Last Updated on May 1, 2025 by Owen McGab Enaohwo

In today’s fast-paced business world, staying ahead means constantly reevaluating and improving how we do things. Business process reengineering (BPR) involves breaking down and rebuilding an organization’s workflows and systems for peak efficiency. It’s an essential move for businesses seeking strategic improvements in performance and customer satisfaction.
Read on to discover how BPR can help revolutionize your organization. Embrace change, enhance productivity, and stay ahead in a competitive marketplace. Ready to start your journey toward streamlined success? Sign up now without a credit card and explore how SweetProcess can be your perfect partner in this transformative journey.
Table of Contents
What Does Business Process Reengineering Really Mean?
Benefits of Business Process Reengineering for an Organization
How to Implement Business Process Reengineering for Your Organization in 6 Steps
How to Manage Your Company’s Business Processes Using SweetProcess
7 Core Principles of Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
Business Process Reengineering Examples From Which You Can Learn
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) Methodologies
Reengineer Your Business Processes Using SweetProcess
What Does Business Process Reengineering Really Mean?

Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is a fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes. This is to achieve significant improvements in crucial present-day measures of performance such as cost, quality, service, and speed. It goes beyond tweaking existing methods or making minor improvements; it’s a profound change, a reinvention of how work is done.
Imagine a company’s workflow as a river. BPR is not about directing the river through small channels or cleaning up the water; it’s about rerouting the river entirely or finding a new source. It involves looking at the very essence of the company’s processes and asking: “If we were to start over today, knowing what we know now, how would we design this process?”
This approach helps identify and eliminate redundant tasks, streamline workflow, and align business needs with the processes more effectively. The concept is particularly relevant in today’s fast-evolving business landscape. Organizations often discover once efficient processes need to be updated. This is primarily due to considerable technological advancements, market shifts, or even internal changes.
BPR allows companies in these situations to step back and revamp every process to better align with their current objectives and market realities. It is a bold strategy, but when executed well, it can result in extraordinary gains in efficiency as well as performance, fundamentally modifying the competitive position of an organization.
For instance, a car manufacturer might use BPR to overhaul their outdated assembly line in the automotive industry. Instead of minor tweaks, they could implement a complete redesign with advanced robotics, significantly cutting production time and costs while enhancing vehicle quality.
Similarly, a healthcare center could transform its operations through BPR, not by small steps like retraining staff but by overhauling the entire service delivery and introducing automation. Introducing software like SweetProcess can streamline everything from patient onboarding to care coordination processes. The streamlined workflows improve operational efficiency and the overall patient experience.
Benefits of Business Process Reengineering for an Organization

Business process reengineering (BPR) offers many benefits to organizations, fundamentally reshaping how they operate and compete in the marketplace.
Increases Efficiency and Speed of Business Operations
BPR often leads to more streamlined processes. By reevaluating and redesigning the workflow, unnecessary steps are eliminated and operations become more efficient. For instance, a company might integrate new technology to automate specific processes and tasks. This speeds up the workflow and reduces manual errors.
Eliminates Unproductive Business Activities
BPR helps identify and get rid of redundant and non-value-adding activities. This pruning of unnecessary tasks saves time and resources, leading to a leaner, more focused operation.
Establishes Clear Ownership of Processes
BPR clarifies roles and responsibilities by redesigning inefficient processes. This clear delineation ensures that every team member knows what they’re accountable for. This leads to better coordination and execution of tasks.
Improves Business Performance and Employee Productivity
Enhanced processes result in improved performance. Employees will spend less time on redundant tasks and more on value-added activities. This boosts employee productivity and, in turn, enhances overall business performance.
Reduces Operational Costs
Streamlining processes via BPR often leads to significant cost savings. Organizations can cut operational expenses by doing away with unnecessary steps, reducing time on tasks, and improving resource allocation.
Improves Competitive Advantage
A perfectly executed BPR strategy can give a company a significant edge. By operating more efficiently and effectively, the company can offer better products or services, respond quickly to market changes, and innovate more rapidly.
Improves Customer Satisfaction and Retention
When processes are efficient, the quality of products or services significantly improves. This enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, as customers enjoy better experiences and value.
Simplifies Operations and Processes
BPR often results in simpler, more straightforward processes. This simplicity makes it easier for employees to understand and execute their tasks and for the management to continually monitor and improve these processes.
How to Implement Business Process Reengineering for Your Organization in 6 Steps

Implementing business process reengineering (BPR) in your organization requires a structured approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to transforming your business processes for maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Diagnose the Existing Problems in Your Business
Start with a deep dive into your current processes. Dissect each process to find inefficiencies such as quality setbacks, cost issues, and delays or bottlenecks that are holding you back.
Beyond identifying obvious issues, this step involves understanding the underlying causes of these problems, ranging from outdated processes and technology to inefficient workflow designs.
Identify gaps and improvement opportunities
Having identified the problems, pinpoint the disconnects in your processes. This stage is about mapping the distance between your current state and where you aspire to be, finding key areas ripe for significant improvement. Leveraging Process Improvement Methodologies, such as Lean, Six Sigma, or process mapping, can help systematically uncover inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and non-value-adding steps within your workflows. This is a chance to reimagine processes to address current shortcomings and position the organization for future challenges and opportunities.
Develop and Test Your Hypothesis
Approach improvements like a scientist by creating hypotheses for improved processes. Experiment with these ideas within smaller settings to check their impact and feasibility. Validating their effectiveness will go a long way in helping you make clear-cut decisions on the next steps to take without disrupting the entire system.
This involves iterating different approaches, refining ideas based on feedback, and identifying the most viable solutions for broader implementation.
Design a Cutting-Edge, Future-State Process Map
Draft a detailed map or blueprint of your envisioned future process with insights derived from the previous steps. This blueprint should clearly illustrate every step of the new, streamlined process.
The design phase goes beyond plotting each process step but also considers how these steps interact and contribute to the overall organizational goals. It’s a comprehensive approach that looks at the process from micro and macro perspectives.
Implement the New Process
Carefully roll out the new process, ensuring your team is well-prepared. This phase is akin to piloting a ship through new waters, requiring careful navigation and adjustment. Once again, all team members must be on board, well-trained to navigate the change and understand their roles in the new system.
