process is perfect, even when it looks so. There are underlying quality issues in processes that continuous improvement efforts can resolve. CQI offers guidelines for offering the best quality without incurring unnecessary costs. It has gained more popularity in healthcare over the years and is used by decision-makers in the sector for operations management.
CQI measures the improvement efforts made to processes by gauging their outcomes and impacts from the consumers’ perspectives. It encourages the collection of feedback from product or service users to understand areas to satisfy them better and promotes strict compliance with regulatory requirements due to the delicacy of services rendered.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven quality control model for creating processes with minimal errors and defects for increased efficiency. A measurement-based improvement system measures a process to identify existing defects, discover their causes, and resolve them for long-term productivity.
Six Sigma’s popularity grew tremendously when Toyota adopted it in scaling beyond its home country Japan. The automobile company was able to maintain high quality in its operations across different regions. Implementing Six Sigma involves five procedures called DMAIC, which stands for define, measure, analyze, improve, and control.
- Define: Define the problem you want to resolve with the process.
- Measure: Measure the current performance of the process to establish a benchmark for improvement and detect bottlenecks.
- Analyze: Troubleshoot the bottlenecks individually to discover how they may be obstructing the process.
- Improve: Enforce improvement strategies based on your analysis of the problem.
- Control: Implement measures to avoid a relapse to the problem.
9 Core Elements of a Quality Management System (QMS)
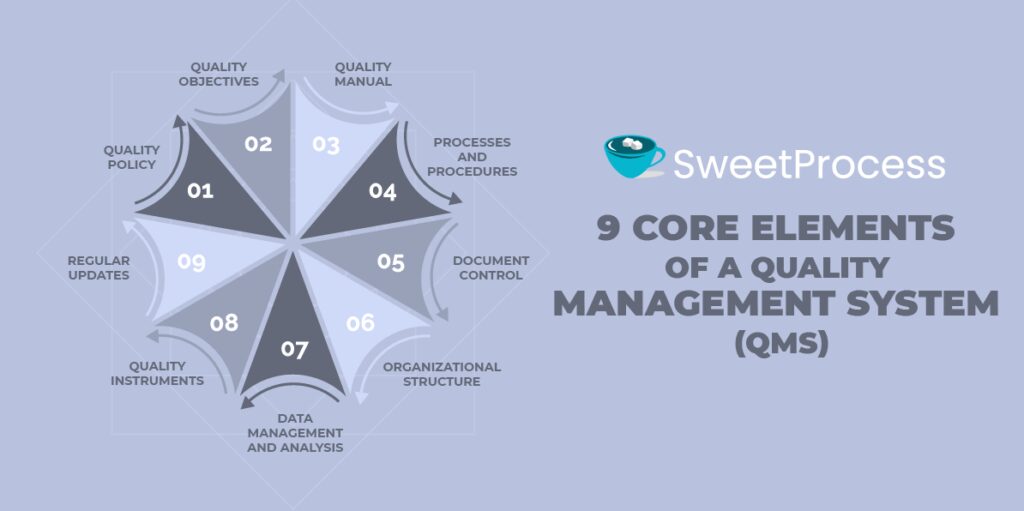
The content of a quality management system determines its relevance. There are essential components that address the various aspects of a business to keep it operable. Here are the Nine core elements of a QMS.
Quality Policy
A quality policy is a statement about an organization’s commitment to prioritize quality products and services. It provides formal evidence to internal and external parties that the organization takes quality management seriously.
Besides stating that a business pays attention to quality standards, the statement outlines how it does so. This includes mentioning the QMS standards or frameworks the organization uses and how it cultivates a quality compliance culture in its employees, customers, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies.
Quality Objectives
Quality objectives are the means for achieving an organization’s quality policy. If your quality policy states that you are committed to delivering high-quality services to customers, your quality objectives could include collecting and implementing customer feedback as one of the ways of meeting that goal.
Effective quality objectives are specific, measurable, actionable, and aligned with your values as a business. They include a commitment to quality improvement—a formula for continuously increasing customer satisfaction. Quality objectives are more achievable when they are communicated to team members with clear instructions on achieving them.
Quality Manual
A quality manual contains information about an organization’s quality system and how it functions and contributes toward achieving its quality objectives. The manual outlines the purpose of a QMS, and the specific information users can find in it.
New employees to a company may not understand the attributes of its QMS. Directing them to the quality manual answers any QMS-related questions they may have. A quality manual is also valuable in auditing as it shows auditors information about quality management in an organization.
Processes and Procedures
Processes and procedures are the how-to instructions for executing tasks. These documents are integral to a QMS for directional purposes. An effective QMS offers tools to create standardized processes and procedures and make them accessible.
Processes and procedures are most effective when they are actionable with step-by-step instructions. Some processes and procedures are more comprehensive in specific formats. The right QMS provides various documentation options, allowing users to choose the most suitable ones. For instance, providing training material in a video format may be better than writing it in some cases. Having the flexibility to document instructions in multiple formats enhances learning and implementation.
Document Control
Policies, processes, procedures, and other relevant business information make up an organization’s documents. There’s a tendency for them to become outdated and abandoned without adequate attention. Document control is creating, saving, sharing, and updating documents so they are relevant and accessible to users.
All business documents are not for everyone. Some documents are meant for certain people due to the sensitive information they contain. Document control ensures that users have the right access privileges. An effective QMS makes it easy to manage access control by clicking a few buttons. It also enhances version history, allowing users to create and access different versions of documents without hassle.
Organizational Structure

An organizational structure showcases the hierarchy in an organization in terms of roles and responsibilities. It displays the flow of activities, outlining the people responsible for certain duties and how the duties connect.
An organizational structure reveals the decision-making process in an organization. The centralized structure, where decision-making is from the top to bottom, is common, but there are other structures like the decentralized structure, where decisions are made at different levels of the organization. A QMS captures all information about an organizational structure as a guide for new employees and stakeholders to avoid confusion.
Data Management and Analysis
Data management is the process of collecting, organizing, and securing information about people who engage with a source. Data in its raw state is of little or no value, hence there’s a need to analyze it for meaning. Data management and analysis are essential in the decision-making process. Errors in those areas lead decision-makers to make wrong decisions with consequences for their organizations. Using a QMS for collecting and analyzing data reduces human errors to the barest minimum.
Businesses have a responsibility to ensure data privacy. They must secure the information of their employees, customers, stakeholders, and other people who use their platforms. How they use collected data must align with privacy laws in their areas. Using a QMS with advanced security features is key to avoiding data exposure. A good QMS also facilitates the lawful use of user data.
Quality Instruments
Quality instruments are the tools incorporated into a QMS for increased efficiency. These tools are just as important as the QMS by association and should be maintained and calibrated accordingly.
Businesses must continuously examine the security and compatibility of other tools integrated into their QMS. Any signs that the instruments may jeopardize the efficiency of their QMS or expose user data must be taken seriously to avoid crises.
Regular Updates

Rising developments in business and society at large require the introduction of new features in quality management software to improve their functionality. Developers have a duty to users to continuously improve their systems, especially in security. Cybercriminals are constantly devising new hacking techniques for gaining unauthorized access to organizations’ data. Access to the latest security features to resist their efforts ensures data security.
How to Set up and Implement a Quality Management System for Your Company
A good QMS gives businesses the leverage to combine human expertise and technology for maximum results. They can also acquire quality management certifications to operate as leaders in their industries. If you would like your business to attain this status, here’s how to set up and implement a QMS.
Define Your Quality Policy and Objectives
Your quality policy is your mission statement about quality. View it from a consumer-centric perspective to capture it succinctly. What is your commitment to customers in terms of quality? A product-based business may be committed to offering its customers products made of durable and sustainable materials. A service-based business may focus on delivering a seamless customer experience to its users. Despite their different environments, both businesses would offer value to their customers if they accomplished their quality policies and objectives.
Develop your objectives by outlining specific actions to take toward actualizing your policy. This could include sourcing your materials from credible suppliers and establishing metrics for certifying quality assurance before releasing your products or services. It could also include engaging closely with customers to meet their dire needs.
Get Leadership Buy-In
Getting leadership buy-in builds a strong foundation for an organization’s QMS. Management staff are there to protect the interest of the company and grow it. They should push back against any initiative they don’t understand or find valuable. It’s your responsibility to convince them by articulating your goal and vision. Why does the organization need a QMS? Your argument should be data-driven, not speculation.
