Last Updated on November 24, 2024 by Owen McGab Enaohwo

Have you ever made a costly mistake because of failing to check and correct errors? Such errors can affect your business and lead to heavy losses. This is where quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) come in. But which of the two should you use in your organization?
For instance, your company needs to design a product. QA will be the architect developing the product blueprint. They outline the specifications, standards, and protocols for creating a high-quality product and establish the guidelines, ensuring that every aspect of the production process aligns with the envisioned outcome.
The QC comes in as the inspector on the assembly line. As the product takes shape, QC examines and tests each component against the predefined standards. This inspection process acts as the last checkpoint, verifying that the final product meets the quality benchmarks set by the QA team during the planning phase.
While QA and QC are frequently used interchangeably, they have key differences. In this article, we’ll examine what you should know about quality assurance versus quality control.
Looking to boost your quality management processes? You need a comprehensive solution like SweetProcess. Sign up for a free 14-day trial of SweetProcess today! No credit card is required!
Table of Contents
What Is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Quality Assurance (QA) Vs Quality Control (QC): Key Differences
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Focus & Goal
Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: Process & Orientation
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Roles & Responsibilities
Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control: Tools
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Duration & Timeline
Quality Assurance (QA) vs. Quality Control (QC): Similarities
Quality Assurance (QA) vs. Quality Control (QC): Examples From Which You Can Learn
How to Improve Your Company’s Quality Assurance and Control Using SweetProcess
Benefits of Implementing Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) in Your Business
Minimize Risks in Your Business by Implementing Quality Control and Quality Assurance
What Is Quality Assurance (QA)?

Quality assurance (QA) is a structured and proactive set of activities designed to ensure that processes are established and adhered to in order to produce products or services of consistent quality.
In business and production, QA is the methodology that sets the standards, guidelines, and protocols governing every step of the process to prevent defects and deviations from quality benchmarks. Therefore, QA managers select development and testing methods to ensure the team uses the right processes.
For instance, in manufacturing, QA may involve:
- Setting strict standards for raw materials
- Implementing rigorous inspection procedures throughout production
- Continually refining processes to enhance overall quality
If the QC team identifies any defect, the feedback is implemented by QA managers. By focusing on prevention rather than detection, QA strives to identify and address potential issues before they impact the final product. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
What Is Quality Control?