A great automation tool is invaluable for implementation. The first step is to sign up for SweetProcess for a smooth transition.
Evaluate Performance
Lastly, analyze the performance of this new process. Regularly review how the new process functions, identifying areas for continuous improvement and fine-tuning.
This phase should involve feedback loops where insights gained from monitoring KPIs, or metrics, are used to refine further and optimize the process. It’s a commitment to ongoing improvement and excellence.
Each step is crucial for a successful BPR implementation, significantly improving organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Manage Your Company’s Business Processes Using SweetProcess
SweetProcess emerges as a transformative tool, offering a comprehensive solution for managing and reengineering business processes. SweetProcess stands at the forefront of digital transformation, providing a user-friendly platform designed to empower organizations in their quest for operational excellence.
How to Create a Business Process on SweetProcess

Creating a process for your business on SweetProcess is quite easy. ShipCalm, an expanding e-commerce fulfillment company, successfully tackled its growth pains by turning to SweetProcess for process streamlining. Leveraging SweetProcess’s user-friendly platform, ShipCalm initiated its business process reengineering.
In a strategic move to address its growth-related challenges, ShipCalm embraced SweetProcess, ensuring its operational expansion met with optimized and synchronized business processes. The seamless integration of SweetProcess allowed ShipCalm to navigate its growth pains effectively and establish a standardized workflow that can adapt to future scalability, demonstrating the platform’s efficacy in facilitating business process optimization for growing enterprises. To take a cue from ShipCalm, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a process using SweetProcess:
1. Access SweetProcess Dashboard:
Log in to your SweetProcess account and navigate to the dashboard.
2. Navigate to Processes:
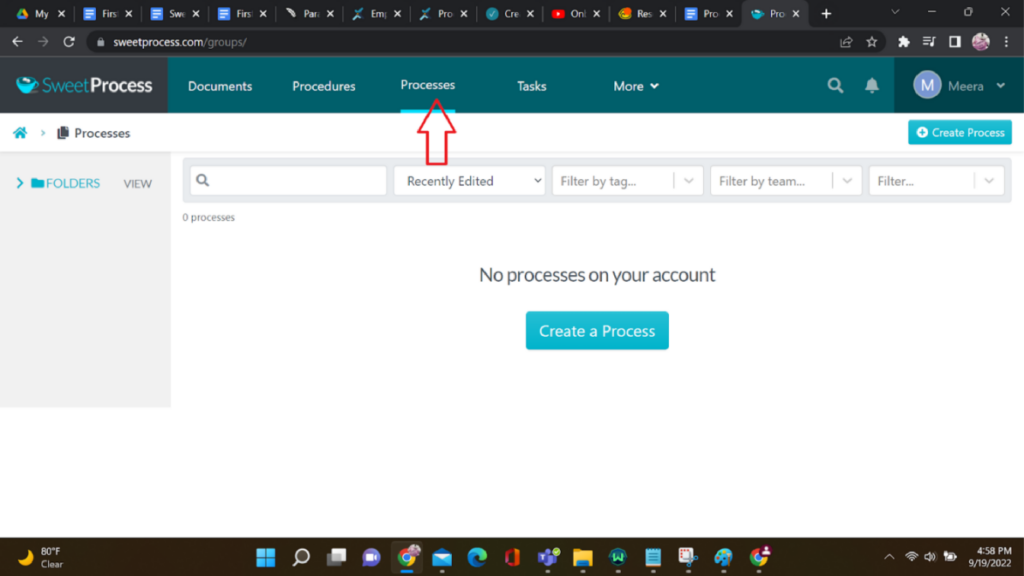
Look for the dedicated “Processes” button on the dashboard. Click on it to initiate the creation of the process.
3. Create a New Process:
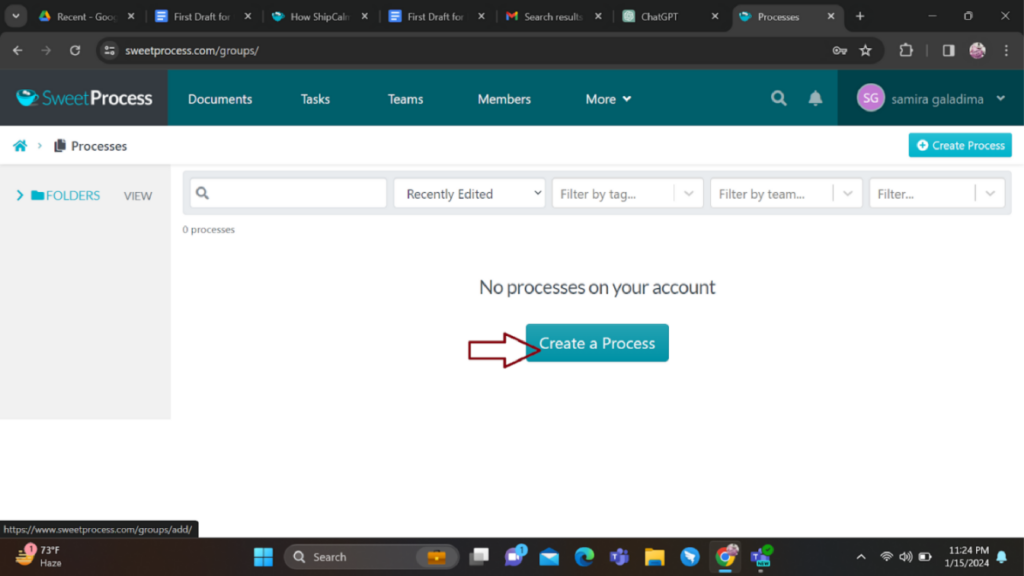
Within the “Processes” section, locate the option to create a new process. Click this button to begin.
