Last Updated on March 2, 2025 by Owen McGab Enaohwo

Lean manufacturing could be the tool you need to boost productivity. Research indicates that those who implemented this principle in their business noticed a 17% rise in productivity.
Lean manufacturing isn’t just a set of principles; it is a complete mindset and cultural transformation of the way your business operates, irrespective of its size.
Having the right tool is crucial to succeeding with the lean manufacturing methodology. This is where SweetProcess comes to the rescue. It is a platform that offers support for your lean manufacturing initiatives. It equips you with tools that help streamline your processes and help you maximize output.
You can try out the SweetProcess platform for FREE using the 14-day trial to unlock the full potential of lean manufacturing tailored to your business needs.
Table of Contents
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing in a Company
How to Implement the Lean Manufacturing Culture in Your Business
How to Build a Lean Culture in Your Company Using SweetProcess
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Major Categories of Waste in Lean Manufacturing
8 Types of Waste (Muda) in Lean Manufacturing
Basic Lean Manufacturing Tools
Why Lean Manufacturing Fails and How to Prevent It
How Lean Manufacturing Works in Real Life: Examples From Which You Can Learn
Lean Manufacturing vs. Lean Management: How They Differ
Lean Manufacturing vs. Agile Manufacturing: How They Differ
Lean Manufacturing vs. Six Sigma: How They Differ
Lean Manufacturing vs. Just in Time: How They Differ
Start Your Company’s Lean Journey With SweetProcess
What Is Lean Manufacturing?

Lean manufacturing is the systemic methodology for minimizing waste within the manufacturing process without compromising productivity. The lean manufacturing strategy stems from the philosophy of achieving more with less.
The origin of lean manufacturing can be traced back to the Japanese manufacturing industry and is closely associated with the Toyota Production System (TPS) developed by Toyota executive Taiichi Ohno.
Toyota got its inspiration from Ford following the failed attempt to integrate their entire production process, which limited the variety made available to customers.
Toyota improved on the principle and delivered its customers versatility, quality, and efficiency.
Others have now redefined and perfected this principle, gaining acceptance beyond manufacturing with applications in healthcare, retail, construction, logistics, and government.
Toyota has since proven the effectiveness of lean methodologies, which have continued to evolve and attract global interest across various industries.
Imagine running an advertising agency where each campaign is a journey from concept to execution. The conventional setup might be chaotic. You can have the creative team coming up with ideas in a vacuum, the strategy team then trying to align these ideas with client objectives, and finally, the execution team scrambling to put things together and make it all happen. This often leads to miscommunication, delays, and a final product that may or may not meet the client’s needs—much like a factory with a poorly managed assembly line.
On the flip side, with lean principles applied to this agency, all teams—creative, strategic, and execution—collaborate from the start. They are on the same page regarding the client’s goals and constraints. Ideas for the project are developed with a clear understanding of the end goal, avoiding the tinkering and back-and-forth that typically wastes time and resources among team members.
The entire process is run like a relay race where each team member knows exactly when to pass the baton, ensuring a smooth, efficient workflow. Regular check-ins and feedback loops ensure that any potential waste (in terms of unaligned ideas or strategies) is identified and eliminated early.
This is the beauty of embracing lean methodologies.
Lean techniques and tools have also emerged, taking different forms to support the overall goal of the organization. Some help with cutting down the cost of production, streamlining processes, and raising profit, while others dwell more on achieving a high rate of customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing in a Company
The ultimate goal of lean manufacturing is to cut down time and improve productivity. Businesses that have embraced the lean manufacturing methodology continue to enjoy its numerous advantages. One key aspect of this approach is lean process improvement, which helps organizations refine their workflows and eliminate inefficiencies. Here are some of the key benefits of lean manufacturing in a company.
Environmentally Friendly
Lean manufacturing is not just all about cutting down production costs—it extends into reducing waste, too. This means that adopting lean manufacturing supports environmental sustainability by minimizing the wastage of materials and resources that would otherwise have contributed to the environmental footprint. Focusing on only what is important helps companies keep up and remain environmentally friendly.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
An improvement in the quality of products in a company does not go unnoticed by its customers. Streamlining processes also enhances productivity and allows for effective delivery, which helps adapt quickly to customers’ needs. This efficiency can help boost customer satisfaction and increase loyalty.
Reduce Lead Time
Improved turnaround times can be achieved when companies identify and eliminate wasteful steps in production. With this comes a more responsive and agile business within the marketplace.
Saves Cost
Implementinglean principles has a direct impact on the bottom line. When waste is reduced in all forms—be it time, effort, or material—it will cut down the overall cost of production. These savings can be channeled toward other areas of your business or passed on to customers, making your offerings more competitive.
Increased Productivity
When processes are optimized, and inefficiencies are removed, employees can then focus on what truly adds value to the company. This leads to a significant boost in employee productivity and enhances the quality of work.
Supply Chain Improvement
Lean manufacturing extends its efficiency beyond just lean production; it streamlines the entire supply chain. By improving communication, reducing inventory waste, and enhancing coordination, lean practices provide companies with a more robust and responsive supply chain.
Creates Happy Employees
One benefit of lean manufacturing, often overlooked, is the positive impact on the morale of employees. With lean manufacturing roles clarified, tasks are streamlined, reducing frustration caused by inefficient processes. This gives a sense of accomplishment and job satisfaction.
Improved Scalability
When you have successfully streamlined your processes, it becomes easier to adjust as your company grows. With the growth and expansion of your business comes the need to scale up your processes. Having lean manufacturing in place ensures that your operation remains efficient, manageable, and primed for continued growth.
How to Implement the Lean Manufacturing Culture in Your Business
Implementing a lean manufacturing culture in your business can be a game changer. It’s all about making your processes more efficient and focusing on what matters. Let’s simplify and break down the key steps on how to implement lean manufacturing:
Gain Leadership Commitment
Leaders need to be on board for lean manufacturing to work. They set the tone and lead by example. When leaders are committed, the whole organization follows.
- Share the Vision: Communicate why your organization is adopting lean.
- Resolve Conflicts: Find and solve any issues that might stop lean implementation.
- Support From the Top: Get a senior leader to actively support and promote lean.
Educate and Train Your Employees
Employees need to understand lean principles to apply them. Regular training keeps everyone up-to-date. Sharing success stories can inspire employees to embrace lean manufacturing principles.