Emphasizing the returns on investment (RIO) is an effective way to get leadership buy-in quickly. They want the organization to succeed. If a QMS is one way to achieve that, they will be interested in giving it a shot.
Choose a Quality Standard
If you are keen on establishing a sustainable quality management system, you need to build it on the framework of an established quality standard like ISO 9001, Six Sigma, and total quality management. Conduct research to identify the ones that are most suitable for your industry. Following the steps and instructions of your chosen quality standard will guide you in setting up a solid QMS that is compliant with regulatory requirements and offers maximum customer satisfaction.
Gather Resources

There are some resources needed to build and run a functional QMS: They could be human, technical, and financial. Identifying effective quality management software is necessary at this level. The place of due diligence can’t be over-emphasized; this is to ensure that the software suits your business needs. Ease of use, compatibility, and security are some factors to consider. You also need to identify the QMS certifications and accreditations your organization needs to acquire if you haven’t done that yet.
Document Processes
The processes in your QMS are standard practice, so documenting them requires the utmost attention to detail. Employees should be able to understand your organizational policies and how to perform tasks with your processes independently. Outline the input for each process and the expected output.
Identify the most critical activities in your operations and start with them. If you have existing documentation, evaluate it to detect vital information that may be missing. Identify the most suitable formats for documenting each process, be it text, video, chart, etc. Incorporate several formats in some of the processes for multimedia appeal.
Document Control Systems
The excitement of developing a quality management system may wear off shortly after you implement it, making you not give it the attention it needs to thrive. Be proactive by creating and documenting control systems to ensure that the components of your QMS are in good condition and operable. Automate some components of the control system, especially those involving repetitive tasks. Some areas may require regular human observation to identify lapses.
Training and Competence Management
You must be confident that your team members have the skills to make the most of your quality system. New and experienced employees may not have the technical skills to perform some quality management tasks, so it’s your responsibility to train them and ascertain their competence after each training.
Training mustn’t be done traditionally in person. You can be more flexible with e-learning. Implementing the right QMS software enables you to do this at no extra cost.
Implement and Monitor Process Performance
A good way to know if your processes are effective is to test them. Set your operations in motion and monitor performance. Pay attention to process defects, and measure them to determine the extent of their damage to the entire workflow. There’s a high chance that the defects will be recurring, so you need to develop a long-term process for resolving them.
Leverage automated monitoring systems for tracking performance. They record performance in real-time and flag down inefficiencies based on outlined settings. You can set notifications for tasks that haven’t been performed by a specific time. This will prompt team members to take deadlines more seriously instead of doing tasks at their convenience.
Collect and Implement Feedback
It’s likely that you will miss some vital performance details because you are championing the processes. Seek feedback from employees who perform the processes to get first-hand knowledge of what it feels like. Is any essential part missing in the process? Is there redundancy?
Customer feedback is just as important too. Find out from them if the current operations meet your quality objectives. Mediums for collecting feedback include surveys, interviews, and direct messages asking for their opinions.
Feedback doesn’t reveal only the negatives of your processes but also the positives. There may be some aspects that your employees and customers really like. Double down on the strengths and correct the weaknesses.
Review Processes Periodically
A functional QMS changes over time. These changes could be a result of emerging deficiencies in human and technical resources. Reviewing your operations in line with your quality objectives helps spot bottlenecks. Familiarize yourself with operational patterns and trends to know when your processes are underperforming.
Data analysis is a reliable instrument for process review and improvement. Check your performance data for changes. Analyze the data to understand the causes and make well-informed decisions on the best improvement alternatives.
How to Create a Quality Management System Using SweetProcess
Quality management systems are developed with specialized tools that have the features for implementing the policies and objectives we have discussed. There are many quality management software on the market but only a few of them offer maximum results. SweetProcess ranks high among QMS alternatives for streamlining business operations to meet regulatory requirements, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve employee performance.
Here are some SweetProcess features and how to use them to create a reliable quality system.
Policy Implementation
SweetProcess offers multiple tools and support to create your quality policy and objectives. There are templates for documenting and sharing organizational policies with ease. A major hassle businesses face in creating their policies and other related information is generating the content. SweetProcess simplifies the process with its automatic content creation tool, SweetAI, which you can use to automatically create all policy content from scratch.
How to Create a Policy Manually in SweetProcess:
Click on “More.”
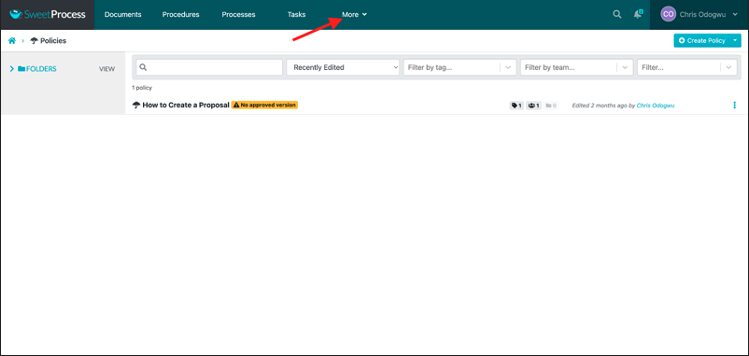
Select “Policies.”
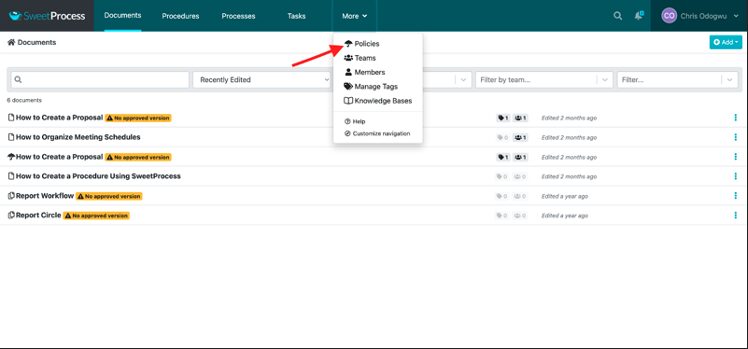
Click on “Create Policy.”
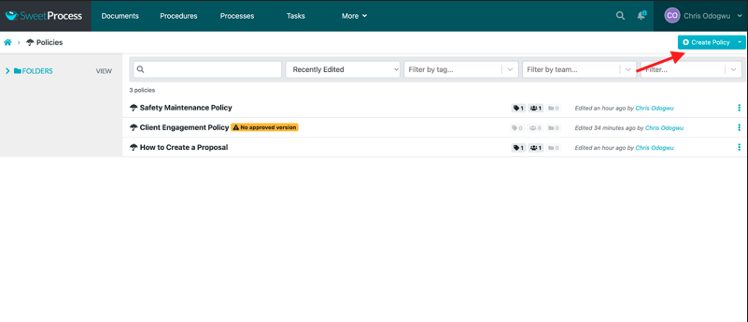
Enter the title of your policy and click on “Continue.”
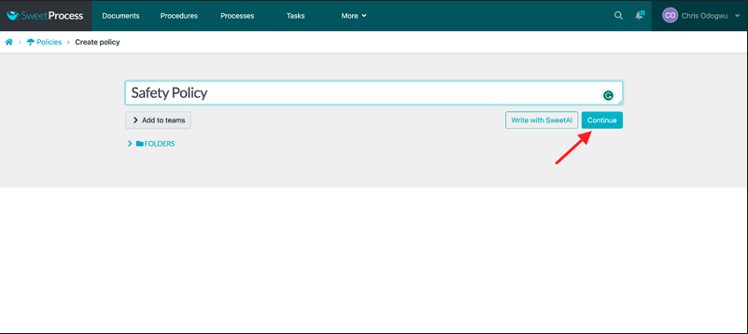
Click on the pencil icon to build your policy.
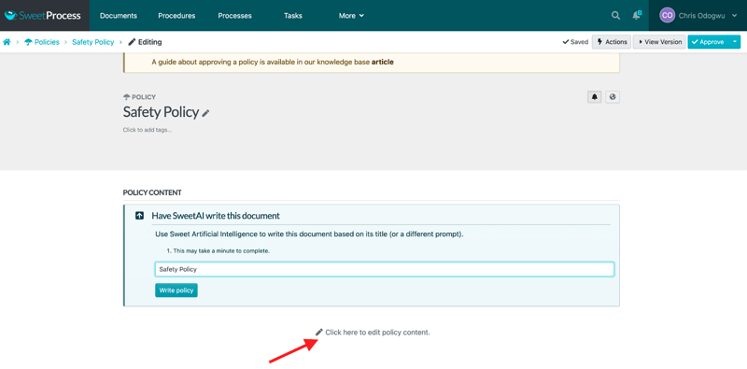
Develop your policy and click “Save changes.”