4. Title and Description:
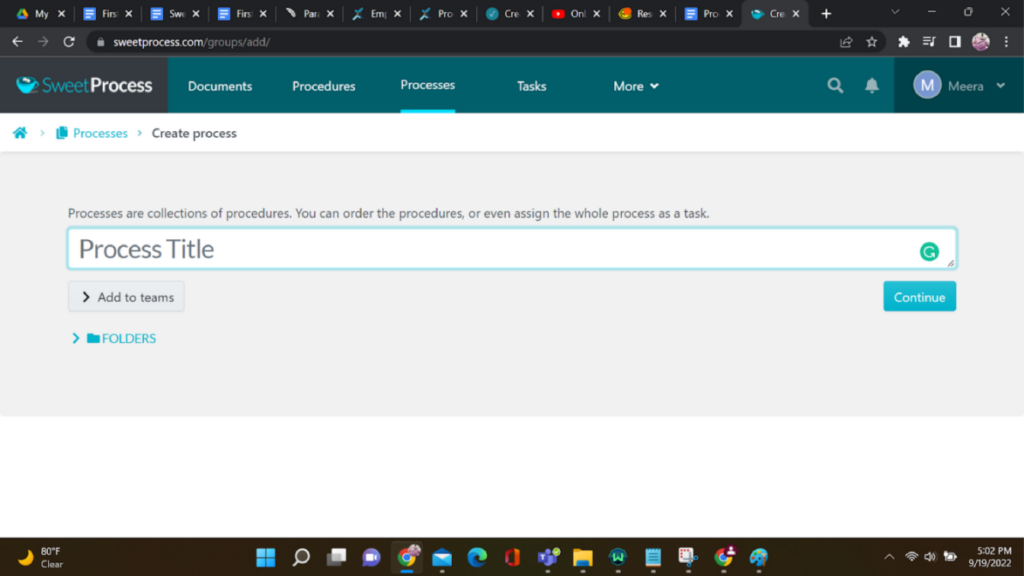
Provide a title and description for your process. Make sure they are clear and concise. After entering the details, click “Continue.”
5. Add to a Team:
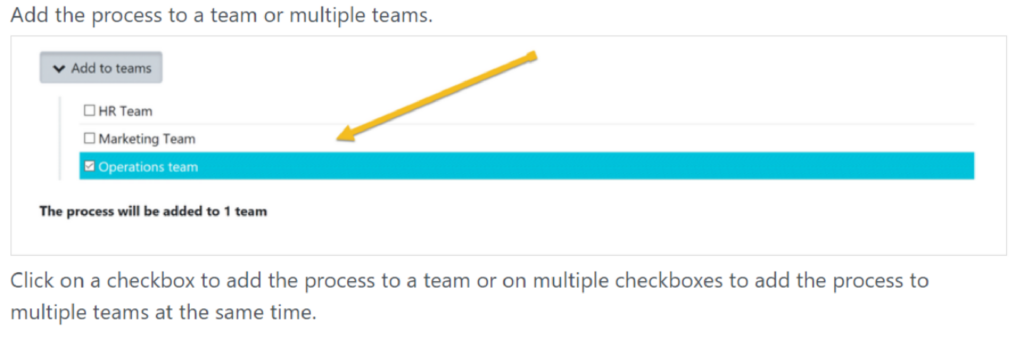
Specify the team to which this process belongs. This helps in organizing and categorizing processes effectively.
6. Additional Description:
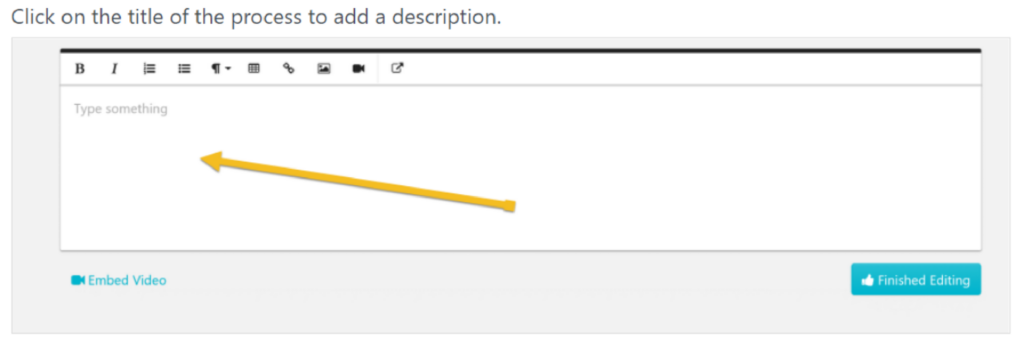
For easier identification, add a description to the title. This could be additional information that gives more context about the process.
7. Add Steps:
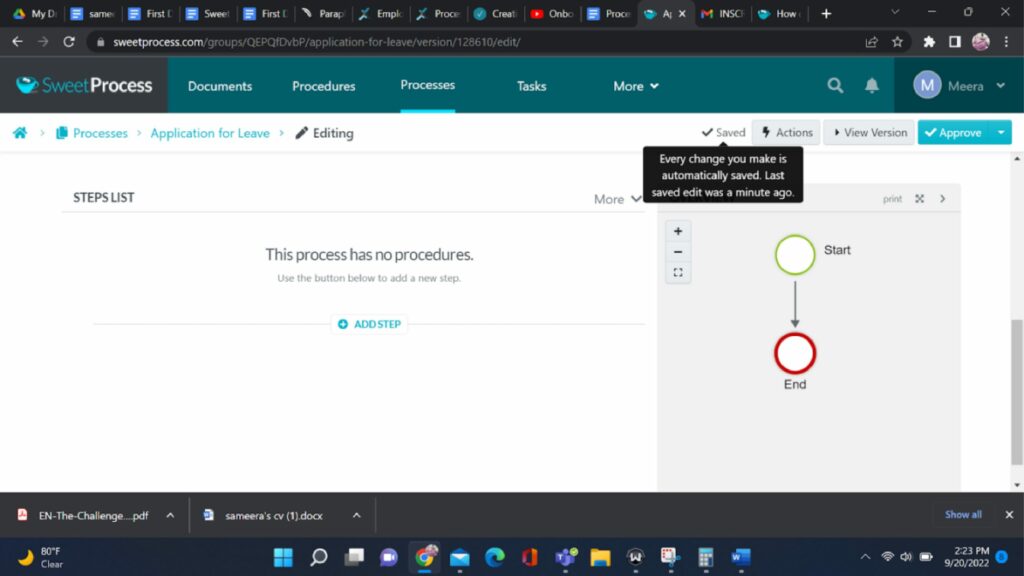
Start adding steps to your process by clicking the “Add Step” button. You can add as many steps as needed. Include a title and description for each step and attach relevant files or images. Additionally, you can assign the step to a specific team member or department.