- Regular Training: Teach employees about lean principles and techniques.
- Practice Lean: Let employees use lean methods in their daily tasks.
- Discussion Forums: Create opportunities for employees to talk about lean manufacturing.
Define What Customers Value
Understanding what customers want is key to lean. It helps focus efforts on what’s important. Regular feedback ensures you’re always meeting customer needs.
- Customer Feedback: Regularly ask customers what they want and need.
- Align Products: Make sure your products match what your customers value.
- Review Regularly: Keep checking to ensure you’re meeting customer needs.
Map Value Streams
Mapping your processes helps identify waste. It shows where you can improve. Getting different departments involved gives a complete picture.
- Value Stream Mapping: Analyze your processes to find where to cut waste.
- Involve Everyone: Get all departments to help with mapping.
- Identify Improvements: Look for specific areas in your process to streamline.
Create Flow
Eliminating bottlenecks speeds up processes. Balancing workloads prevents overburdening. Simplifying processes ensures smooth operations.
- Fix Bottlenecks: Identify and address slowdowns in your process.
- Balance Work: Make sure work is evenly distributed.
- Simplify Tasks: Streamline your processes for better workflow.
Implement Pull Systems
Pull systems respond to customer demand. It helps reduce inventory and meet needs faster. Kanban boards are a great tool for managing this.
- Demand-Based Production: Produce items as customers need them.
- Lower Inventory: Keep only necessary stock levels.
- Kanban Boards: Use visual tools to manage workflow and inventory.
Visualize Processes
Seeing your processes makes them easier to understand. It helps identify issues quickly. Visual tools make processes clear to all employees.
- Use Visual Tools: Use charts and diagrams to show your processes.
- Display Progress: Show how far along processes are in real time.
- Access for All: Ensure everyone can see and understand these visualizations.
Standardize Processes
Standard procedures ensure consistency. They make sure everyone does tasks the same way. Regularly updating these keeps them relevant.
- Create SOPs: Develop standard procedures for key tasks.
- Ensure Consistency: Make sure tasks are done the same way each time.
- Review Regularly: Keep updating your procedures to stay current.
Implement Kanban System
Kanban helps manage tasks and inventory. It makes sure you have what you need when you need it. It’s a visual way to track progress.
- Visual Task Management: Use Kanban to track and manage tasks.
- Limit Tasks: Set limits on how much work is in progress.
- Continuous Review:Regularly check your Kanban system for improvements.
Monitor and Improve
Keeping an eye on how you’re doing helps you get better. Feedback from employees is crucial. Kaizen, or continuous improvement, is a key lean principle.
- Track Progress: Measure how well your processes are working.
- Employee Input: Get suggestions from employees on how to improve.
- Keep Improving: Use techniques like Kaizen to continually enhance processes.
Cultivate Supplier Relationships
Good relationships with suppliers support lean efforts. It’s about working together for efficiency. Regular communication keeps everyone on the same page.
- Work Closely with Suppliers: Collaborate with suppliers for mutual benefit.
- Streamline the Supply Chain: Make the supply process more efficient.
- Regular Talks: Keep in constant communication with your suppliers.
Encourage Collaboration
Teamwork is crucial in lean manufacturing. Shared goals unite different departments. Open communication helps everyone work together better.
- Teamwork Across Functions: Encourage different departments to work together.
- Common Goals: Align everyone around the same objectives.
- Open Communication: Make sure information flows freely among teams.
Celebrate Success
Recognizing achievements boosts morale. Sharing success stories can inspire others. Rewards for continuous improvement motivate employees.
- Acknowledge Achievements: Celebrate both individual and team successes.
- Share Success Stories: Communicate how lean has positively impacted the business.
- Align Everyone Around Lean Goals: Make sure all teams share the same lean objectives.
Implementing a lean manufacturing culture requires a holistic approach involving everyone, from the top leadership to the operational teams. It’s a journey of continuous improvement, where the entire organization collaborates to create more value with less waste.
How to Build a Lean Culture in Your Company Using SweetProcess

When it comes to transforming and streamlining your processes to reduce waste, you need the right lean tools to help. SweetProcess has proven to be a great tool for streamlining your processes, documenting SOPs, and enhancing collaboration, consequently reducing unnecessary waste. Here are the steps you can take to build a lean culture with SweetProcess:
Avoid Time Wastage in Answering Repetitive Questions by Creating a Knowledge Base in SweetProcess
As your team members execute their daily tasks, they might need to clarify certain questions. Over time, you might notice that, despite everyone knowing what to do, some repetitive questions just keep popping up. Taking care of these questions ensures you don’t leave room for doubts or mistakes. A comprehensive knowledge base will help you answer questions that appear simple but take up an unexpected amount of time and energy if addressed individually each time.
Here are the steps to take when creating a knowledge base to enhance your processes:
Step #1: Gather Your FAQs: Begin by rounding up all those repetitive questions. Collect the most-asked queries for every process within your company.
Step #2: Create a Knowledge Base in SweetProcess: Next you need to create the actual knowledge base using the questions collected earlier. Here’s how to create that ultimate go-to library in SweetProcess:
- Sign up for a SweetProcess account: To get started, you need to sign up for an account on SweetProcess. You can use the 14-day free trial with no credit card required. Fill out the necessary details to create your account.
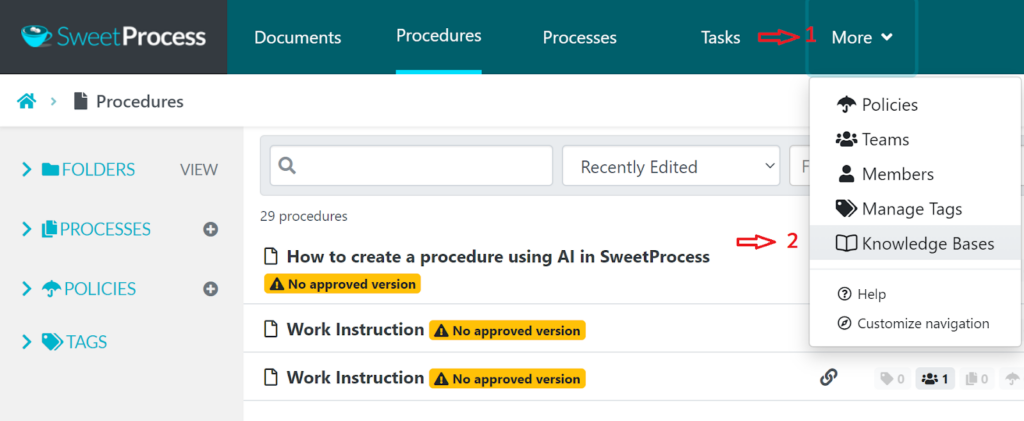
- Open your SweetProcess dashboard: On the dashboard, navigate to the “More” tab option, then click on the “Knowledge Bases” tab.