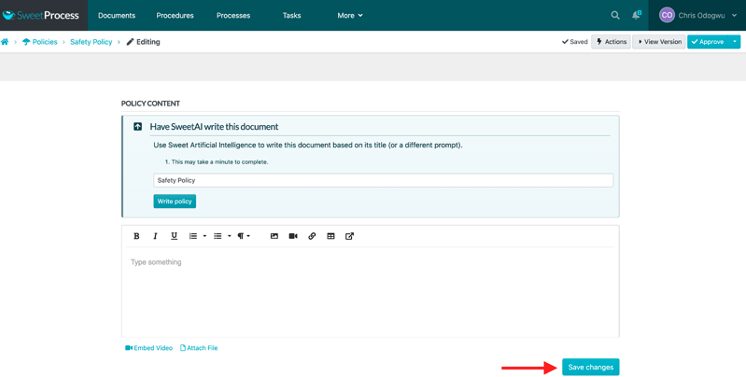
How to Create a Policy Automatically in SweetProcess With Artificial Intelligence (SweetAI)
Click on “More.”
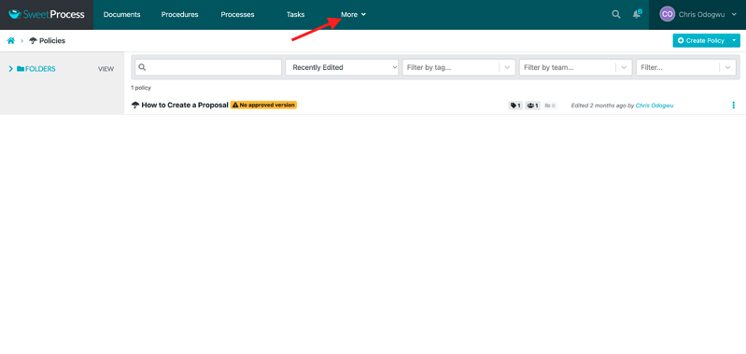
Select “Policies” and click on “Create Policy.”
Enter the title of the policy and click on “Write with SweetAI.”
Procedure and Process Documentation
SweetProcess offers simple templates for capturing the steps in a procedure. Effective procedures show a task in action, and SweetProcess facilitates that by providing various tools in its content editor to visualize procedures. You have the option of using text, video, charts, etc. in your procedures. The ability to add video to documentation has simplified work for Amy Walls, president and financial advisor at Thimbleberry Financial. The number of employees asking her questions about performing tasks was reduced because they found the videos to be comprehensive.
“It has made it so that my time is not needed to explain the same things to every team member. We now make a lot of videos around training and those videos get added into SweetProcess and the questions get answered,” Amy says.
SweetProcess also creates processes, which are a series of procedures used for executing longer tasks. You can arrange your procedures in the correct sequence, showcasing how they connect from start to finish. Writing procedures for every task is tedious and time-consuming. You have fewer things to worry about as you can create procedures automatically in SweetProcess using its artificial intelligence tool called SweetAI.
How to Document a Procedure Manually in SweetProcess
Click on “Procedures” and then click on “Create Procedure.”
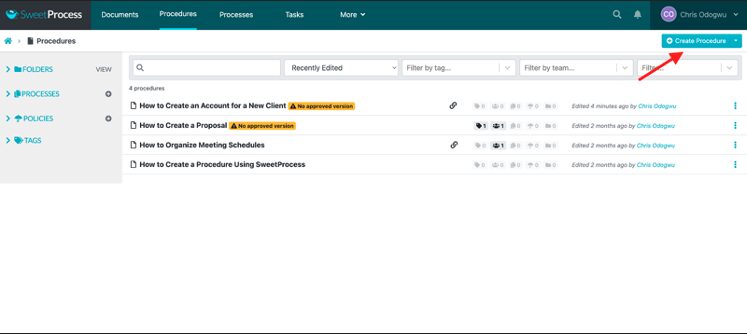
Enter your procedure title and click on “Continue.”
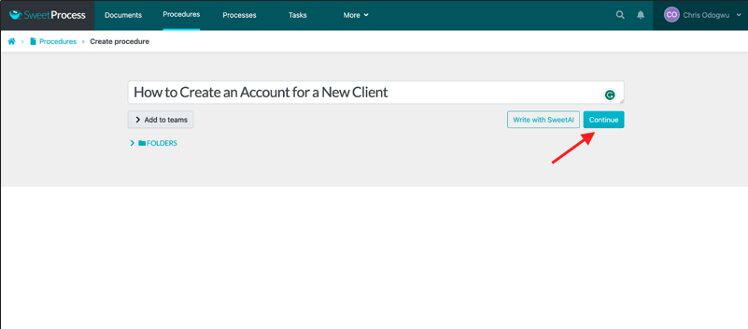
Click on the pencil symbol beside the title.
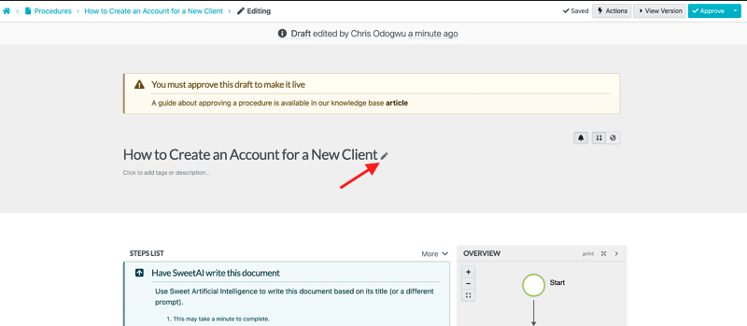
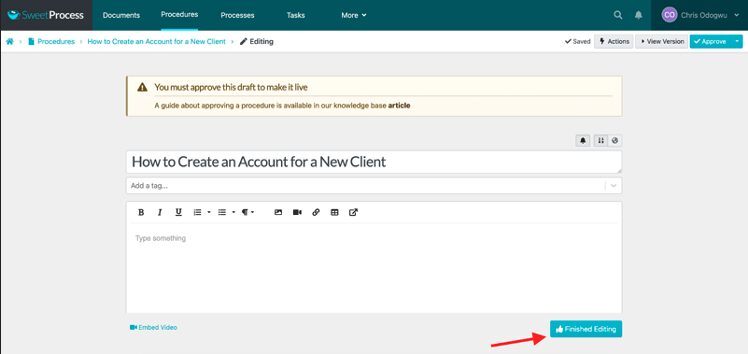
Fill out the details of your procedure and click on “Finished Editing.”
How to Document a Procedure in SweetProcess Automatically With SweetAI
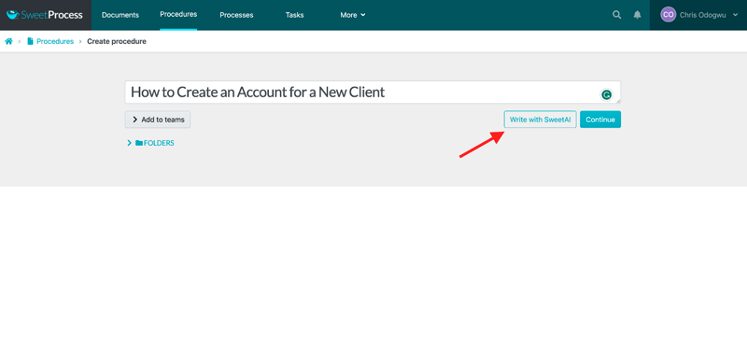
Click on “Procedures” and then click on “Create Procedure.”
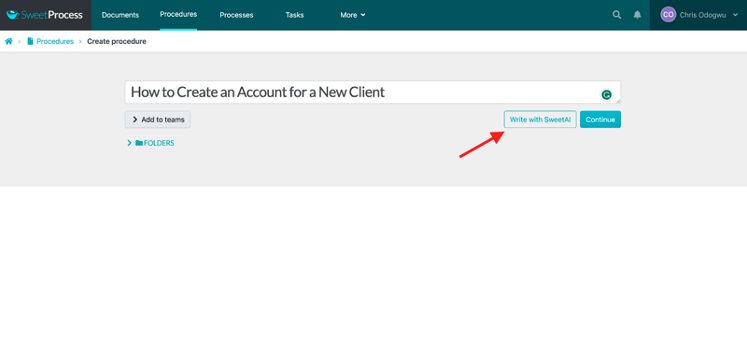
Enter the title of the procedure and click on “Write with SweetAI.”