8. Order and Edit Steps:
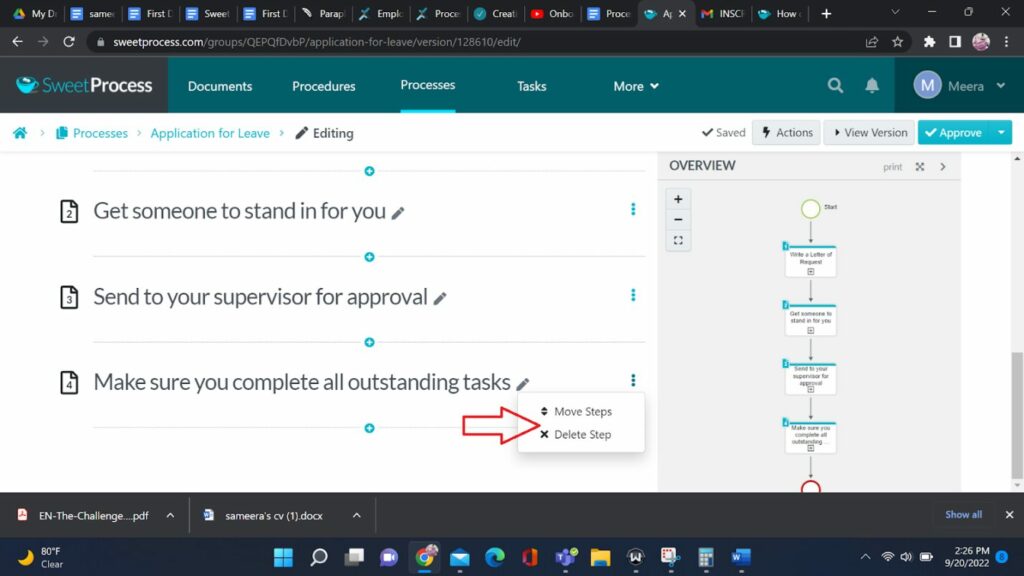
SweetProcess provides flexibility in reordering steps. You can easily move steps around to achieve the desired sequence. Delete any steps that you feel are unnecessary.
9. Review and Finalize:
Take a moment to review the entire process. Ensure that all steps are clear and well-defined. Edit as needed to enhance clarity.
10. Publish the Process:
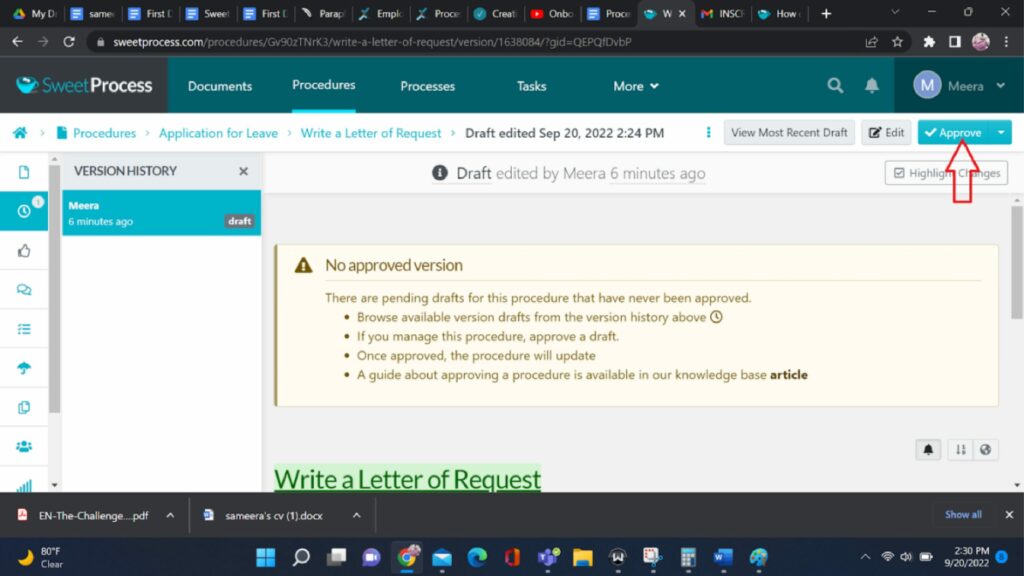
Once you’ve added all the necessary steps and reviewed the process, it’s time to make it live. Click the “Approve” button or a similar option. Your process is now published and visible to team members.
11. Final Confirmation:
Confirm that your process is now live and accessible to the designated team.
12. Completion:
Congratulations! You have successfully created your first process on SweetProcess. Your team can now follow this standardized workflow for efficient operations.
How to Create a Procedure Using SweetAI

Select the procedure tab on the dashboard or from the “More” dropdown menu.
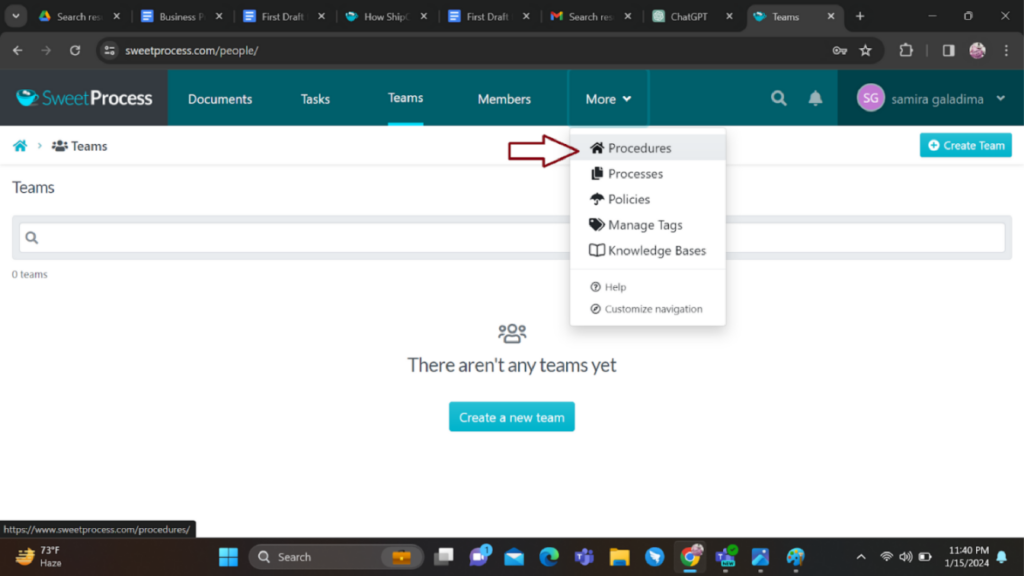
Include the title of the procedure and select “Write with SweetAI” as indicated below. You will also receive suggestions for common procedures in your business industry.