Quality control (QC) is a quality management approach that ensures that the final products or services meet specified quality criteria. QC involves inspections, testing, and evaluations conducted during or after the production process to detect and address any defects or deviations from established standards.
For example, in manufacturing, QC might involve inspecting a sample of finished products to ensure they meet the predefined quality specifications. In software development, QC could include rigorous software testing to identify and rectify any bugs or issues before its release.
Unlike quality assurance, which focuses on preventing defects, QC is about identifying and correcting issues that arise during or after the production phase. They ensure that the end product aligns with the set quality standards before it goes to the client.
Quality Assurance (QA) Vs Quality Control (QC): Key Differences
Although quality assurance and quality control have a similar foundation, they are different. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at how they differ.
Goal
The primary goal of QA is to prevent defects and maintain consistency in quality throughout the entire process. It focuses on setting standards, implementing best practices, and continuously improving processes to ensure that the end product or service meets or exceeds customer expectations.
On the other hand, QC helps identify and correct defects in the service or final product. Once the product gets to the final stage, the QC team evaluates the output to confirm if it meets the predetermined quality criteria.
Which Comes First
You should know which comes first to implement QA and QC in your company. QA is integral to the planning and design phase; therefore, it’s implemented before the actual work begins. This is where the processes and standards are established. QC comes after or during the production work. The QC activities primarily focus on the final output.
Approach
QA is proactive, while QC is reactive. This is because QA activities are designed to prevent defects from occurring in the first place. These teams perform regular audits to ensure the final product is delivered without issues.
On the other hand, the QC team will monitor and observe the quality of the final product and provide feedback on quality improvement areas. They react when standards haven’t been met and report them to the QA team to correct.
Focus
The other main difference between these two elements of quality management is that QA is process-oriented while QC is product-oriented. This is because QA concentrates on procedures and methods employed to achieve consistent quality. Therefore, they look at the entire lifecycle of the project or process to prevent future errors.
QC focuses on the end result and whether it meets predefined quality standards. QC activities identify and fix problems with the specific output or deliverable to ensure that the company delivers the best product in the market.
Responsibility
With QA, the entire product development team is involved. The responsibility is shared among all team members to ensure that the information and materials are available to deliver the product according to the guidelines.
However, QC has a dedicated team to inspect and test product quality. This team is responsible for identifying and correcting defects in the final product. For instance, if your manufacturing company deals with different products, you’ll have dedicated QC personnel for every product line.
Duration
QA activities are usually ongoing throughout the project or process lifecycle. They are integrated into every phase, ensuring continuous quality improvement. On the other hand, QC is short-term.
Orientation
QA is forward-looking because it emphasizes continuous improvement and adherence to standards to prevent future defects. In contrast, QC is backward-looking since it involves detecting and correcting deviations in the final output. Therefore, the QC team has to constantly look at what went wrong in the production and send back the product for improvement.
Emphasis
The emphasis of QA is the prevention of defects through systematic planning, process adherence, and continuous improvement. Therefore, most of this work is during the planning and creation phase. On the other hand, QC is more focused on verification once the product is ready to ensure that it has no issues.
| Criteria | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
| Goal | To prevent defects and ensure adherence to standards throughout the entire process | Identify and correct defects or deviations after the product or service is produced |
| Which Comes First | Precedes the production process | Implemented after the completion of work |
| Approach | Proactive—focuses on process improvement and preventing issues | Reactive—concentrates on identifying and correcting issues found in the final product |
| Focus | Process-oriented, focus on the methods and procedures to achieve consistent quality | Product-oriented, concentrating on the result and verifying if it meets predefined standards |
| Responsibility | Shared across the entire team | Primarily lies with a dedicated inspection or testing team |
| Duration | Ongoing throughout the project or process lifecycle | Typically, this occurs toward the end of the production cycle or after the completion |
| Orientation | Forward-looking, emphasizing continuous improvement | Backward-looking, emphasizing the detection and correction of deviations |
| Emphasis | Prevention of defects | Detection and correction of defects through inspections |
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Focus & Goal

The primary goal of QA is to ensure that processes are in place to prevent defects and deviations from established standards throughout the entire project or production process. To achieve this goal, QA teams place their focus on:
- Process improvement
- Adherence to standards
- Implementation of best practices
QA creates a quality-centric environment by addressing the root causes of potential issues before they can manifest in the final product or service. QA establishes a foundation for the entire team to follow by setting guidelines and standards.
This approach slightly differs from QC, which aims to identify and correct defects or deviations in the final product or service. Unlike QA, which works to prevent issues throughout the entire process, QC is specifically concerned with evaluating the end result to ensure it meets the predefined quality criteria.
Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: Process & Orientation

QA and QC teams work together in most organizations to achieve total quality management. However, they differ in the way they implement their quality measures. On one end, quality assurance is process-oriented and preventive; therefore, the team systematically plans and implements methodologies to ensure consistent quality throughout the entire project or production process.
The main processes include:
- Documentation: The QA team creates reports and recommends how defects should be corrected to reduce the risk of them happening again.
- Training: The QA team requires training on all levels to be efficient. With this information, they can identify and fix any production issues and maintain standards.
- Audits: A QA audit is essential for every organization. These audits examine whether the business adheres to the set quality requirements.
- Monitoring: The QA process also involves monitoring the activities to ensure that the quality standards are implemented.
In contrast, quality control processes use a product-oriented approach. Since QC is backward-looking and reactive, it’s concerned with validating the outcome against the predefined standards. Quality control processes include:
- Product sampling: Conducting a QC assessment on every product will be costly. Therefore, the QC team randomly selects a set of items from the assembly line to test the quality. This data is used to determine if the products are of good quality.
- Inspection: The QC inspection process involves examining and measuring services, products, and processes to verify if they conform to standards. During this activity, the team can remove defective products and stop further work on spoiled goods.
- Lab tests: For companies that make chemical products or food items, the QC teams have to conduct lab tests to confirm that the products are high quality and free from contamination.
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Roles & Responsibilities