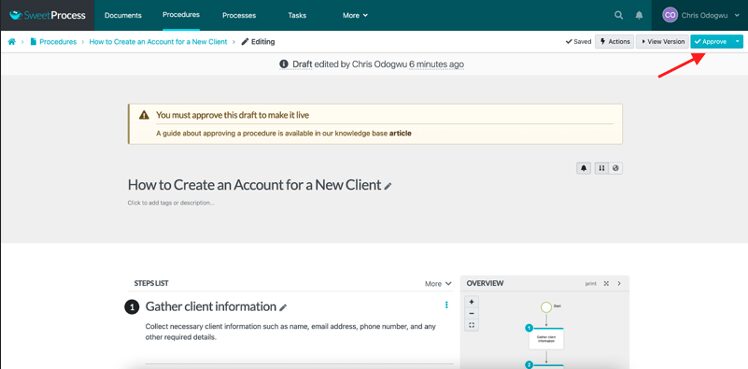
Click on the pencil icon to edit the content if you want.
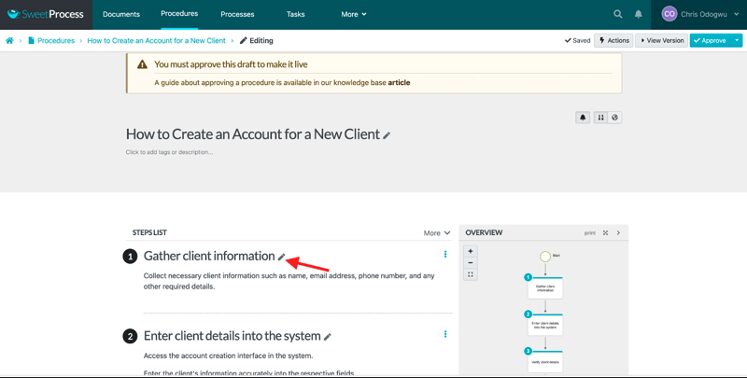
Click on “Approve” to publish the document.
How to Document a Process in SweetProcess
Click on “Processes” and then click on “Create Process.”
Enter the title of the process and click on “Continue.”
Click on “Add Step.”
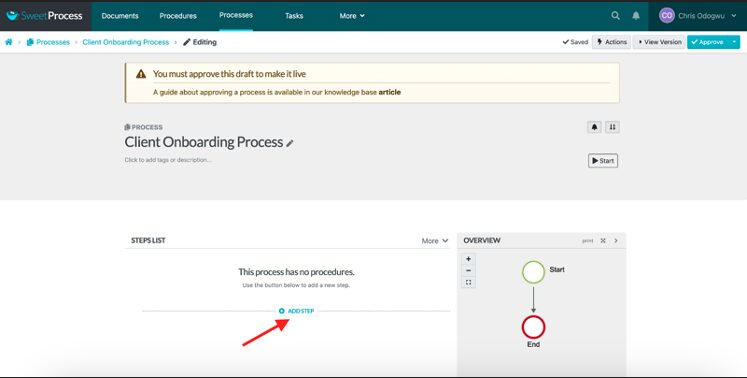
Click on “Procedure.”
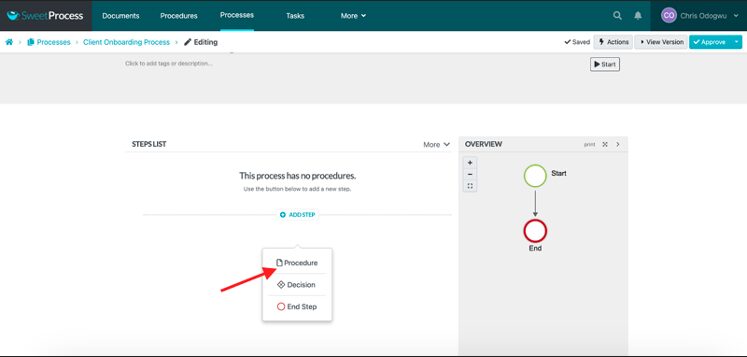
Select the procedure from the menu.
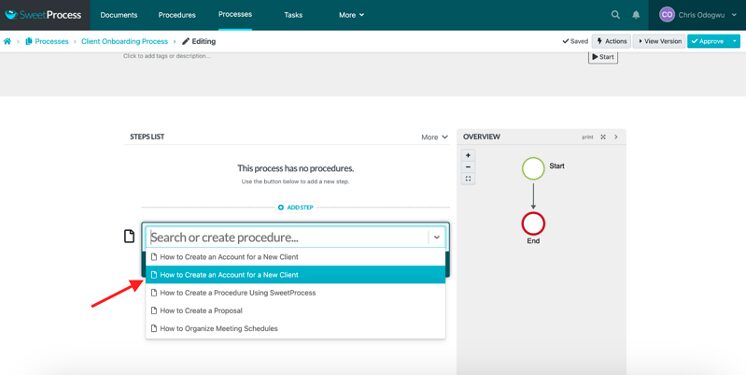
Click on “Add Step” and then “Procedure” to add another step in the process.
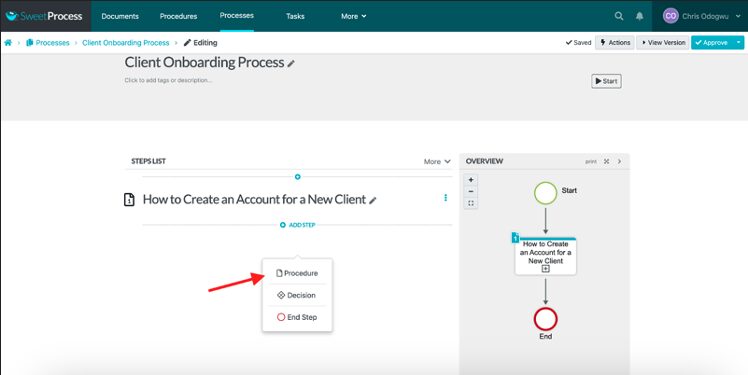
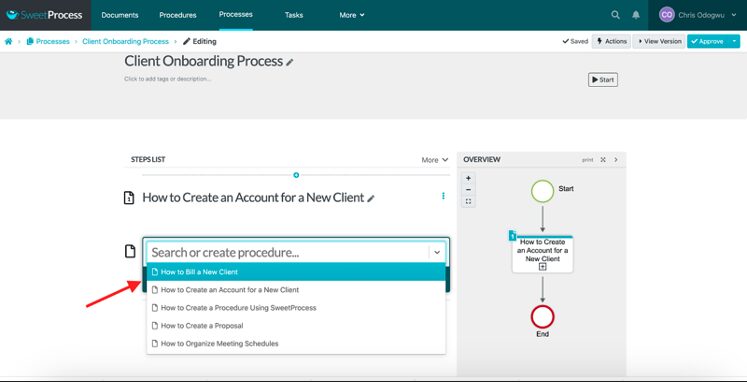
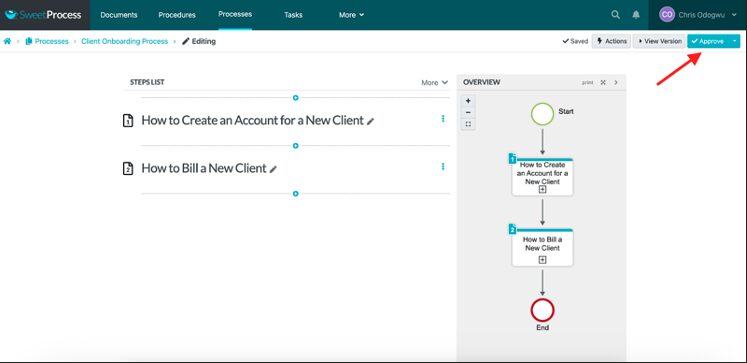
Click on “Approve” to publish your process.
Employee Training

Employee training is a hassle for many organizations as they invest a lot of time and resources to educate new and established workers on how to perform tasks.
SweetProcess simplifies training with its flexible and convenient training tools. Training materials can be created in preferred formats and shared with employees online regardless of their location. Gretchen Pisano, co-founder and CEO at pLink Leadership, found this feature very useful in onboarding and training employees in her organization.