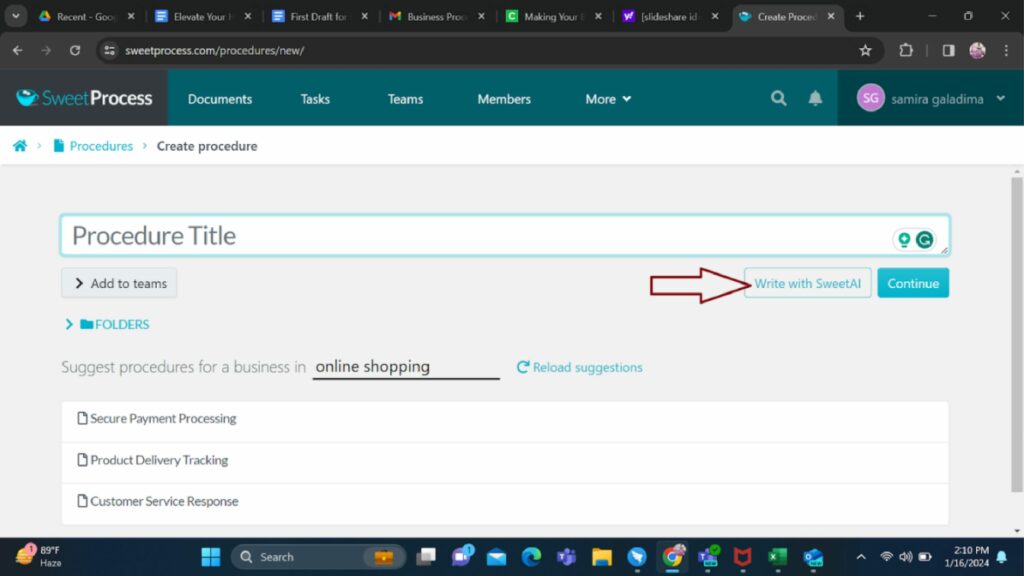
Next, you have a well-written procedure. You may decide to edit by clicking on the pencil icon and adding more steps or leave it just as it is.
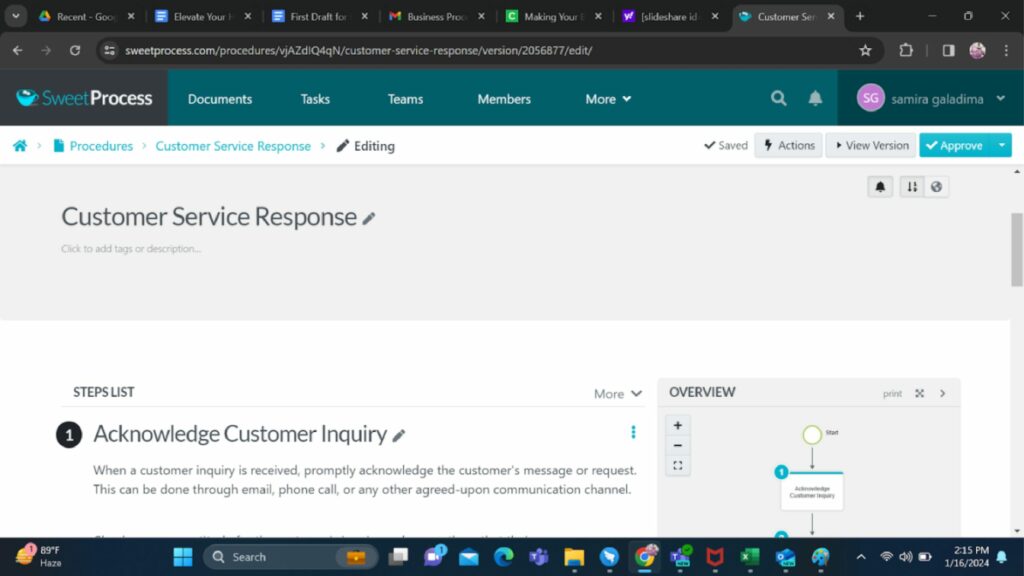
There you have it, with your flowchart (a visual representation) on the side of the screen. The flowchart allows you to view the workflow for easy understanding.
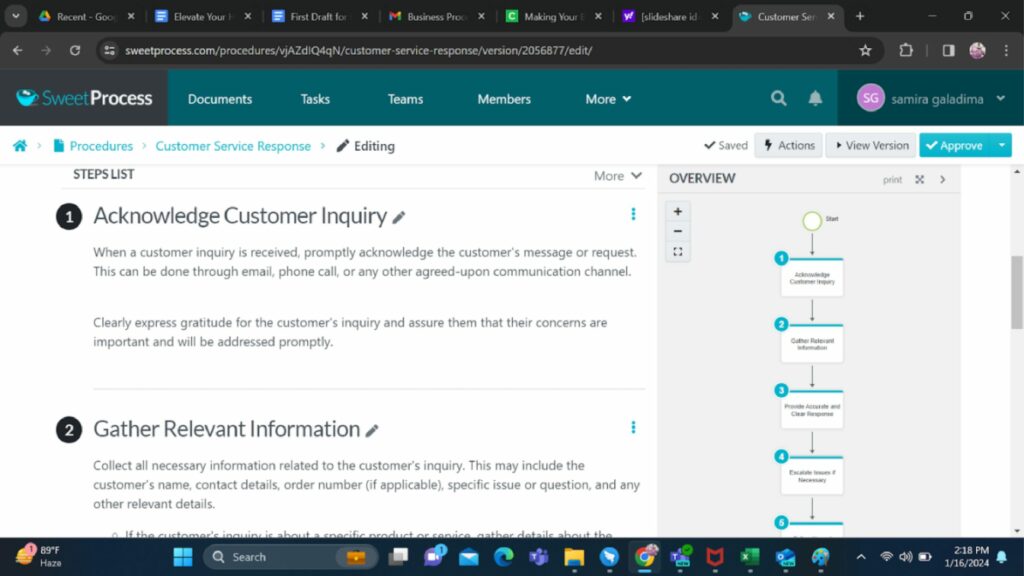
How to View the Version History of a Process in SweetProcess

SweetProcess allows you to view the history of all activities carried out on a process. You have the liberty to see who did what and when, and this increases accountability. Stone & Wood, a brewing company, needed help updating work procedures and processes once they found SweetProcess.