If your company has a QA and QC team, they need to work together to optimize your business processes. However, they have different roles and responsibilities. Here are the main roles of the quality assurance team:
- Project manager: This role is responsible for the entire product development. As a manager, this individual has to balance the budget, productivity, team, and output. Additionally, they guide the team on which defects should be handled first.
- Quality assurance manager: Everyone on the team might not be aware of all the quality standards. The role of a QA manager is to develop these standards and ensure that the team adheres to them.
- Quality control reviewer: This is the individual responsible for reviewing the product or service quality before it reaches the final stages.
On the other hand, the QC roles and responsibilities are essential for testing and inspecting the final product. Here are the roles of the quality control team:
- Quality control officers: These individuals reject products not up to standard. They also train QA teams, conduct assessments, and report issues that need attention.
- Document designer: The quality control team needs a designer to develop the document with the quality standard requirements.
- Checkers: These roles are reserved for individuals who review the designer’s work to confirm that the document meets the standards. You can have two different independent checkers to ensure that you don’t have any errors.
Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control: Tools

While people like Kaoru Ishikawa developed the initial QA and QC tools, they have evolved over time, and various organizations and individuals have contributed to their creation. The tools often come from a combination of industry best practices, methodologies, or quality management system initiatives.
QA tools enhance the production system to ensure there are no errors. Some of the common tools include:
- Project management software: These tools help set and track project goals to ensure that standards and guidelines are well-documented and accessible to the team.
- Quality audits: Audits are conducted to evaluate the company’s quality management system. The team can determine what’s missing or needs to be rectified from these reviews.
- Process analysis: To understand the business process, you should analyze and review all the components, including procedures, input, and output.
For quality control, you can use the following tools:
- Statistical process control (SPC) charts: Control charts help monitor the stability and consistency of a process over time. They visually represent data to identify patterns or trends that may indicate variations in quality.
- Checklists: QC teams use inspection checklists during the examination of products or services to systematically verify that each aspect complies with the established quality criteria.
- Pareto analysis: This tool helps prioritize and focus efforts on the most significant factors contributing to defects. The 80/20 rule is often applied, where a large majority of issues come from a small number of causes.
- Histograms: Histograms provide a visual representation of the distribution of data. In QC, they can be used to understand the frequency and distribution of defects, helping to identify patterns and outliers.
- Scatter diagrams: You can use these tools to display the relationship between two variables. They identify correlations between factors and defects, making it easy for the QC teams to pinpoint root causes.
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Duration & Timeline

QA is a continuous and ongoing process that is integrated into the entire project or production lifecycle. It’s not constrained to specific phases; therefore, the timeline starts during the project planning and persists throughout the execution and delivery. Because of this, the process is medium to long-term.
However, with QC, the timeline is more concentrated and occurs during or after the completion of work. QC is short-term for the team to examine the final product just before it’s released to the customer.
Despite this difference, both QA and QC work together to boost quality management. Your team needs to understand these distinct durations and timelines to make it easier to establish comprehensive quality management practices throughout the lifecycle of the projects.
Quality Assurance (QA) vs. Quality Control (QC): Similarities

You should understand how QA and QC work to establish a quality management system for your business. The two concepts have key similarities. Let’s examine them.
Policies, Procedures, and Methodologies
Both QA and QC put an emphasis on establishing robust policies, procedures, and methodologies to ensure product excellence. QA sets guidelines for the entire development process and a commitment to quality standards and continuous improvement. Similarly, QC implements policies focused on inspecting and verifying the final product, aligning with predetermined quality criteria.
Additionally, they both enforce standardized practices to integrate quality seamlessly. The teams rely on structured methodologies to ensure that they identify and address defects. Both QC and QA share a commitment to deliver high-quality outcomes.
Securing a High Quality Product
One of the things that both QA and QC address is ensuring your company secures a high-quality product. Although they might have distinct approaches, these disciplines play a complementary role in delivering products that meet or exceed quality expectations.
Therefore, if you have any issues with the quality of your services or products, you should hire teams to implement both.
Preventing Major Issues
Production issues can cost your company a lot of money. Ultimately, you could lose customers, especially if you release faulty products into the market. To avoid such problems, you can rely on QC and QA to enhance the overall quality of the final product. This combination works perfectly because QA focuses on proactive measures, and QC offers reactive defect identification.
Involve Some Cost and Time Investment
It’s going to cost you to provide quality products and services. Both QA and QC require you to invest money and time. For starters, you must hire teams that can implement these quality management measures. You also need to organize training sessions to ensure your entire team is updated on all quality standards.
Additionally, QC activities require resources for testing equipment, inspection tools, and the actual evaluation of products. The time investment is crucial for thorough testing procedures.
Improve How the Organization Makes Products
Most organizations strive to improve their production process. Therefore, if you want to make better products, both QA and QC will help you achieve this objective. QA focuses on refining processes and methodologies throughout the product development lifecycle, while QC provides feedback that aids in refining the production process.
You can use both processes to drive improvements in product development.
Quality Assurance (QA) vs. Quality Control (QC): Examples From Which You Can Learn