“One huge thing it’s impacted is the way that I’m onboarding new folks. In the past, when we were training somebody new because we are 100 percent virtual, that person is shadowing effectively, and it’s just very slow. Whereas now they go directly to SweetProcess to find out what they need to know or they can go there when they’re doing something on their own,” Gretchen reveals.
SweetProcess fastens the training process, allowing employees to perform tasks as early as their first day at work. You can confirm employees’ knowledge of the training subject by giving them a quiz at the end before assigning them a task.
How to Assign Training Materials to Employees in SweetProcess
Open the procedure or process and then click on “Actions.”
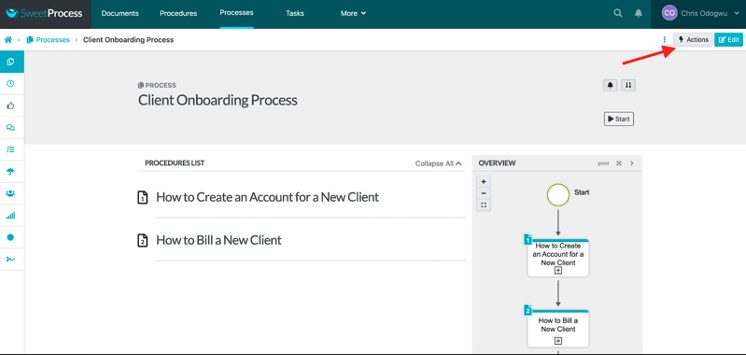
Click on “Assign as Task.”
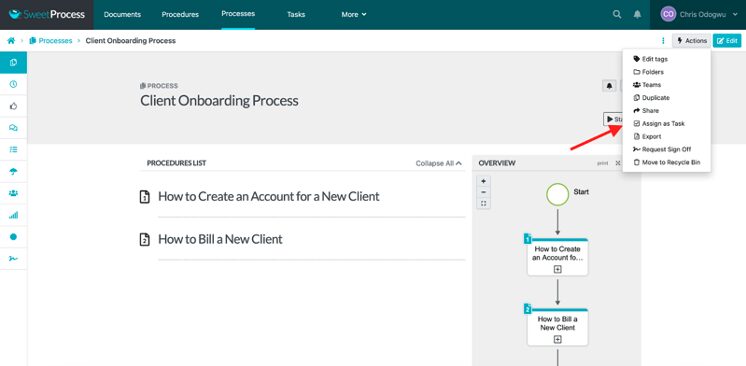
Click on “Assign.”
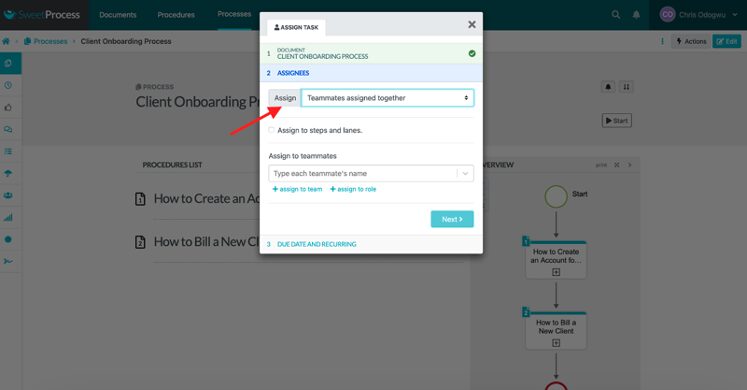
Click on “Teammates assigned their own task” to assign it to one person. Click on “Teammates assigned together” to assign it to multiple people.
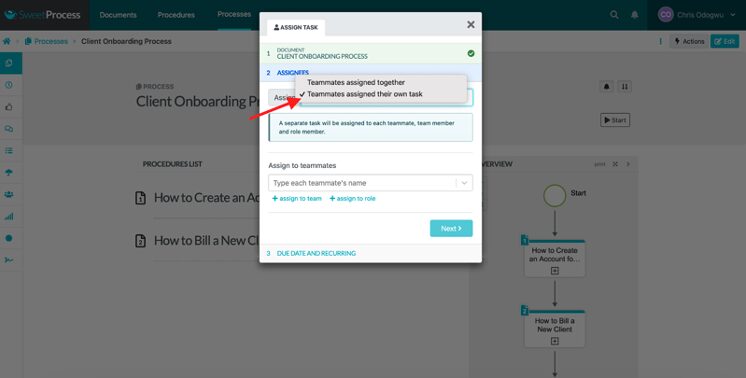
Select the teammate.
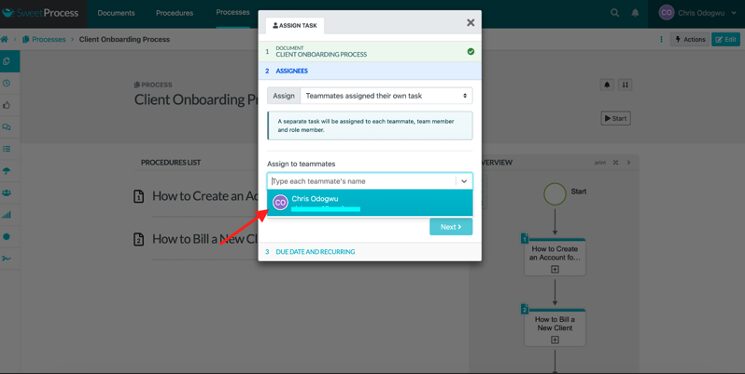
Enter the task name, due date, time, and frequency, and click on “Assign Task.”
Version History
SweetProcess supports organizations in managing documents in their systems with version history. You can create multiple copies of a single document and track the changes you make to each one. This allows you and your team to work on similar projects with different specifications. Adi Klevit, business process consultant at Business Success Consulting Group, who is familiar with many quality management software, finds SweetProcess’s version history to be an effective tool for businesses.
“You know what changes were made, so it makes it very easy to see the changes and the edits from one time to another. You can see the difference. You don’t have to read the entire procedure—you can see what was edited or added,” Adi says.
How to Identify a Version of a Document in SweetProcess
Open the document and click on the clock icon on the left. Hover your mouse on it to view “Versions.”
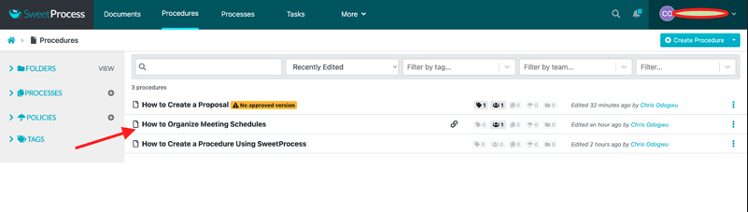
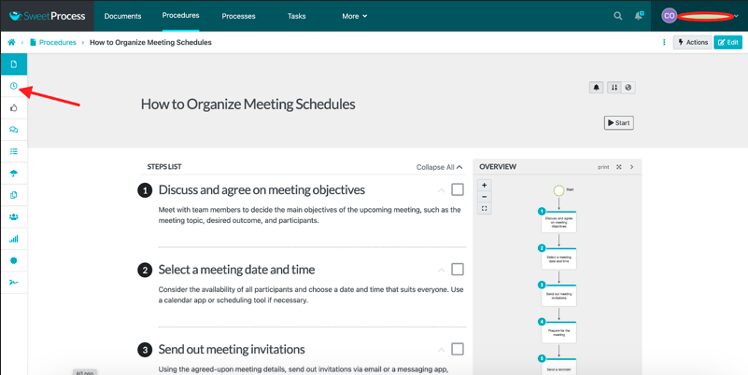
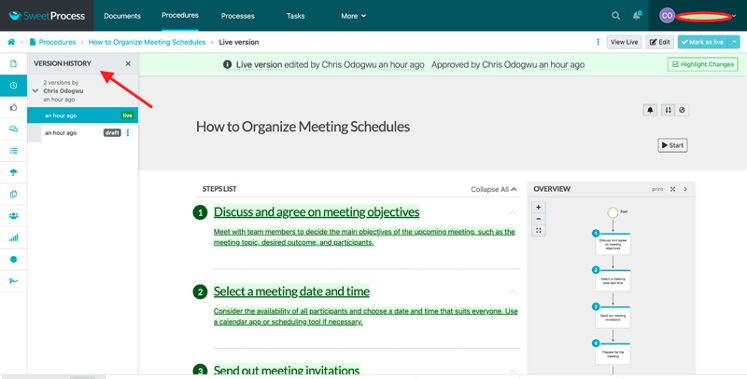
There’s a sidebar showing the various versions of the document, with the most recent one at the top.