SweetProcess significantly transformed Stone & Wood’s operations, addressing challenges in onboarding, process updates, knowledge distribution, and compliance. The platform streamlined employee onboarding, making tasks and learning more efficient. Mobile functionality simplified on-the-spot process updates, while its role as a centralized knowledge base improved information accessibility.
The sign-off feature enhanced communication transparency. SweetProcess also facilitated regulatory compliance, providing evidence of employee training. In summary, SweetProcess emerged as a comprehensive solution, enhancing efficiency across various operational facets for Stone & Wood.
You may also tap into these features by following these steps to view version history when using the tool. Start by clicking the clock icon on the left side of the screen, as shown below.
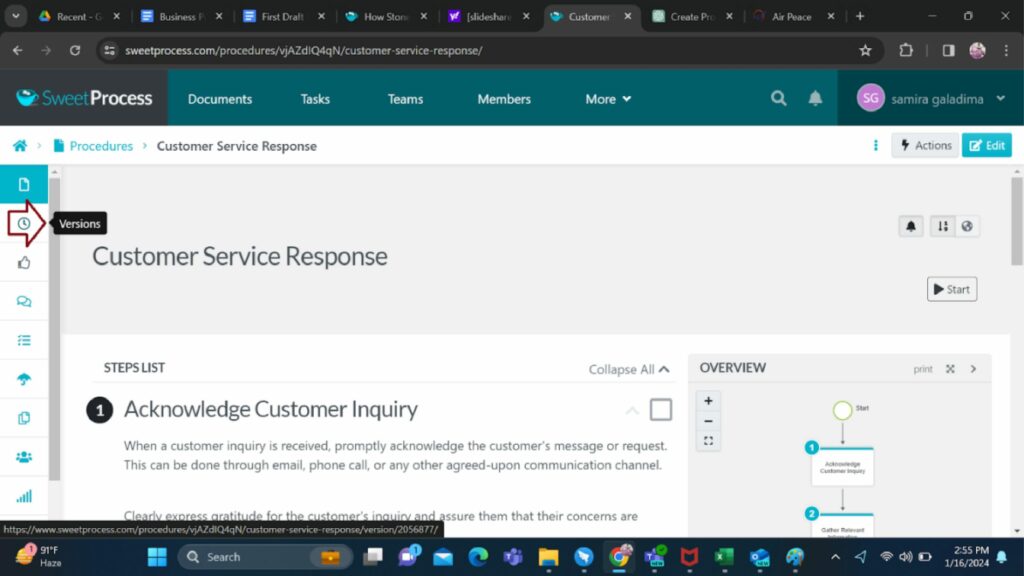
This shows you the live and draft versions and the time the drafts and approvals were made. However, if you do not like the approved version, you can undo it and go back to drafts. This ensures that you have the flexibility to amend your procedures seamlessly.
Organizations have been turning to SweetProcess to help them with business process reengineering. One such is Rise25, which looked to SweetProcess software to restructure its workflow. The team was astounded by how simple it was for them to design and administer procedures with the program. Co-founder of Rise25, Dr. Jeremy Weisz, attested that SweetProcess made it easier for staff members to locate items and helped them manage their standard operating procedures.
The group discovered that the software made it simple to set goals and monitor their advancement. They found it simple to maintain everyone’s focus and guarantee that projects were finished on schedule as a result.
According to Jeremy, peace of mind was the game-changer. They were no longer concerned about an employee misplacing some paperwork because everything was automated. Click here to sign up for a free trial of SweetProcess.
Further Reading: 11 best SOP software & tools to manage your operations
7 Core Principles of Business Process Reengineering (BPR)

These seven core business process reengineering (BPR) principles are essential guidelines that help organizations radically rethink and redesign their processes.
Here’s an overview of each principle:
Principle 1: Organize around outcomes, not tasks
Beyond just focusing on the outcome, this principle requires a fundamental shift in organizational mindset. It means defining roles and responsibilities not by the tasks employees perform but by the results they are responsible for.
This approach encourages a more results-oriented culture within the organization, fostering greater accountability and clarity in achieving business objectives.
Principle 2: Identify all the processes in an organization and prioritize them in a redesign urgency order
After identifying all processes, the next step involves evaluating their impact on the organization’s strategic goals and customer satisfaction. Processes with the greatest impact on these areas should be prioritized for redesign.
This systematic approach ensures that the most critical processes are optimized first, leading to more effective and immediate improvements in overall performance.
Principle 3: Have those who use the output of the process perform the process
BPR advocates for process ownership by those who directly benefit from or use the output of the process. This principle emphasizes that individuals who understand the needs and expectations of end users are best suited to drive improvements in the corresponding processes.
Principle 4: Treat dispersed resources from various areas as though they were centralized
Centralization enables better utilization of resources, as it allows for more efficient allocation and management. BPR allows organizations to leverage technology and communication tools to treat geographically dispersed resources as if they were centralized.
This reduces redundancies and operational costs. It also promotes a unified organizational strategy, as resources from various departments are aligned toward common goals.
Principle 5: Link activities that are parallel in the workflow
BPR encourages connecting similar activities to create a more cohesive and efficient workflow. This principle aims to synchronize parallel tasks to minimize idle time and ensure a continuous workflow.
It’s about creating synergy between simultaneous processes and enhancing the overall speed and efficiency of operations. By focusing on the flow of activities, organizations can avoid bottlenecks and improve overall process speed.
Principle 6: Make performance the ultimate decision point and build control into the process
BPR recommends decentralizing decision-making to the point where the work is performed. This principle empowers front-line employees to make decisions based on their expertise, reducing bureaucracy and facilitating quicker response times. Simultaneously, building control mechanisms directly into the process helps maintain consistency and quality.