- Once the page opens, click on the “Create Knowledge Base” button.
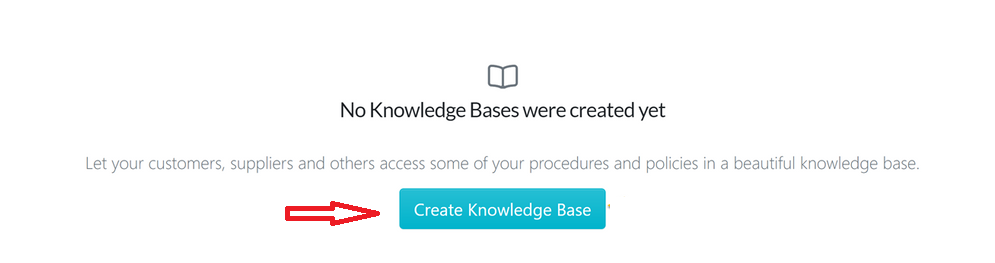
- Give your knowledge base a title and click the “Continue” button to complete the process.
- Write articles: For each FAQ, create a new knowledge base article. Think of each one as a golden nugget of information. Write down the answers in a clear, concise, and friendly manner. If you’re answering a question, be direct and thorough. If it’s a process, lay out the steps in an easy-to-follow manner.
- Include visuals (optional): A picture speaks a thousand words. If it makes sense, add screenshots, diagrams, or any other visual aids that can help clarify the information.
- Organize and label: Sort these articles into categories and tag them for easy navigation. It’s like organizing books in a library.

- Revise and polish: Give everything a once-over to ensure it’s accurate and easy to understand.
Step #3: Make the Knowledge Base Accessible: Share this reservoir of knowledge with your team. It’s like distributing a map that leads to instant answers. You can have team members access the knowledge base directly within the SweetProcess platform, or you can create a subdomain link for the knowledge base and share that instead.
A knowledge base is a living resource. You need to regularly update it with new information and review older articles to keep them current. Finally, encourage your team to give feedback on the knowledge base. Their insights can help you refine and improve it over time.
Let’s take a look at how pLink Leadership eliminated fear among its employees with a strong knowledge base. Before SweetProcess, pLink struggled with an overwhelming 85-page document that quickly became outdated, leading to slow processes and frustrated employees.
The challenge was clear: they needed an efficient way to manage and access vital information, and they proceeded to create a knowledge base for team members to access. This brought an end to employees’ frustrations and reduced the time spent trying to get answers to important questions.
Just like pLink Leadership, your business can sail smoothly toward efficiency and productivity by leveraging the power of SweetProcess.
“One huge thing it’s impacted is the way that I’m onboarding new folks. In the past, when we were training somebody new, because we are 100 percent virtual, that person was shadowing effectively and it was just very slow. Whereas now they go directly to SweetProcess to find out what they need to know or they can go there when they’re doing something on their own. I have a lot more confidence to say, ‘Hey take this task. And the first step, if you have a question, is to go to the SweetProcess. If you still have a question, then we’ll tag it, and we’ll have a conversation about it.”
—Jennifer Schneider, Chief Design Officer at pLink Leadership
Reduce Error and Rework by Creating SOPs in SweetProcess
Creating standard operating procedures (SOPs) in SweetProcess is a great way to achieve precision that reduces error. SOPs are like your business’s playbook: They ensure everyone knows the right moves to make at the right time.
Here’s how you can create SOPs in SweetProcess to minimize errors and maximize efficiency:
Step #1: Identify Processes Needing SOPs: Start by pinpointing which processes or tasks frequently experience errors or rework. Think of it as finding the weak links in your business operations chain.
Step #2: Create Your SOPs in SweetProcess: Write clear, step-by-step standard operating procedures (SOPs) in SweetProcess. Here’s how to get done:
- Sign up for an account if you do not have one as described above.
- After signing up, navigate to the “Procedure” tab and click on “Create Procedure.”
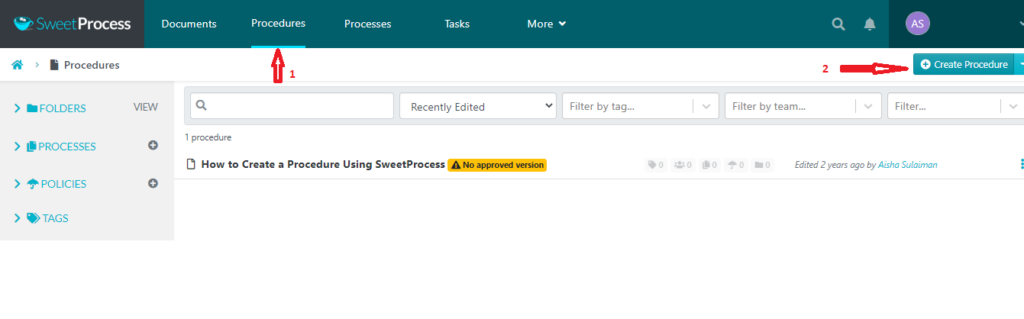
- Next, give a title to your procedure and add it to the folder in which you want to save it. After adding the title, click on “Continue” to save it.