Quality control and quality assurance processes can be used in almost all sectors. In this section, we’ll provide some examples from which you can learn.
Software Development
In a software development company, both QA and QC are integral components to ensure you deliver high-quality software products.
A software development company establishes comprehensive QA processes and methodologies that include:
- QA teams will conduct rigorous code reviews to ensure adherence to coding standards and best practices.
- Developers should write tests before code implementation, allowing for early identification and correction of potential issues.
- Automation tools should be employed to ensure that code changes are regularly integrated, tested, and deployed, minimizing the risk of integration issues.
- QA teams will ensure that each line of code is aligned with specific requirements, preventing deviations and enhancing product reliability.
The QC team will come in at the end to identify and rectify defects in the final software product before it reaches the end user. This involves manual and automated performance and usability testing, user acceptance testing to get feedback, and the use of defect tracking systems to prioritize identified issues.
Healthcare
As one of the most critical industries, healthcare requires high standards. You should provide a safe environment for your patients and healthcare workers. Here are the quality assurance steps you should take:
- Implementing guidelines that ensure that healthcare providers follow standardized practices in patient care.
- QA involves ongoing training programs to ensure healthcare professionals stay updated on the latest medical advancements, technologies, and protocols.
- Identifying potential risks in patient care and implementing protocols to mitigate those risks.
- Double-checking all test results.
- Implementing measures such as incident reporting systems to improve patient safety continually.
- Keeping the hospital free of hazards.
The QC team then focuses on verifying and rectifying issues in patient care to ensure adherence to quality standards. They should conduct regular audits of patient records and clinical procedures. The activities should also cover testing and calibration of medical equipment and diagnostic tools to ensure accurate results.
QC in these facilities also involves tracking patient outcomes and conducting assessments to ensure that treatment plans align with quality standards.
Customer Service
If your company has a customer service team, you need quality assurance and quality control measures to help you interact with customers better. Here are the activities for the QA team:
- QA includes comprehensive training programs for customer service representatives to ensure they possess the necessary skills and communication abilities.
- Set guidelines to ensure timely responses to customer inquiries.
- Implementing systems for collecting and analyzing customer feedback to allow the company to identify areas for improvement.
- QA establishes consistent and positive communication guidelines, ensuring a uniform and professional customer experience.
With these measures in place, the QC team can check customer interactions by listening to recorded customer calls. This allows them to assess representative performance and how they adhere to scripts and resolve customer issues. QC also includes assessments of written communication, such as emails and chat transcripts, to ensure clarity, accuracy, and professionalism.
Food Industry
The food industry is a critical sector that needs proper QA and QC measures. You should check the final product to ensure it meets the set standards. Here are examples of QA measures for a company in this industry:
- Rigorous vetting and monitoring of suppliers to ensure the quality and safety of raw ingredients.
- Have a document containing clear information on the ingredients for food production.
- Ongoing training for food handlers and production staff to uphold hygiene standards and follow proper procedures.
- Regular checks to determine whether the production process is following and meeting specifications or not.
- Implementation of traceability systems to quickly identify and remove potentially unsafe products from the market.
- Collection of customer feedback to improve food quality.
In the QC phase, the team should test food products for taste, texture, nutritional content, and microbiological safety. There should also be random sampling and testing of batches to ensure conformity to quality specifications. The teams should also inspect packaging materials to guarantee they meet safety standards and protect the product from contamination.