Principle 7: Get information once and at the source
Implementing this principle minimizes errors and misinformation that often arise from multiple data entries. It ensures that the data is accurate and reliable, which is crucial for making informed decisions. This approach also streamlines data collection and processing, saving time and reducing employee workload.
These principles are not just theoretical concepts; they are practical guidelines that, when implemented effectively, can significantly improve how an organization functions, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving service delivery.
In other words, these principles help create a robust framework for business process reengineering.
Business Process Reengineering Examples From Which You Can Learn

Various companies across different industries have effectively implemented Business Process Reengineering (BPR). Here are some real-life examples that illustrate how BPR can transform business operations:
1. Ford
Before BPR, Ford’s accounts payable system needed to be more efficient and staff-heavy. Implementing BPR, they re-engineered the process, adopted a new database system, and eliminated data entry redundancies. Post-BPR, Ford significantly reduced its workforce in this department while improving efficiency and accuracy in its accounting processes.
Also, in the 1990s, Ford Motor Company struggled to keep up with global competitors such as Toyota and Honda. Ford was dealing with several supply chain issues. Extended lead times, elevated inventory costs, and a need for clearer visibility into supplier performance were among the primary concerns.
These factors impeded Ford’s ability to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands, putting it at a disadvantage against more agile competitors. Ford turned to business process reengineering (BPR) initiatives to enhance its competitive edge, aiming to streamline operations and cut costs.
This was done by adopting the Ford Production System (FPS), a new strategy designed to overhaul Ford’s operations. The FPS was instrumental in reducing lead times and inventory costs while enhancing supplier performance.
Additionally, it improved transparency across the supply chain, enabling Ford to be more responsive to shifts in customer demand. The impact of these changes was significant. Ford not only achieved increased efficiency in its operations but also saw improvements in customer satisfaction.
This strategic move helped Ford boost its profitability and solidify its position in the highly competitive automobile market. Through these BPR efforts, Ford demonstrated how rethinking and reinventing internal processes could lead to substantial business improvements and success in a dynamic industry landscape.
2. Amazon
Amazon’s inventory management initially took a lot of work, leading to delays and inefficiencies. The company revolutionized its warehousing and distribution processes through BPR, introducing advanced automation and AI. This transformation led to faster order processing, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Amazon has transformed its operations using cloud technology and big data, creating a unique business model that embraces automation and continuous adaptation to customer needs.
Amazon’s automated marketing tailors recommendations to individual customers’ behaviors, enhancing the shopping experience with personalized suggestions.
Now an e-commerce leader, Amazon has expanded into logistics, data storage, and payment services. With 85 million Amazon Prime subscribers in the US alone, calling Amazon just an e-commerce company is an understatement. Its continued growth offers valuable lessons to businesses in all sectors.
3. Taco Bell
Taco Bell’s growth trajectory from a $500 million business in 1982 to a $3 billion empire in the early 1990s is a testament to the power of business process reengineering (BPR). The company completely revamped its business model, shifting focus to retail service and centralizing food preparation.
Introducing the K-minus program meant that ingredients were prepped in central kitchens and assembled at restaurants upon order, streamlining the service.
The reengineering efforts addressed several issues Taco Bell was facing:
● The company tackled the issue of an unclear business vision by completely reorganizing its HR department.
● The operational system underwent a dramatic redesign, shifting the focus from processes to customer satisfaction.
● The management structure was simplified by replacing area supervisors with market managers and reducing their number, leading to a leaner, more responsive management team.
● In a bold move, the kitchen’s physical space was reduced from 70% to 30%, while customer space was increased accordingly, doubling the seating capacity.
● This structural change allowed for a greater focus on customer service, as resources were reallocated from kitchen space to areas that directly impact customer experience.
Post-BPR, Taco Bell enjoyed many improvements, including better employee morale and increased customer focus. Quality control was tightened, resulting in fewer accidents and injuries and more significant savings for the company.
The changes allowed Taco Bell to save on operational costs and invest more resources into enhancing customer service, which played a significant role in the company’s impressive growth.
4. IBM Credit Corp
IBM Credit, the financial arm of IBM Corporation, revolutionized its application processing by streamlining the procedure that once took up to two weeks into a mere 90-minute task. The revelation that applications were merely idling on desks for most of the processing time prompted a radical reengineering.
They replaced the previous system, where four specialists handled different application stages, with a “deal structurer”—a generalist equipped with a new computer system that consolidated all necessary tools and data. This system expedited routine applications and maintained specialist support for complex cases.
The transformation led to remarkable outcomes. The turnaround time for applications plummeted from an average of seven days to just four hours. Moreover, without expanding their staff, IBM Credit experienced a surge in productivity, now handling a volume of credit applications a hundredfold greater than before the BPR initiative.
This case clearly demonstrates how rethinking and retooling business processes can lead to extraordinary gains in efficiency and output.
5. Hallmark
Previously, Hallmark’s process for launching new products to the market typically spanned three years. As they identified more specific market segments, Hallmark’s leadership realized the need to overhaul their product development approach. They set an ambitious target through reengineering: cutting down the development cycle to just one year.
Upon scrutinizing their process, Hallmark discovered that a significant portion of the product cycle—about two-thirds—was consumed in the planning and conceptualization phase, contrary to the earlier belief that most time was spent on printing and production. It turned out that the concepts were mostly idling, waiting for creative staff to finalize new iterations.
The transformation that followed was impactful. Hallmark formed a cross-functional team dedicated to product development, which led to more efficient and streamlined operations. In 1991, this strategic change bore fruit as Hallmark successfully launched a new line of cards in just eight months, well ahead of the usual schedule.
This significant reduction in time to market marked a notable achievement for Hallmark, showcasing the effectiveness of business process reengineering in speeding up product development and adapting to market needs more rapidly.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) Methodologies
Business process reengineering (BPR) has several methodologies that guide organizations through the radical transformation of their processes. Each offers a unique perspective on deconstructing and reconstructing workflows for optimum performance.
1. Hammer/Champy Methodology
Michael Hammer and James Champy’s BPR methodology is considered a cornerstone in this field. They argue for fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements.