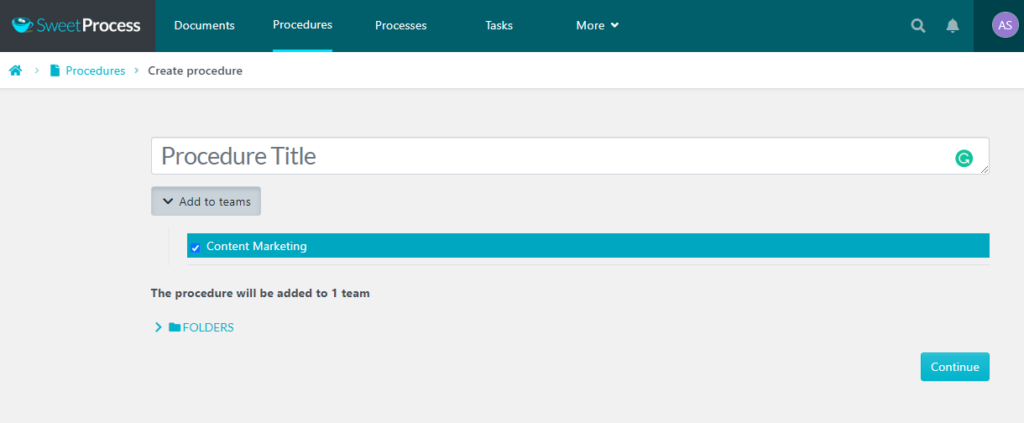
- Proceed to edit the procedure based on your requirements. At this point, you can also assign team members who need to work with that particular procedure. Upon publishing, they will receive a notification and they can view the procedure from their end.
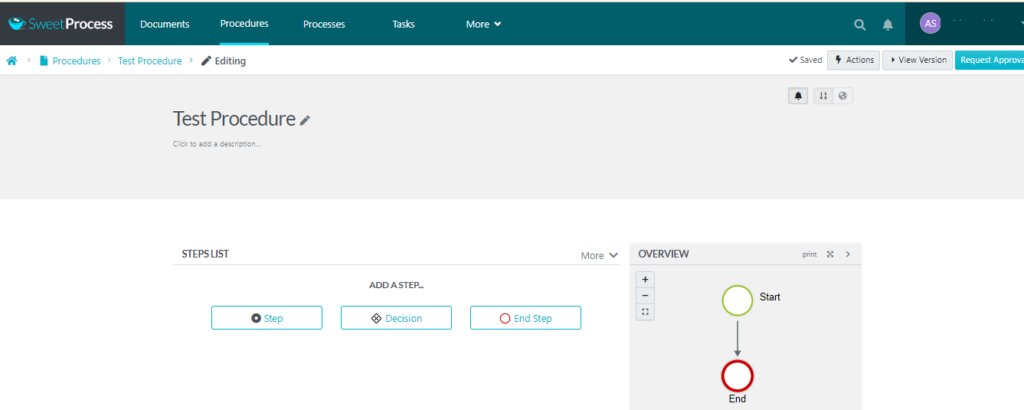
An overview of the procedure is also generated as you edit the procedure.
- Add visuals (optional): Sometimes words alone aren’t enough. Where needed, add screenshots, diagrams, or videos. Adding multimedia is fully supported by SweetProcess.
- Review and refine your SOP: Once you’ve drafted your SOP, review it for clarity and completeness. Make sure it’s easy to understand and covers all necessary steps.
- Publish and share the SOP: After finalizing your SOP, publish it on SweetProcess and share it with your team. Make sure everyone who needs to follow the SOP knows it’s there and understands how to use it.
- Train your team on the SOPs: It’s not enough just to create and share the SOPs. Spend time training your team on these new procedures to ensure they understand and can follow them correctly.
- Gather feedback and iterate: After your team has started using the SOPs, gather feedback on what’s working and what could be improved. Use this feedback to refine and update your SOPs.
- Regularly review and update SOPs: SOPs should evolve with your business. Regularly review and update them to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Creating and managing SOPs with tools like SweetProcess is quite easy for businesses to implement. It contributes toward your journey to minimize errors and streamline your process. Now you can empower your team with the tools and knowledge they need to do things right every time.
Document and Eliminate Unnecessary Steps by Creating Processes and Procedures Using SweetProcess
When it comes to streamlining your business operations, it’s like decluttering your workspace: getting rid of what you don’t need and organizing what you do. That’s where SweetProcess shines, helping you to document and eliminate those unnecessary steps in your processes and procedures. It gives you the tools to eliminate inefficiencies, making your business run smoother and smarter.
Step #1: Evaluate Your Current Processes: To streamline your business, you need to take a close look at your current processes. Find those steps in your workflow that seem redundant, time-consuming, or no longer serve their purpose.
Step #2: Document a Refined Process: Once you’ve identified these areas, log in to your SweetProcess account as stated previously to proceed. This platform is your digital decluttering kit, ready to help you tidy up your operational processes.
- While on the dashboard, navigate to the “Processes” tab and create a new “Process.” Alternatively, you can opt for the existing templates or upload an existing process.
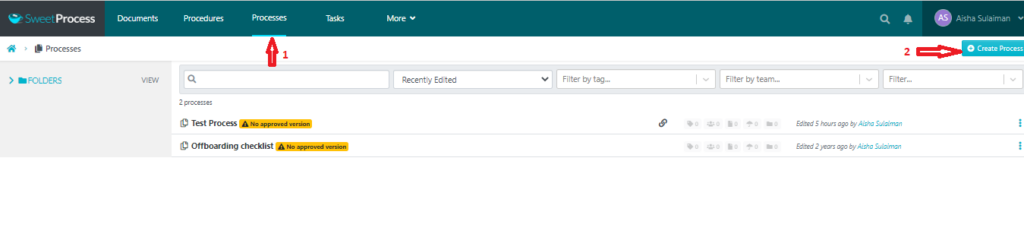
- Next, give a title to the process to help identify and file the process accordingly and save it.
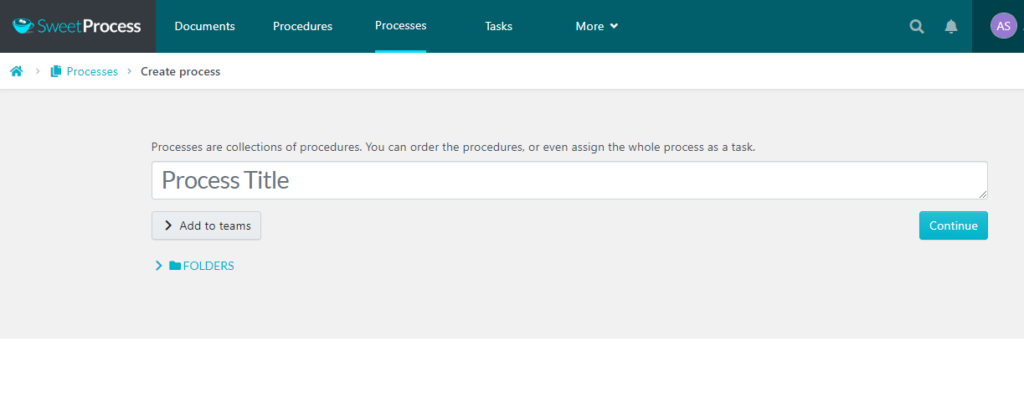
- After creating the process title, you can begin to edit it and add the steps required to complete that process. You can also add team members and assign tasks associated with the steps in that process.