Open the version you need.
Task Management
SweetProcess facilitates task management by allowing admin users to assign tasks to team members either individually or collectively. This flexibility creates a healthy work environment for employees to execute some tasks independently and collectively with others. You can also track how team members engage with assigned tasks in real-time.
How to Assign Tasks to Team Members in SweetProcess
Open the procedure or process and then click on “Actions.”
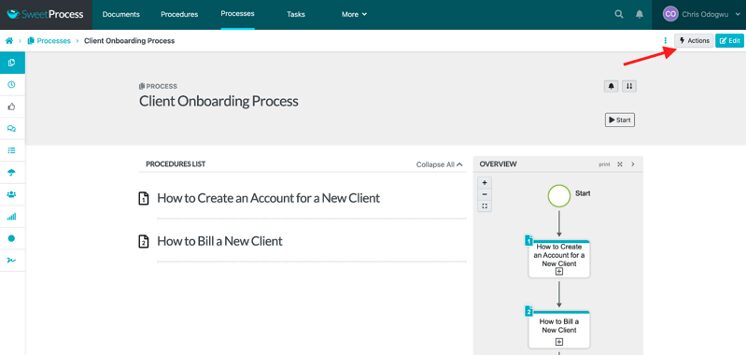
Click on “Assign as Task.”
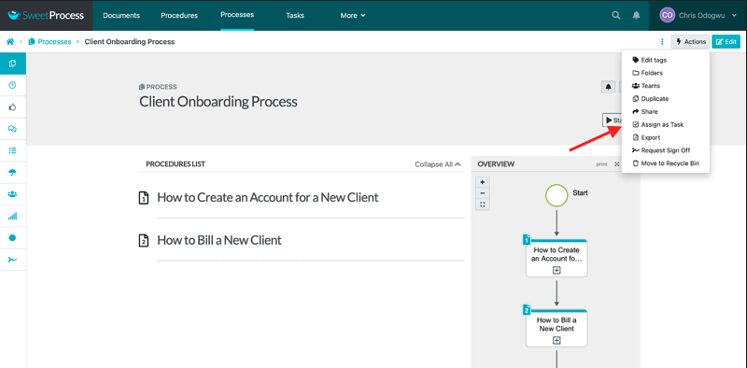
Click on “Assign.”
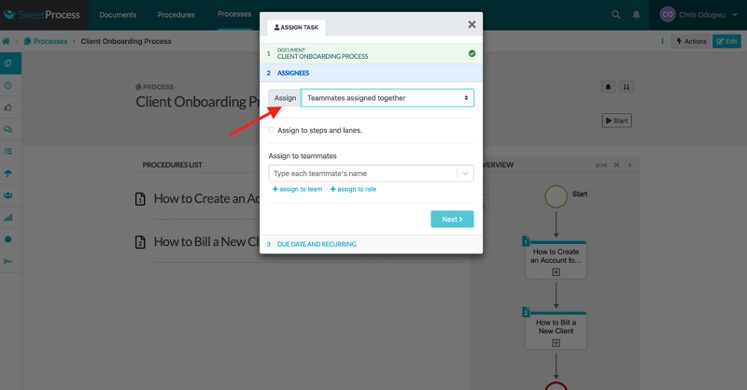
Click on “Teammates assigned together” or “Teammates assigned their own task” based on your choice.
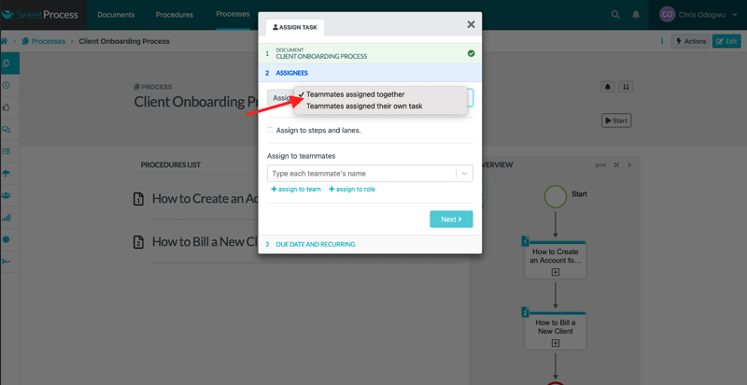
Select the teammate(s) from the drop-down menu.
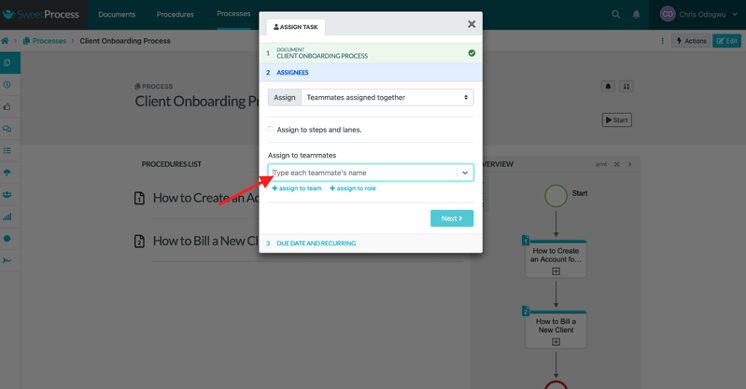
Enter the task due date, time, and frequency, and then click on “Assign Task.”
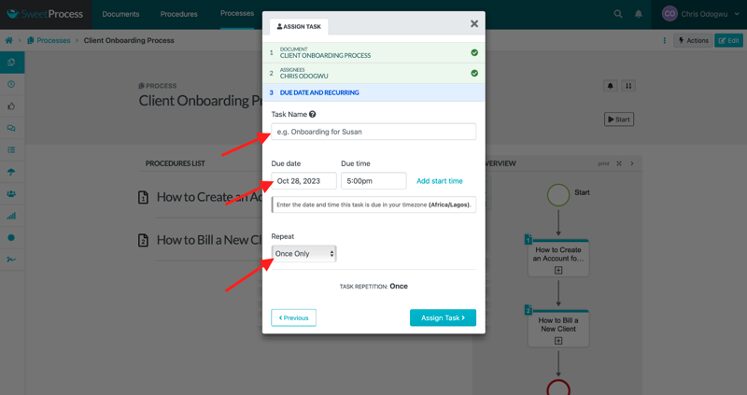
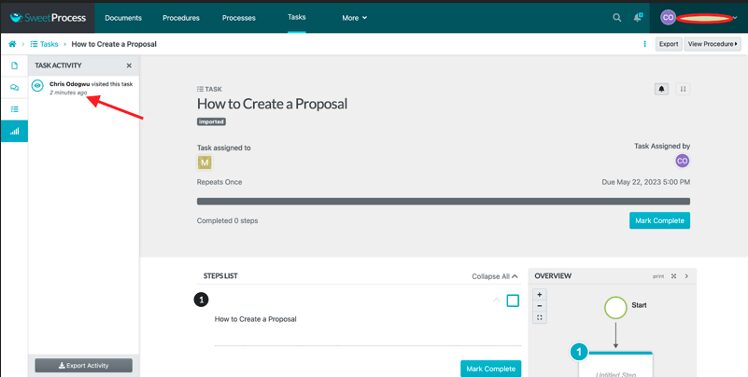
How to Track Ongoing Tasks in SweetProcess
Click on “Tasks” to view your active tasks.
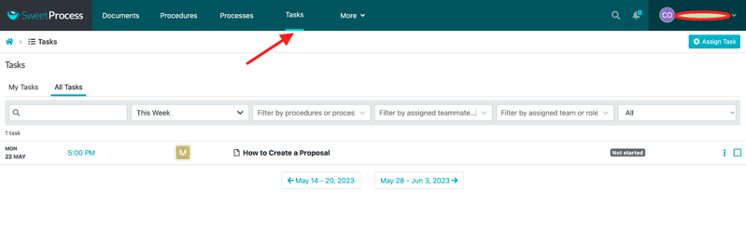
Click on a specific task.