This approach calls for discarding old systems and starting afresh, focusing squarely on the processes and customer satisfaction, often using technology as a critical enabler.
This principle champions innovation and encourages companies to harness new technologies to facilitate transformative changes, leading to a more agile and customer-centric business model.
2. The Davenport Methodology
Thomas Davenport’s methodology places information technology at the heart of BPR, seeing it as an essential tool for enabling significant business transformation.
Rather than broad, sweeping changes, Davenport advocates for focusing on specific, strategic business outcomes and making incremental changes that can be built upon over time.
This method allows businesses to evolve with technology, applying incremental changes that collectively result in significant transformation without disrupting a complete overhaul. It’s an approach that aligns closely with the continuous improvement philosophies found in methodologies like Kaizen, focusing on evolution rather than revolution in business processes.
3. Manganelli/Klein Methodology
Developed by Raymond Manganelli and Mark Klein, this methodology emphasizes speed, advocating for rapid BPR. It’s about quickly identifying and eliminating non-value-adding activities and streamlining processes for immediate improvements.
This action-oriented approach aims to deliver quick wins and maintain momentum in the process transformation journey.
The Manganelli/Klein methodology encourages organizations to act decisively, removing procedures that don’t add direct value and swiftly implementing streamlined workflows. This strategy aims to achieve rapid results, injecting energy and focus into BPR initiatives.
It’s well-suited for businesses that need immediate performance uplifts and can quickly adapt to new, more efficient ways of operating. By securing early successes, this approach helps to build confidence in the BPR process and galvanizes the organization toward further change.
4. Kodak methodology
Emerging from Eastman Kodak’s practical experience with BPR, their methodology stresses the importance of process ownership and collaborative, cross-functional teams.
By having clear process owners and involving employees from various departments, the Kodak approach ensures a holistic view when redesigning processes, which aids in achieving enduring process improvements.
Simultaneously, it advocates for collaboration among diverse teams, bringing together various perspectives and expertise. Such a structure ensures a comprehensive approach to process redesign, considering multiple facets of the business.
This methodology fosters a sense of accountability and encourages diverse insights, leading to sustainable and well-rounded improvements in business processes. It’s a testament to the value of inclusive and collaborative work cultures in driving successful organizational change.
Each methodology, with its distinct focus and strategies, provides organizations with various lenses through which to view their process reengineering efforts. Organizations may choose one or blend elements from several to suit their unique needs, ensuring a tailored approach to their BPR initiatives.
BPR vs. BPI vs. BPM vs. CI
| Aspect | Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | Business Process Improvement (BPI) | Business Process Management (BPM) | Continuous Improvement (CI) |
| Focus | Radical redesign of existing processes for breakthrough improvements | Incremental changes to enhance specific processes | Holistic management of processes to achieve organizational goals | Ongoing, gradual enhancements to processes |
| Scope of Change | Wide-ranging and transformative changes across the organization | Limited in scope, targeting specific processes or areas | Comprehensive, organization-wide improvement | Continuous, iterative improvements |
| Objective | Achieve radical improvements in efficiency, effectiveness, and competitiveness | Enhance specific processes to achieve better results | Align processes with organizational goals and improve overall performance | Sustain and enhance performance over time |
| Frequency of Change | Infrequent, undertaken as a major initiative with significant organizational impact | Occasional, as needed, based on identified improvement opportunities | Ongoing, adaptable to changing business needs | Continuous and part of the organizational culture |
| Approach to Technology | Embraces new and disruptive technologies for radical process redesign | Adopts technology to support incremental improvements | Leverages technology to manage and optimize processes | Integrates technology for continuous enhancements |
| Timing of Implementation | Typically, a one-time, major initiative with a longer implementation period | Implemented as needed, with shorter timelines for specific improvements | Ongoing and adaptable, with phased implementations | Continuous and embedded in day-to-day operations |
| Degree of Process Analysis | In-depth analysis of existing processes, often involving a complete rethinking of workflows | Analyzes specific processes to identify improvement opportunities | Comprehensive analysis of all processes, often utilizing BPM tools | Regular analysis with a focus on continuous optimization |
| Employee Involvement | Requires significant employee involvement and cultural change | Involves employees in specific improvement projects | Involves employees in process design and encourages continuous improvement mindset | Emphasizes employee engagement in improvement initiatives |
| Key Tools and Techniques | Process reengineering tools such as SweetProcess, change management methodologies | Lean Six Sigma, Kaizen events, process mapping tools such as SweetProcess | Performance measurement tools and BPM software automation tools such as SweetProcess | Lean, Six Sigma, Kaizen, Deming’s Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle tools such as SweetProcess |
This table provides a concise overview of the key differences between business process reengineering (BPR), business process improvement (BPI), business process management (BPM), and continuous improvement (CI). Each approach has its unique characteristics, focus, and methodologies, catering to different organizational needs and objectives.
Reengineer Your Business Processes Using SweetProcess

Reengineering your business processes can be a pivotal step toward significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and overall performance. SweetProcess offers an ideal platform to guide and facilitate this transformative journey for your business.
SweetProcess stands out with its intuitive tools designed to streamline the process of documenting, managing, and optimizing your business workflows. Its user-friendly interface simplifies mapping out existing processes, identifying inefficiencies, and envisioning new, more effective procedures. This clarity and organization are crucial for successful business process reengineering (BPR).
Moreover, SweetProcess excels in fostering collaboration. Allowing team members to contribute their insights and suggestions ensures that the reengineered processes are practical, efficient, and well-aligned with the team’s actual working dynamics. This collective approach enhances the quality of the redesigned processes and encourages buy-in and smoother implementation.
SweetProcess also provides robust tracking and reporting features. These tools enable you to monitor the effectiveness of your newly implemented processes and make ongoing adjustments. This continuous improvement aspect ensures that your BPR efforts deliver lasting benefits.
If you’re considering reengineering your business processes, SweetProcess is an invaluable tool. It’s tailored to support you at every stage of the process, from initial analysis to implementation and continuous improvement. Whether you’re aiming for a complete overhaul with BPR or prefer the route of continuous improvement, SweetProcess has the flexibility to adapt to your strategy.
Ready to take the first step in transforming your business processes? Sign up for a free trial of SweetProcess today and experience firsthand how it can enhance your business operations.