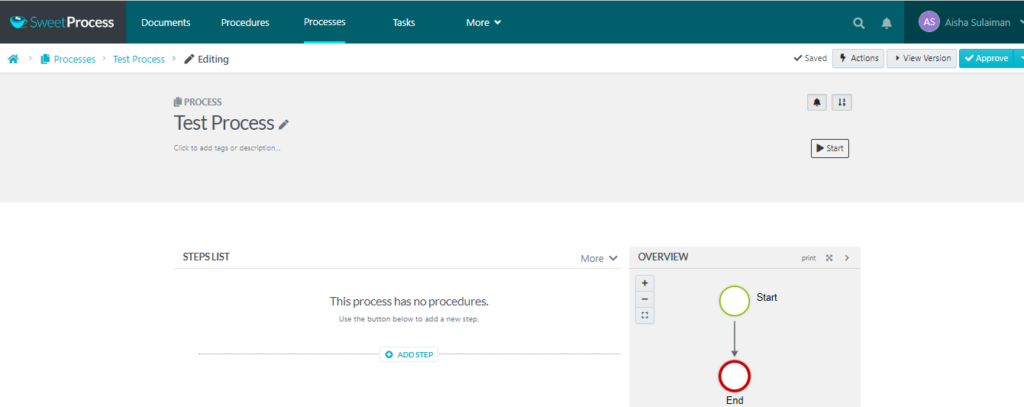
SweetProcess makes the creation and documentation of processes seamless. There is no steep learning curve, and you can explore existing templates instantly.
When Benchmark Wealth Management embarked on its journey to streamline operations, it faced the all-too-common challenge of tangled and inefficient processes. Under the guidance of Sarah Beach, the branch operations manager, along with the right lean manufacturing tool, Benchmark Wealth Management transformed its operations from a maze of confusion into a model of clarity and efficiency.
Using SweetProcess, they were able to document each procedure, ensuring that every team member was on the same page and working in unison. This shift not only saved time and reduced errors but also empowered their employees with a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities.
The result? A leaner, more productive operation that could focus on delivering top-tier financial services to their clients, proving that with the right tools, even the most intricate processes can be elegantly simplified.
Do you want to start your lean manufacturing journey on SweetProcess too? Take advantage of the 14-day FREE trial to see how it works!
Reduce Delays and Misunderstanding by Leveraging Collaboration Tools in SweetProcess
SweetProcess offers a suite of collaboration tools designed to synchronize your team’s efforts. Here’s how you can leverage these tools:
- Centralized communication: The first step is to centralize your communication. SweetProcess provides a platform where conversations about specific processes or SOPs can happen in context. It’s like having a group chat specifically for each piece of the project so everyone knows what the discussion is about without any confusion.
- Real-time notifications and updates: Keep everyone in the loop with real-time updates. Whenever a process is updated or a new SOP is added, SweetProcess can notify relevant team members. This ensures that everyone is working with the most current information, reducing the chances of delays caused by outdated procedures.
- Commenting and feedback features: SweetProcess allows team members to comment directly on documentation and SOPs. This feature invites collaborative review and feedback, ensuring that all voices are heard, and any potential misunderstandings are cleared up quickly.
- Task assignments and tracking: Delegate and track tasks efficiently within SweetProcess. Assign specific steps of a process to team members and track their progress. This not only keeps everyone accountable but also provides transparency in who is doing what, significantly reducing delays in handoffs and task completion.
- Accessible documentation: With all your processes and SOPs documented in one place and accessible to all team members, SweetProcess eliminates the confusion and delays caused by searching for information across multiple platforms or documents.
- Integration with other tools: SweetProcess can integrate with other tools your team uses, bringing everything into a cohesive system. This integration ensures seamless workflow across different platforms, reducing delays that occur due to switching between various applications.
- Regular review and updates: Regularly review your processes and collaboration practices within SweetProcess to identify and address any new bottlenecks or misunderstandings.
By using SweetProcess’s collaboration tools, you’re tuning each part of your team’s efforts to the same frequency, ensuring a harmonious and efficient workflow.
It’s about moving beyond the solo performances and fostering a well-coordinated ensemble where delays and misunderstandings are significantly reduced, if not eliminated.
Sign up for the 14-day free trial of SweetProcess and start eliminating waste in your business today!
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing

Lean manufacturing operates based on a systematic approach focused on minimizing waste and optimizing efficiency within the process of production. Lean manufacturing is based on the following core principles:
Value
Thisprinciple highlights the understanding of what your customers value in a product or service. The goal here is to improve every step of the production process to increase the perceived value of the customer.
Any aspect that does not contribute to improving the perceived value should, therefore, be eliminated. When your company focuses on delivering value, unnecessary features or processes are excluded, and customer satisfaction improves.
Value Stream
The value stream involves all the processes taken to deliver a product to customers from conception to the final stage. It covers everything from design to production and delivery.
Value stream is an important lean tool used for identifying the action taken through the production pathway. The idea is to map out these activities and then analyze them for waste. Streamlining the value stream helps in reducing cycle times and eliminating non-value-adding activities, leading to more efficient production and delivery.
Flow
The principle of flow ensures that the production systems work smoothly without any form of interruption. It involves organizing the workplace in such a way that each step is logically connected with the next, with minimal delay or waiting time between them.
By improving flow, companies can reduce lead times, minimize work in progress, and increase productivity.
Pull
The pull principle is about producing only what is needed when it’s needed. This approach is quite different from traditional manufacturing systems, where production is often based on schedules or forecasts. In a pull system, production is driven by customer demand.
Implementing a pull system helps you cut down overproduction, maximize inventory levels, and align production with actual market demand. Techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) production are often used in pull systems to ensure that products are manufactured just in time to fulfill customer orders.