Education
You also need QA and QC in education to help you deliver standardized learning experiences. Here are some examples of how QA is implemented:
- Continuously develop and review curricula to ensure alignment with educational standards and relevance to current knowledge.
- Comprehensive training programs for educators to enhance teaching methodologies.
- Creating fair and reliable assessments that accurately measure student learning outcomes.
- Spot-checking for any quality issue.
The QC teams can regularly observe classroom sessions to assess teaching methods, student engagement, and overall instructional quality. They can also check grading assessments and use student feedback surveys to identify areas of improvement.
How to Improve Your Company’s Quality Assurance and Control Using SweetProcess
SweetProcess is a business tool that helps with the smooth implementation of quality assurance and quality control in areas such as process and procedure documentation and task management. This cloud-based tool provides the systemization you need to scale and grow your business.
You can improve and master your processes and collaborate with all your team members from one centralized location. Let’s explore some of the key SweetProcess features:
How to Create a Procedure on SweetProcess
SweetProcess has straightforward features. To create a procedure for your quality standards:
- Log in to your account.
- Click on the “Procedures” tab on the main menu.
- Tap “Create Procedure.”
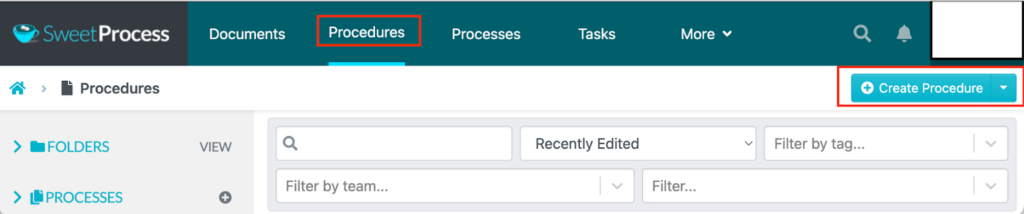
- Add a procedure title.
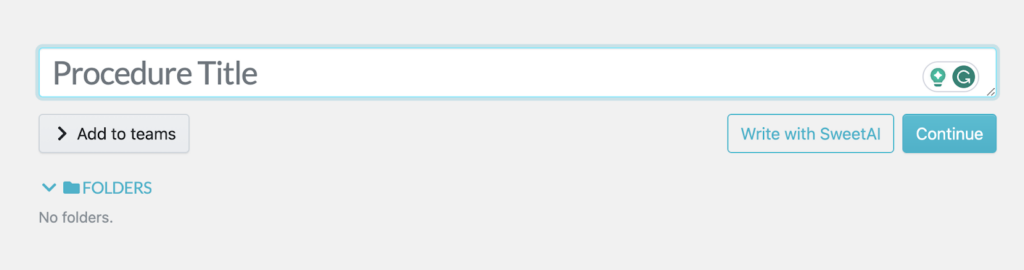
Add more details for your QA or QC document on the next tab. These details can be images, videos, or tags that make the procedure more comprehensive. Once you are done, you can assign it to specific teams.
How to Create a Process on SweetProcess
You can follow these steps for process documentation:
- Log in to your SweetProcess account.
- Click on the “Processes” tab on the main menu.
- Select “Create Process.”
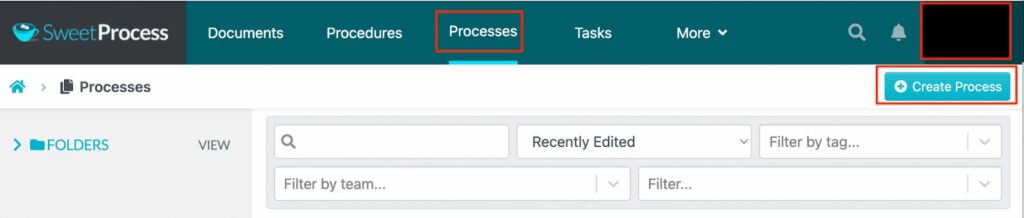
- Add the process title.
Include details about the process, such as tables and links.
Once all your processes are added, SweetProcess organizes them on the dashboard. All team members can view the QA or QC processes from one place.
How to Assign and Manage Tasks on SweetProcess
If you want to assign tasks from your QA and QC documents, you can use SweetProcess easily. To assign these tasks:
- Tap the “Tasks” button on the main menu.
- Select “Assign Task.”
Select the team members and assign the specific tasks. You can add details like the employee name, task name, and due date for better efficiency.
If you have multiple teams, they can collaborate from one place. To monitor the progress, open the “My Tasks” tab. This section will show you what tasks are overdue and what’s due soon.
What are companies saying about SweetProcess?
The co-founder of Spark Marketer, Carter Harkins, was running a successful marketing company in the home services industry. Although the business was thriving, a business consultant reviewed their processes and pointed out that they were operating without SOPs. Because of this, collaboration was a problem.
Additionally, the team relied heavily on tribal knowledge to work. This approach led to disorganization and affected the quality of work. The business leaders started looking for an alternative tool, which led them to SweetProcess. With this new development, the company now has proper documentation and a knowledge base for all employees. Additionally, they could train employees, which helped standardize operations and output quality.
The other customer successfully using SweetProcess is Tom Vranas, the innovation and culture vice president at Everywhere Wireless. The organization had SOPs but had a challenge distributing them to all team members. Because of this, employees were always asking work-related questions to execute their tasks.
The manual system affected the quality of their work; therefore, Tom started looking for a better platform. With SweetProcess, the employees can access all company details from one place to execute their tasks. This has boosted uniformity and standardized the company’s products and services.
Streamline your operations and ensure a consistently high-quality output that sets your business on the path to success with SweetProcess. Claim your free trial of SweetProcess.
Benefits of Implementing Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) in Your Business