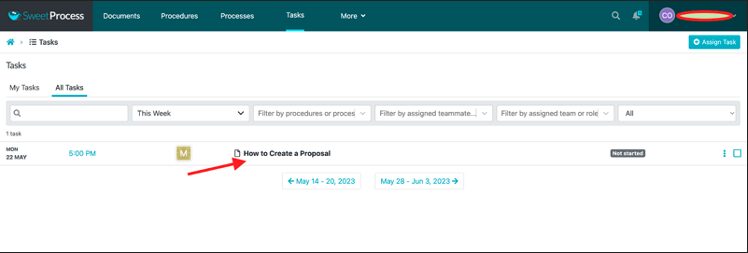
Click on the network bar signal on the left side of the page. Hover your mouse to reveal “Task Activity.”
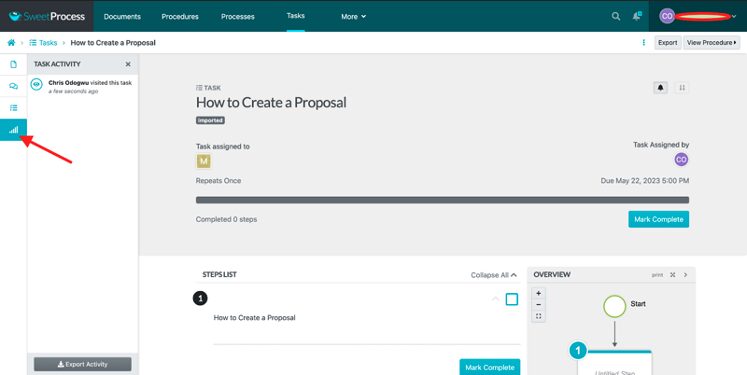
You’ll see a report of users who have engaged with the task and their engagement levels.
Private and Public Knowledge Bases
One of SweetProcess’ unique selling propositions as a QMS is its knowledge base which empowers employees at all levels with information to excel in their duties. It eradicates tribal knowledge as authorized workers can access information to perform certain tasks when employees responsible for those tasks are indisposed.
Organizations can also use SweetProcess as a knowledge base for their customers. They can create and publish documents offering valuable information to customers and other members of the public. This is a great feature for publishing frequently asked questions (FAQs).
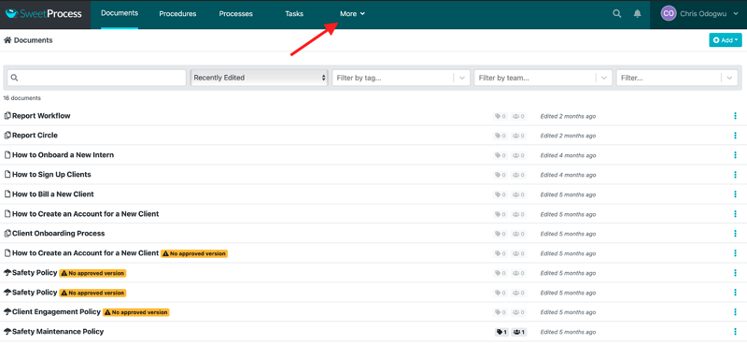
How to Create a Private Knowledge Base in SweetProcess
Click on “More” at the top and then click on “Knowledge Bases.”
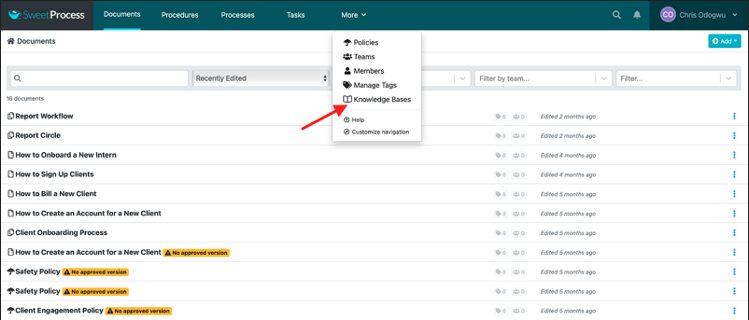
Click on “Create Knowledge Base.”
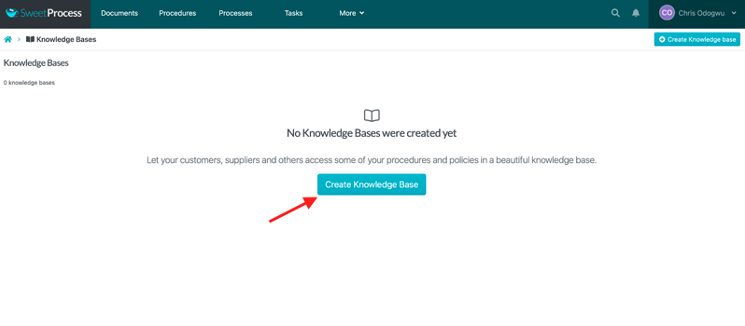
Enter the title of the knowledge base and click on “Continue.”
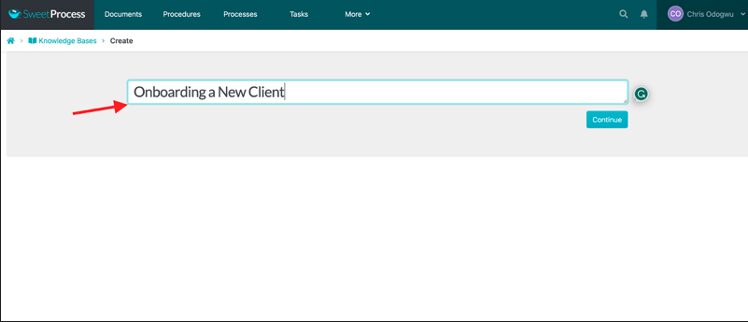
Click on the pencil icon beside the title.
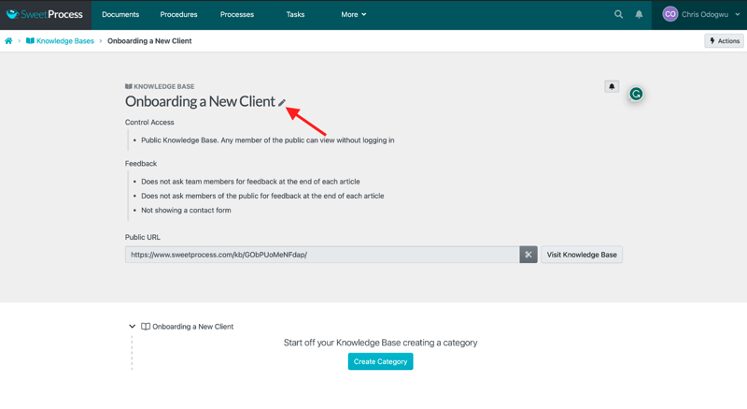
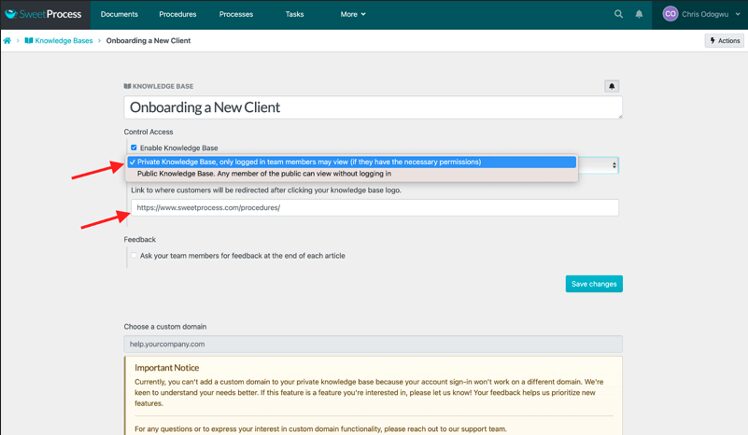
Click on the column below “Control Access” and select “Private Knowledge Base, only logged-in team members may view (if they have the necessary permission).”
Enter the URL you want team members to be redirected to when they click on the title of your knowledge base.
How to Create a Public Knowledge Base in SweetProcess
Click on “More” at the top and then click on “Knowledge Bases.”