Perfection
The final principle of lean manufacturing is the pursuit of perfection. This involves continuous improvement, where the goal is to constantly look for ways to reduce waste and improve all aspects of the production process. It’s about striving for zero defects, minimizing delays, and maximizing value to the customer.
Continuous improvement is a never-ending process, and companies are always looking for ways to be more efficient and deliver higher-quality products.
Implementing these core lean manufacturing principles helps companies to become more efficient, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
The focus is always on delivering the most value to the customer while using the least possible resources and creating the least waste. Lean manufacturing is not a one-time change but a continuous journey toward improvement and excellence.
Major Categories of Waste in Lean Manufacturing

In lean manufacturing, there are three main types of waste that you need to focus on to streamline your processes and eliminate waste. Here are the three categories:
Mura
Think of mura as the ups and downs in your work process. Sometimes you’re swamped and other times it’s quiet. This inconsistency can mess up your workflow. To tackle mura, the goal is to balance things out. This means setting a steady pace in work processes so everything runs more smoothly and predictably.
Muri
Muri is all about stress—either on your team or your equipment. Imagine pushing your car to go faster than it can, or loading it up with too much weight. It’s the same with your team or machines. If they’re overloaded, they can break down or burn out. Avoiding muri involves keeping workloads reasonable and making sure everyone and everything has what it needs to do the job well without getting overwhelmed.
Muda
Muda is probably the most talked about. It’s anything in your process that doesn’t help or add value from the customer’s point of view.
There are several types, like doing too much work, waiting around for the next step, or moving things unnecessarily. The key with muda is to cut out these pointless parts of your process, making everything leaner and more efficient.
In essence, lean manufacturing is about looking out for these three types of waste. By identifying and reducing mura, muri, and muda, you make your operations smoother, less stressful, and more focused on what matters—creating value for your customers.
8 Types of Waste (Muda) in Lean Manufacturing

There are eight types of waste, collectively known as muda, each impacting productivity and efficiency. Here’s a closer look at each one:
Defects
Any product or component that is not up to standard is considered to be defective. They can lead to rework, scrap, and dissatisfaction among customers. The cost of defects is not just in material and time but also in potentially damaging a company’s reputation.
Think of a car manufacturing line where a car comes out with a faulty brake system. That’s a defect. It means you’ll need to spend extra time and money to fix it, and if it slips through, you get disappointed customers.
Reducing defects can be achieved by improving quality control processes, training workers, and implementing robust testing mechanisms.
Overproduction
Overproduction means making more products than necessary or producing them before they are needed. This waste is particularly problematic because it ties up resources and capital in inventory. It can also lead to additional waste, like excess storage.
Imagine a bakery making 100 cakes daily, but only 50 are sold. The rest go to waste. That’s overproduction. The key is to produce only what’s needed and companies implement just-in-time production to combat overproduction.
Waiting
This form of waste occurs when time is lost waiting for the next step in a process. This can be due to inefficient workflow, machine breakdowns, or unbalanced workloads. If a process in manufacturing is delayed, everything else has to wait. It’s a domino effect—one delay leads to another. Streamlining your processes and ensuring smoother workflow transitions is the solution.
Non-Utilized Talent
When companies do not use the skills, talents, and knowledge of the employees they have, it becomes a big waste. It leads to a lack of engagement and underperformance. It’s like having a skilled guitarist in your band but only letting them play the tambourine. If employees have skills or ideas that aren’t being used, that’s a waste.
Companies should focus on continuous employee training and development and also ensure that the right people are in the right roles to curb this form of waste.
Transportation Excess
This type of waste involves the unnecessary movement of products or materials within a facility. It can lead to increased costs and potential damage to products. Think of moving a product from one end of a huge factory to another multiple times. It’s like making multiple trips to carry groceries from the car.
Minimizing transportation waste involves optimizing the layout of the facility and ensuring efficient material-handling procedures.
Inventory Excess
Excess inventory ties up capital and space and can lead to issues like obsolescence. It’s often a result of overproduction or poor demand forecasting. Having a garage full of stuff you never use is similar to excess inventory in manufacturing.
It ties up space and money in stocks that are just sitting there. Practicing demand-driven production and improved forecasting can keep this in check.
Motion Excess
Excess motion refers to unnecessary movements by workers or machines that don’t add value. It can lead to worker fatigue and inefficient processes.
This is like taking five steps to complete a task when you could do it in two. If workers are moving around too much to get their job done, it’s inefficient. Optimizing your workspace so everything is within easy reach can help.
Excess Processing
This waste occurs when more work is done on a product than what is required by the customer. It can result from poor design, unclear customer specifications, or over-engineered processes.
Imagine adding fancy decorations to a basic phone case that customers don’t want. That’s excess processing. The focus should be on keeping things simple and customer-focused to avoid this form of waste.
Companies can address this waste by streamlining their manufacturing processes, making them more efficient and customer friendly. It’s about cutting out the unnecessary to focus on what adds value.
Basic Lean Manufacturing Tools

There are several tools used in lean manufacturing to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Here’s a look at some of the key tools used in this methodology:
Total Production Maintenance (TPM)
This tool focuses on helping your company improve the quality of your systems through employees, processes, equipment, and machines altogether. TPM aims for proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize the efficiency of your equipment. It helps you avoid breakdowns, eliminate defective products or slow performance, and avoid accidents within the production process. It is a tool that encourages more participation and involvement of employees.
Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)
SMED is a lean manufacturing concept and methodology. The primary goal of SMED is to reduce the setup or changeover time required to switch a manufacturing or production process from one product to another. Shigeo Shingo developed SMED, which is often associated with the Toyota Production System and is known for its efficiency and waste reduction principles. The key principles and techniques of SMED include:
- Separating internal and external setup activities
- Standardizing and streamlining setup procedures
- Using tools and equipment to simplify setups
- Reducing the number of changeover parts
- Training and involving operators
By implementing SMED principles, organizations can significantly reduce changeover times, increase production flexibility, and reduce waste in terms of time, materials, and resources.
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state for the series of events that take a product or service from its beginning through to the customer. With value stream mapping, you can easily see where delays or unnecessary steps occur in your processes. Improving or streamlining your processes and creating flowcharts takes care of the time that would have been wasted.
5S
The 5S tool stands for sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. This tool aims to prioritize safety and efficiency while maintaining lean manufacturing. It is a detailed and thorough process of making sure that everything is in its place so work gets done faster and safer by the employees.