Why should you use quality assurance and quality control in your business? Here are the expected benefits:
Deliver High-Quality Output
If you’ve been struggling with quality output, you need QA and QC in your business. The two disciplines ensure that you adhere to established standards and processes. This way, organizations can minimize defects and errors, resulting in a final output that meets or exceeds customer requirements or expectations.
For instance, in the manufacturing industry, these processes may involve stringent checks at each production stage, ensuring that raw materials meet specifications and workers follow standardized procedures.
Helps an Organization Have Set Guidelines and Standards
QA and QC contribute to the establishment of clear guidelines and standards. This approach provides a framework for consistent and efficient operations within an organization. These guidelines help align the team’s efforts toward common objectives and quality benchmarks.
Therefore, if you are in software development, you’ll have defined coding standards and protocols. Having these standards in place helps the team work cohesively.
Eliminate Waste
In industries like manufacturing and the food industry, wastage can be a costly affair. However, with QA and QC practices, you can identify and rectify issues early in the production process, reducing the likelihood of wastage in terms of materials, time, and resources.
Additionally, when you minimize errors, you can operate more efficiently and reduce unnecessary rework or product recall costs.
Increase Operational Efficiency
Every company strives to be efficient. You can achieve this by implementing quality assurance and quality control measures in the business. Since the processes are standardized, you can streamline operations and minimize errors. Ultimately, efficient operations lead to reduced costs and improved overall productivity.
Provide Customer Satisfaction
In this competitive business world, you need to satisfy your customers. If your products are always faulty, you could lose a market share of loyal clients. You need QA and QC processes to help you deliver quality products or services. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations contributes to customer loyalty and positive brand perception.
Encourage a High Level of Confidence and a Motivated Team
Having robust QA and QC processes in place instills confidence in the team, knowing that their work aligns with established standards and quality expectations. A motivated team is more likely to consistently produce high-quality output and actively contribute to the organization’s success. Ensure that the team is well-trained to keep up with the standards.
Identifies and Corrects Problems as They Occur
One of the key benefits of QA and QC is the ability to identify and correct problems as soon as they arise. For instance, if your business is in construction, the QA processes may involve adherence to building codes and safety standards, while QC activities include on-site inspections and quality checks.
Once the team identifies any construction defects in the building process, they can be corrected to prevent issues from escalating and impacting the final structure.
Minimize Risks in Your Business by Implementing Quality Control and Quality Assurance
Implementing quality control and assurance in your business is a strategic move toward minimizing risks and ensuring consistent quality. QC focuses on verifying and rectifying issues in the final output, while QA emphasizes proactive measures to prevent defects throughout the entire process.
To seamlessly integrate QA and QC into your business processes, consider leveraging a powerful tool like SweetProcess. This platform facilitates the creation and implementation of standardized procedures, ensuring that your team follows established guidelines and protocols. With SweetProcess, you can enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain high quality across all aspects of your business.
Ready to take control of your processes and minimize risks? Sign up for a free trial of SweetProcess today. No credit card is required!