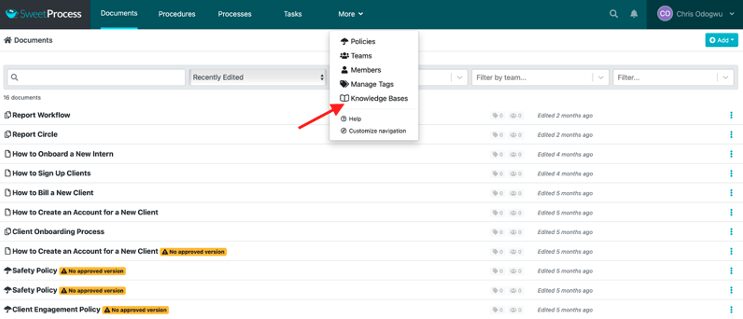
Click on “Create Knowledge Base.”
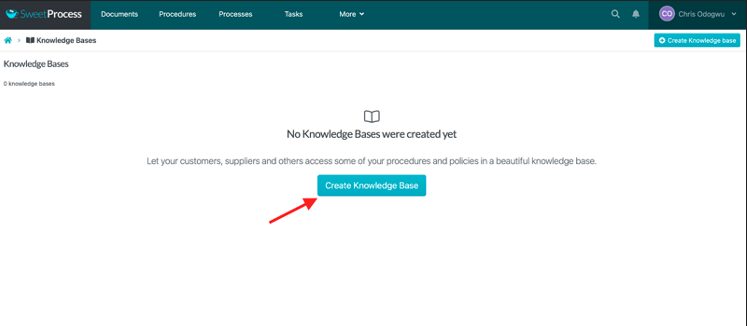
Enter the title of the knowledge base and click on “Continue.”
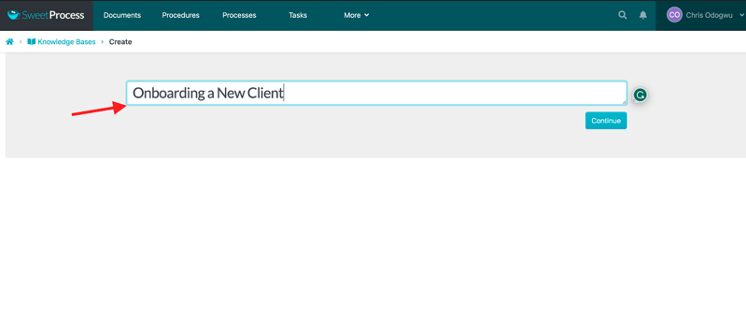
Click on the pencil icon beside the title.
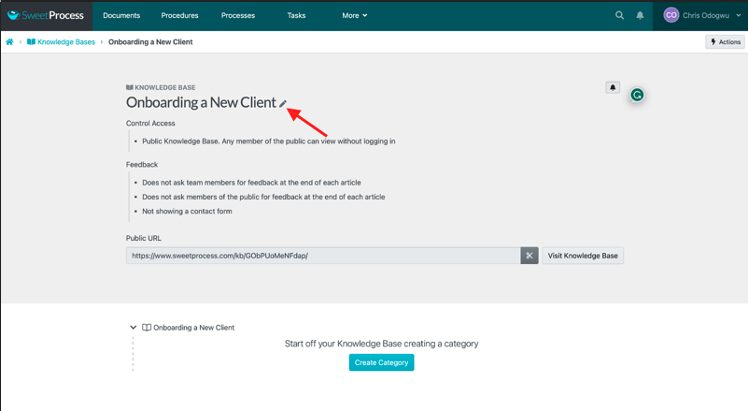
Click on the column below “Control Access” and select “Public Knowledge Base. Any member of the public can view without logging in.”
Enter the URL you want customers to be redirected to when they click on the title of the knowledge base.
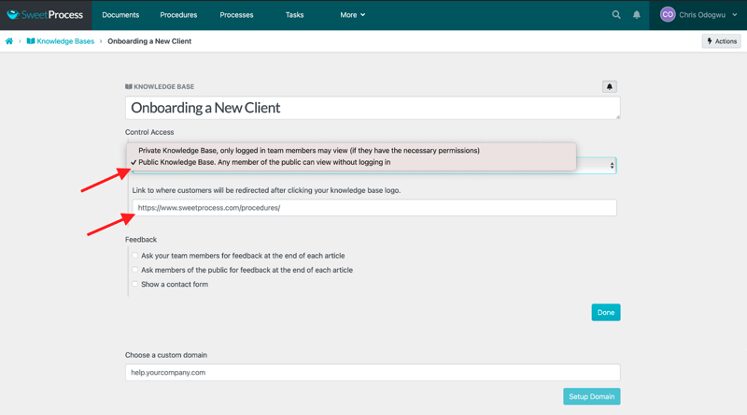
You can redirect customers to a custom domain if you want.
SweetProcess is suitable for organizations in all industries. Its flexibility allows customizing it to your unique business needs.
Why don’t you take a cue from other organizations and check it out? It’s even more flexible as you can sign up for a 14-day free trial with access to all its features at no cost without a credit card.
Principles of Quality Management System You Must Imbue in Your Organization
Quality management principles are beliefs that have been proven to enhance the validity of a quality management system. This set of principles was developed by the International Standard for Organizations (ISO), an authority in quality management.
Customer Focus
Most businesses operate to meet customer expectations. The demand for their products or services sustains them. Organizations must be deliberate in their customer satisfaction efforts to maintain long-term demand.
Understanding customer needs is the first step in customer satisfaction. This guides businesses in the right direction to offer products and services that customers are happy to patronize. Prioritizing quality in meeting those needs builds customer loyalty with a preference over competing brands.
Leadership
Every organized group or society needs to be united to achieve set goals. The leadership of an organization must build team spirit among employees and motivate them toward achieving the organization’s quality policy and objectives. This involves creating a conducive environment for team members to thrive.
Effective communication builds good relationships between staff and management. Employees feel left out if they are kept in the dark about developments in the organization and withdraw from active participation. They are inspired to work harder when they sense that their opinions matter.
Engagement of People
Activities and areas in the workplace are connected either directly or indirectly. It’s only a matter of time before underperformance in one department affects other departments. Engaging with people at different levels promotes meaningful contributions and generates higher value.
Engagement also entails delegating responsibilities to employees based on their expertise. Assigning teammates to their areas of strength builds their self-confidence and increases productivity. Create opportunities for collaborations where employees can work closely and realize their shared interests in attaining organizational success.
Process Approach
Performing business operations with standard processes generates consistent and measurable results. Organizations must shift from an operational model that relies on the expertise of individuals to thrive because it promotes tribal knowledge and slows growth.
A quality management system establishes the relationship between processes. This allows for predicting how processes connect. Understanding that a single process affects the entire workflow encourages management to take processes more seriously. This prevents redundancy and saves costs.
Improvement
Cultivating a culture for continuous improvement opens businesses to endless possibilities and opportunities. The zeal to improve current performance eradicates complacency by identifying and resolving deficiencies that would have jeopardized the workflow.
Prioritizing improvement enables companies to identify growth opportunities and adapt to developments in their industries for favorable outcomes. This proactiveness gives them a competitive edge as they can better navigate challenges that may take their competitors by surprise.
Evidence-Based Decision-Making
Evidence-based decision-making reduces negative outcomes to the barest minimum. Organizations sometimes need to make decisions quickly to address urgent situations. A QMS establishes decision-making models that encourage choosing the best alternatives based on data. This enables them to respond to situations swiftly, considering all aspects.
The decision-making models in a QMS emphasize cause-effect relationships. Available data shows the outcomes of options on the table. Decision-makers can weigh the risks associated with all outcomes to determine the best alternative.
Relationship Management
There’s hardly an organization that operates in isolation. Businesses engage one another to meet some of their needs. The relationship an organization cultivates with its suppliers and other interested parties impacts its operations either negatively or positively. A QMS promotes a deliberate attempt to build and sustain cordial relationships with associated entities. This ensures that a business can access external resources and collaborate with others in executing valuable projects.
Relationships between organizations thrive on value. A business must identify the value it offers and recognize the value it benefits from other businesses. Such values can be long-term or short-term, depending on their needs.
Skyrocket Your Business Operations With Quality Management Systems
Organizations must play to their strengths to succeed in today’s competitive market. Several other businesses are offering the same products or services as you, so you must stand out to thrive.
Implementing a quality management system can be daunting if you have no help and have to do everything from scratch. SweetProcess offers the help you need.
Automatically creating content with SweetAI for your policies and procedures is a game-changer—it frees up your time to be more productive.
High quality is assured when you pay attention to the little details. Capturing every single important detail in SweetProcess and availing it to teammates reduces errors to the barest minimum.
Don’t take our word for it—sign up for a 14-day free trial without a credit card and confirm it yourself.