Poka-Yoke
Poka-yoke means “mistake-proofing” or “error-proofing” in Japanese. This tool helps to prevent and detect errors in the manufacturing process. It’s about designing your processes and equipment in a way that makes it impossible, or at least very difficult, to make mistakes.
Kaizen
Kaisen is a philosophy of continuous improvement. It’s about everyone in the company, from the top down, constantly looking for small ways to improve how things are done. Kaizen can apply to any work but is most notable for its use in lean manufacturing.
Using these tools helps make manufacturing processes run more smoothly and efficiently, which is great for the company and the customer.
Why Lean Manufacturing Fails and How to Prevent It
While lean manufacturing offers significant benefits, its implementation can sometimes fail. Understanding the common reasons for failure and how to address them can help ensure successful adoption. Here are some key reasons for failure and solutions for each.
Resistance to Change
People naturally resist change, especially when it alters their routine or comfort zone. This resistance can derail lean manufacturing initiatives.
Solution: To overcome resistance, it’s important to communicate the benefits of lean manufacturing clearly to all employees. Engaging employees in the process and seeking their input can also help reduce resistance. Gradual implementation and celebrating small wins can encourage acceptance and adaptability.
Unrealistic Expectations
Sometimes companies expect too much too soon from lean manufacturing, leading to disappointment and abandonment of the process.
Solution: Set realistic goals and timelines for lean manufacturing implementation. Understand that it’s a gradual process that yields results over time. Educating the team about the nature of lean transformations can help set realistic expectations.
Lack of Standardization
Without standardization, any lean manufacturing process can become inconsistent and inefficient.
Solution: Develop and enforce standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all processes. Regular audits and reviews can ensure that these standards are maintained and updated as necessary.
Insufficient Training
Without proper training, employees may struggle to understand and apply lean principles.
Solution:
Offer continuous learning opportunities through refresher courses and hands-on practice.
Provide comprehensive training programs that reinforce Continuous Quality Improvement strategies.
Lack of Leadership Support
Lean manufacturing requires commitment and support from the top leadership. Without it, the initiative may not receive the necessary resources and attention.
Solution: Ensure that leadership is actively involved in the lean implementation process. Leaders should not only support the initiative but also be visible champions of the change, demonstrating their commitment through actions and decisions.
By addressing these common pitfalls with thoughtful strategies, organizations can significantly improve the chances of successful lean manufacturing implementation, leading to increased efficiency, reduced waste, and better overall performance.
How Lean Manufacturing Works in Real Life: Examples From Which You Can Learn

Lean manufacturing isn’t just a theory but a practical approach that has gained successful application in various industries. Let’s take a look at how different sectors have implemented lean principles.
Construction Industry
In construction, lean manufacturing helps to streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve delivery times. Imagine a construction site where every step, from laying the foundation to the final paint touch-up, is optimized. This translates to completing projects on time and reducing waste for extended delays.
Retail
Implementing lean methodology in retail is like having a secret weapon aimed at ensuring customer satisfaction.
Stores analyze shopping trends, adjust their stock accordingly, and make sure you don’t spend ages in the checkout line. This helps in reducing overstocking and understocking.
Checkout processes can also be streamlined to cut down waiting times and improve customer satisfaction.
Government Services
This is yet another lean manufacturing example. Imagine a world where government agencies operate with the sleek efficiency of a top-tier tech startup. That’s the power of injecting these principles into public service. It’s about cutting through the bureaucratic red tape and turbocharging administrative processes.
Less paperwork, faster responses to citizens’ needs—it’s like streamlining a clunky old machine into a hyper-efficient engine that delivers what people actually need.
It turns sluggish, cost-laden operations into dynamic, cost-effective powerhouses that serve the public, not just adequately but remarkably.
Automotive
In the high-octane world of car manufacturing, lean manufacturing is not just a strategy—it’s a revolution. Picture this: sleek production lines humming with precision, where every movement is calculated, every resource optimized.
Techniques like total productive maintenance (TPM) can ensure that machines purr with efficiency. The result is a dramatic reduction in production hiccups and a lineup of cars that aren’t just machines but marvels of quality and reliability.
Healthcare Sector
Lean manufacturing is like a breath of fresh air within the health sector. Imagine a hospital where everything runs like clockwork: patients don’t have to wait ages for their appointments, surgeries are scheduled efficiently, and there’s no scrambling around for medical supplies.
That’s what lean can do!
It’s all about cutting out the fluff and focusing on what matters: top-notch patient care without burning a hole in the budget.
Lean is not a one-size-fits-all principle. It is adaptable and useful in various sectors, from construction to retail and beyond. In each case, lean manufacturing is the secret sauce for ramping up efficiency, making customers happy, and boosting overall performance. With the right approach, you can do more with less, no matter the industry.
Lean Manufacturing vs. Lean Management: How They Differ
Sometimes, lean manufacturing gets confused with lean management, but they’re like two sides of the same coin: similar, yet different. Let’s break it down in a way that makes sense.
Lean Manufacturing: The Efficiency Expert on the Factory Floor
Lean manufacturing is like that smart, efficiency-loving friend who hangs out on the factory floor. It’s all about making sure everything in the manufacturing process—from the way parts are ordered to how a product is assembled—is as smooth and waste-free as possible. Think of a car assembly line where every tool, part, and process is fine-tuned to eliminate delays, reduce costs, and increase the quality of the final product. It’s like cooking a meal in the most efficient way possible—no unnecessary steps, no wasted ingredients.
Lean Management: The Big-Picture Boss
Lean management is like the big-picture boss who sees everything from a bird’s-eye view. It’s not limited to the factory floor. Instead, it applies the principles of lean—like reducing waste and focusing on value—to every part of a business. This could involve optimizing call center operations, enhancing inventory management in retail stores, or streamlining patient flow in hospitals. Applying the efficiency-first approach of lean manufacturing to the entire company, be it in production, customer service, or administration, is the way to go when it comes to applying lean.
The Key Differences
So what sets them apart? Scope and application. Lean manufacturing is specific to the production side of things—it’s hands-on and tangible. Lean management, meanwhile, is broader. It takes the lean principle and applies it to the entire process of managing a business. It’s more about the mindset and culture of the entire organization.
In a nutshell, while lean manufacturing gets its hands dirty on the production line, lean management oversees the entire organization, ensuring that every department is running lean and mean. Both are important and when they work in synergy, they can transform a business into a streamlined and highly efficient powerhouse.
So there you have it—two peas in a pod, each playing its important role in the lean world.
Lean Manufacturing vs. Agile Manufacturing: How They Differ
Let’s evaluate the nitty-gritty of lean manufacturing vs. agile manufacturing. Imagine we’re talking about two superheroes of the manufacturing world in which both have their unique strengths and approaches to saving the day (or, in this case, making manufacturing processes better).
Lean Manufacturing: The Efficiency Guru
Lean manufacturing is like that guru who’s all about doing more with less. It’s about cutting the fat, focusing on efficiency, and making sure everything in the production process—from the supply chain to the assembly line—is streamlined. Lean is the master of reducing manufacturing waste, whether it’s excess inventory, unnecessary steps, or time delays. It’s like cooking a meal but making sure you don’t waste a single ingredient and everything is cooked just right—no more, no less.
Agile Manufacturing: The Flexibility Champion
Now consider agile manufacturing, the champion of flexibility and adaptability. Agile is like that friend who’s always ready for anything. It’s all about being able to switch gears fast and respond to changes in the market or customer demands within the twinkle of an eye. Agile manufacturing focuses on being quick, responsive, and adaptable. It’s like a chef who can whip up a new dish on the fly because a customer wants something that’s not on the menu.
The Key Differences
So what’s the main difference between these two? It boils down to focus and approach. Lean manufacturing is laser-focused on efficiency and reducing waste. It’s about perfecting and streamlining what you already do. On the other hand, agile manufacturing is about being fast and flexible, ready to pivot and adapt when needed. It’s more about responding quickly to new opportunities or customer needs.
In essence, while lean manufacturing is like a well-oiled machine that runs smoothly and efficiently, agile manufacturing is like a quick-footed athlete, ready to jump in a new direction at a moment’s notice. Both bring immense value to the table, and depending on your business needs, you might lean more toward one than the other—or even find a way to blend the best of both worlds. Lean for efficiency, agile for flexibility: Together they’re a dynamic duo in the world of manufacturing!
Lean Manufacturing vs. Six Sigma: How They Differ
Lean manufacturing and Six Sigma are like two champions in the world of efficiency and quality improvement. They both aim to make manufacturing processes better, but they have their unique approaches. Let’s quickly dive into how they differ.
Lean Manufacturing: The Efficiency Expert
Lean manufacturing is like that efficiency expert in the room, always looking to streamline processes, reduce waste, and make everything more efficient. It’s all about finding the fastest, most streamlined way to do something without any unnecessary steps. Think of it as decluttering your production process—only keeping what you need and making sure everything runs smoothly.
Six Sigma: The Quality Perfectionist
Six Sigma, on the other hand, is like a perfectionist who’s obsessed with quality and accuracy. It’s all about reducing defects and improving the quality of the end product. Six Sigma uses a lot of data and statistics to identify and eliminate errors and variability in processes. It’s like having a super meticulous inspector who checks every tiny detail to make sure everything is as close to perfect as possible.
The Key Differences
The main difference between lean and Six Sigma? Focus. Lean manufacturing is focused on speed and efficiency, cutting out waste and making processes faster and smoother. Six Sigma zeroes in on quality and precision, reducing errors and making sure the final product is top-notch.
Both lean manufacturing and Six Sigma are incredibly valuable in their own right. Some companies even blend the two (hello, lean Six Sigma!) to get the best of both worlds: super-efficient processes that also produce top-quality products. So whether you’re looking to speed things up with lean or get things just right with Six Sigma, both approaches offer great tools to improve your manufacturing game.
Lean Manufacturing vs. Just in Time: How They Differ
Lean manufacturing and just-in-time (JIT) are like two key players on a basketball team: both critical to the game, but with different roles to play. Let’s break down how they differ in a straightforward, no-fluff way.
Lean Manufacturing: The All-Rounder Efficiency Playmaker
Lean manufacturing is like the player who’s good at everything—it focuses on reducing waste in all forms, be it time, materials, or effort. Think of it as an approach that looks at the entire game plan, from how the team practices to how they execute plays during the game. Lean is about making the entire manufacturing process as efficient and streamlined as possible, ensuring that every move counts and nothing is wasted.
Just in Time (JIT): The Master of Timing
Just in time, on the other hand, is like the player who’s an expert at timing. It’s all about having exactly what you need, right when you need it, not a moment too soon or too late. JIT is a strategy that focuses on inventory efficiency. It’s like passing the ball at the perfect moment so that the player gets it just as they’re ready to shoot. In manufacturing terms, this means producing and delivering products exactly when they’re needed, reducing the need to store excess inventory.
The Key Differences
So what sets them apart? Lean manufacturing is about overall efficiency—reducing all types of waste across the board. JIT is more specific. It’s a component of lean that focuses on timing and inventory reduction. While lean looks at the big picture, JIT zooms in on one crucial aspect: ensuring inventory is managed perfectly to match demand without overproducing.
Both lean manufacturing and JIT are crucial for a streamlined, efficient manufacturing process, much like how both players are vital to a winning basketball team. Lean provides the broad strategy while JIT hones in on the specifics of inventory timing. Together they create a dynamic duo that can significantly improve manufacturing operations.
Start Your Company’s Lean Journey With SweetProcess

Starting your company’s lean journey can feel like stepping into a new world of efficiency and productivity, and SweetProcess is here to be your guide. Think of SweetProcess as the compass that points your business in the right direction on this journey. It goes beyond just cutting costs or speeding up production; it’s about creating a deep-rooted culture where efficiency and continuous improvement are at the forefront of your company. From streamlining your processes to eliminating waste, SweetProcess offers you the right tools and support needed to make your transition to lean seamless.
Imagine a workplace where every process is optimized and every team member is empowered to contribute to improvements. That’s the power of lean manufacturing, and with SweetProcess, you can make this vision a reality for your business. You can now have a system that continually evolves and adapts to meet the changing needs of your business and customers.
So, are you ready to transform your business with lean manufacturing? Start your journey with SweetProcess today. Sign up for your free trial now and see how SweetProcess can help you streamline your operations, enhance efficiency, and drive growth. Lean into the future with confidence backed by the power of SweetProcess.
